Intro
Learn about RSV virus information, symptoms, and treatment options. Understand Respiratory Syncytial Virus causes, diagnosis, and prevention methods to protect against infection.
The Respiratory Syncytial Virus (RSV) is a highly contagious virus that affects people of all ages, but it is most severe in young children and older adults. RSV is a major cause of respiratory illness, and it is estimated that nearly all children in the United States will have had an RSV infection by their second birthday. The virus is spread through close contact with an infected person, usually through touching, shaking hands, or sharing food and drinks. It can also be spread through the air when an infected person coughs or sneezes.
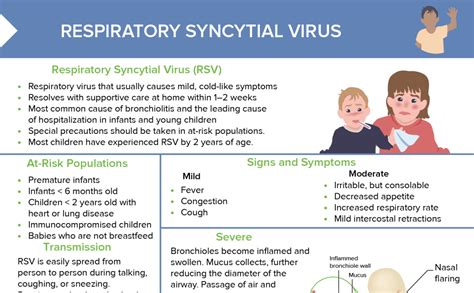
RSV infections typically occur during the fall and spring seasons, with the peak season usually occurring between December and February. The virus can cause a range of symptoms, from mild to severe, including runny nose, coughing, sneezing, fever, and loss of appetite. In severe cases, RSV can cause bronchiolitis, pneumonia, and other respiratory complications that require hospitalization. According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), RSV is responsible for approximately 57,527 hospitalizations among children under the age of five in the United States each year.
Understanding the risks and symptoms of RSV is crucial for preventing the spread of the virus and seeking medical attention when necessary. Parents, caregivers, and healthcare professionals must work together to educate themselves and others about the importance of RSV prevention and treatment. By taking proactive steps to prevent the spread of RSV, we can reduce the number of cases and hospitalizations, and ultimately save lives. This article will provide an in-depth look at RSV, its symptoms, prevention methods, and treatment options, as well as discuss the latest research and developments in the field.
What is RSV?

Types of RSV
There are two main types of RSV: RSV-A and RSV-B. Both types can cause severe illness, but RSV-A is more commonly associated with severe disease. RSV-A is also more likely to cause outbreaks in communities, while RSV-B is more commonly associated with individual cases. Understanding the different types of RSV is important for developing effective prevention and treatment strategies.RSV Symptoms
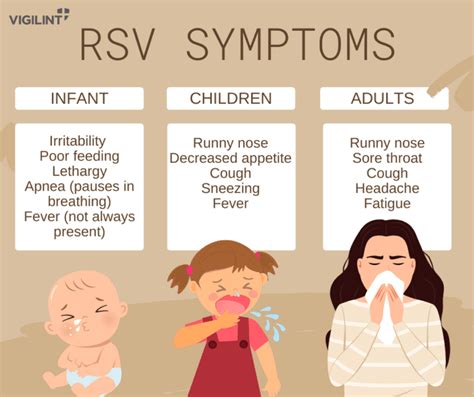
RSV in Children
RSV is a significant concern for young children, as it is a leading cause of respiratory illness in this age group. Children under the age of two are at the highest risk for severe RSV illness, and those under six months are at the highest risk for hospitalization. Premature infants, children with underlying health conditions, and those with weakened immune systems are also at increased risk for severe RSV illness. Parents and caregivers must take proactive steps to prevent the spread of RSV, such as washing hands frequently, avoiding close contact with infected individuals, and keeping surfaces clean.RSV Prevention

RSV Vaccination
There is no vaccine available for RSV, but researchers are working to develop an effective vaccine. In the meantime, palivizumab (Synagis) is a monoclonal antibody that can help prevent severe RSV illness in high-risk infants. Palivizumab is typically given to premature infants and those with underlying health conditions. It is essential to consult with a healthcare professional to determine the best course of action for preventing RSV.RSV Treatment
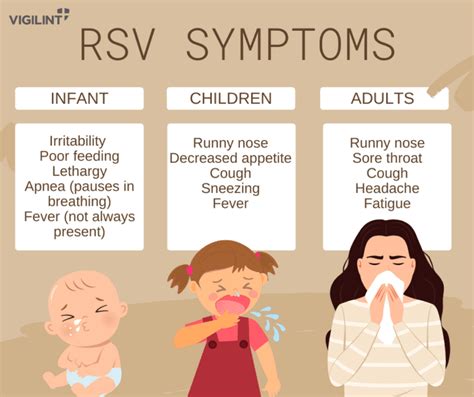
RSV Hospitalization
In severe cases, RSV can cause respiratory complications that require hospitalization. Hospitalization is usually necessary for individuals who experience severe symptoms, such as difficulty breathing, rapid breathing, or a decrease in oxygen levels. In the hospital, patients may receive oxygen therapy, mechanical ventilation, and other supportive care to help manage symptoms and prevent complications.RSV Complications
RSV and Asthma
RSV has been linked to an increased risk of developing asthma, particularly in children. Research suggests that RSV infection may trigger an allergic response, leading to the development of asthma. Understanding the relationship between RSV and asthma is crucial for developing effective prevention and treatment strategies.RSV Research
RSV and COVID-19
The COVID-19 pandemic has highlighted the importance of respiratory virus research, including RSV. Researchers are working to understand the relationship between RSV and COVID-19, as well as develop effective prevention and treatment strategies for both viruses. Understanding the similarities and differences between RSV and COVID-19 is crucial for developing effective public health strategies.What is RSV?
+RSV is a type of virus that affects the respiratory system, including the nose, throat, and lungs.
How is RSV spread?
+RSV is spread through close contact with an infected person, usually through touching, shaking hands, or sharing food and drinks.
What are the symptoms of RSV?
+The symptoms of RSV can range from mild to severe, and include runny nose, coughing, sneezing, fever, and loss of appetite.
How can I prevent RSV?
+Preventing RSV involves washing hands frequently, avoiding close contact with infected individuals, keeping surfaces clean and disinfected, and avoiding sharing food and drinks.
Is there a vaccine for RSV?
+There is no vaccine available for RSV, but researchers are working to develop an effective vaccine.
In conclusion, RSV is a significant public health concern that affects people of all ages. Understanding the risks and symptoms of RSV is crucial for preventing the spread of the virus and seeking medical attention when necessary. By taking proactive steps to prevent RSV, such as washing hands frequently and avoiding close contact with infected individuals, we can reduce the number of cases and hospitalizations. We encourage readers to share this article with others, and to take action to protect themselves and their loved ones from RSV. Together, we can work towards a future where RSV is no longer a significant threat to public health.
