Intro
Discover how Sed Rate works with 5 key methods, including inflammation detection, blood testing, and medical diagnosis, to measure erythrocyte sedimentation rate and diagnose conditions like arthritis and autoimmune diseases.
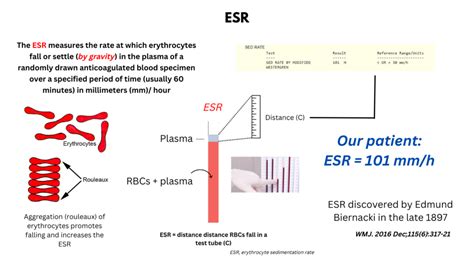
The sedimentation rate, commonly referred to as the sed rate, is a blood test that measures how quickly erythrocytes (red blood cells) settle at the bottom of a test tube containing a blood sample. It indirectly measures how much inflammation is in the body. The sed rate is a simple yet effective test that has been used for decades to help diagnose and monitor various conditions, including inflammatory and autoimmune disorders. Understanding how the sed rate works and its applications can provide valuable insights into the management of health and disease.
The importance of the sed rate lies in its ability to indicate the presence of inflammation in the body. Inflammation is a natural response of the body's immune system to injury or infection, but chronic or excessive inflammation can lead to various diseases. By measuring the sed rate, healthcare providers can gauge the level of inflammation and make informed decisions about diagnosis, treatment, and monitoring of conditions such as rheumatoid arthritis, lupus, and other inflammatory diseases.
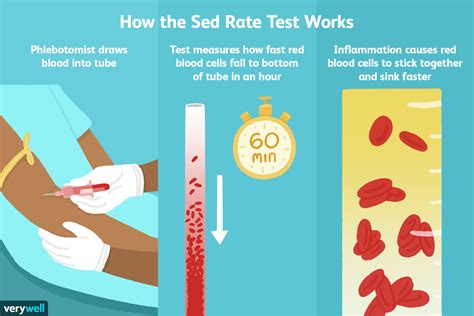
The sed rate test is performed by taking a blood sample from a vein, usually in the arm, and placing it in a tall, thin tube. The blood is then allowed to settle, and the rate at which the red blood cells fall to the bottom of the tube is measured. This rate is influenced by the presence of proteins (such as fibrinogen) in the blood that are produced in response to inflammation. These proteins cause the red blood cells to clump together, which increases their density and causes them to settle more quickly.
Introduction to Sed Rate
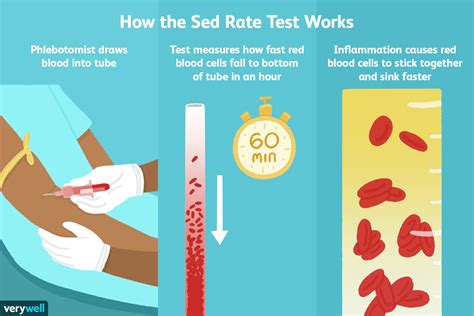
How Sed Rate Works
Factors Influencing Sed Rate
Several factors can influence the sed rate, including age, gender, and the presence of certain medical conditions. For example, sed rates tend to be higher in women than in men, and they increase with age. Certain conditions, such as pregnancy, can also cause an increase in sed rate due to the natural changes in the body's inflammatory response during pregnancy. Understanding these factors is crucial for interpreting sed rate results accurately.Applications of Sed Rate
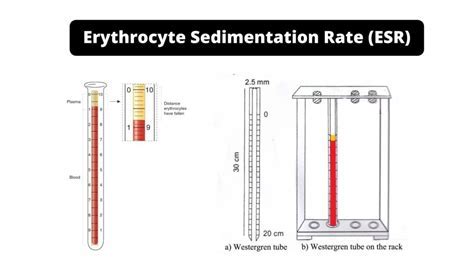
Interpreting Sed Rate Results
Interpreting sed rate results requires careful consideration of the individual's overall health status and medical history. A high sed rate may indicate the presence of an inflammatory condition, but it can also be influenced by other factors such as age, gender, and the presence of other medical conditions. Healthcare providers use sed rate results in conjunction with other diagnostic tests and clinical evaluations to make accurate diagnoses and develop effective treatment plans.5 Ways Sed Rate Works in Diagnosis
Limitations and Considerations
Future Directions
The sed rate has been a cornerstone of diagnostic testing for decades, but there are ongoing efforts to develop more specific and sensitive tests for inflammation. Advances in technology and our understanding of the inflammatory response are leading to the development of new biomarkers and diagnostic tests that may eventually replace or complement the sed rate. However, the sed rate remains a widely used and valuable tool in clinical practice due to its simplicity, low cost, and ability to provide rapid results.Conclusion and Next Steps
What is the sed rate used for?
+The sed rate is used to diagnose and monitor inflammatory and autoimmune conditions, such as rheumatoid arthritis and lupus, by measuring the level of inflammation in the body.
How is the sed rate measured?
+The sed rate is measured by taking a blood sample and allowing it to settle in a test tube. The rate at which the red blood cells fall to the bottom of the tube is then measured, usually in millimeters per hour (mm/h).
What can cause a high sed rate?
+A high sed rate can be caused by various factors, including inflammatory and autoimmune conditions, infections, pregnancy, and certain medications. It can also be influenced by age, gender, and other medical conditions.
How is the sed rate interpreted?
+The sed rate is interpreted in conjunction with other diagnostic tests and clinical evaluations. A high sed rate may indicate the presence of an inflammatory condition, but it can also be influenced by other factors, and therefore, requires careful consideration of the individual's overall health status and medical history.
Can the sed rate be used to monitor treatment response?
+Yes, the sed rate can be used to monitor the response to treatment in individuals with inflammatory or autoimmune conditions. By monitoring changes in sed rate over time, healthcare providers can adjust treatment plans to optimize outcomes.
We hope this comprehensive overview of the sed rate has provided you with valuable insights into its role in diagnosing and managing inflammatory and autoimmune conditions. If you have any further questions or would like to share your experiences with the sed rate, please do not hesitate to comment below. Your feedback and engagement are crucial in helping us improve our content and provide the most accurate and helpful information possible. Thank you for reading, and we look forward to your comments and shares!
