Intro
Discover how sedimentation rate works through 5 key methods, including erythrocyte sedimentation, blood testing, and more, to diagnose inflammation and disease with accurate lab results and medical analysis techniques.
The sedimentation rate, also known as the erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR), is a blood test that measures how quickly erythrocytes (red blood cells) settle at the bottom of a test tube containing a blood sample. It indirectly measures how much inflammation is in the body. The sedimentation rate is a crucial diagnostic tool used to detect and monitor various medical conditions, including inflammatory diseases, infections, and cancers. Understanding how the sedimentation rate works is essential for healthcare professionals and patients alike. In this article, we will delve into the world of sedimentation rates, exploring the mechanisms, benefits, and practical applications of this vital medical test.
The sedimentation rate has been a cornerstone of medical diagnostics for decades, providing valuable insights into the body's inflammatory response. By analyzing the rate at which red blood cells settle, healthcare professionals can identify potential health issues and monitor the effectiveness of treatments. The sedimentation rate is a simple yet powerful tool that has revolutionized the field of medicine, enabling early detection and intervention in a wide range of diseases. As we explore the intricacies of sedimentation rates, we will discover the fascinating science behind this test and its significance in modern medicine.
The sedimentation rate is a fascinating topic that has garnered significant attention in recent years. With the increasing prevalence of chronic diseases, the importance of accurate diagnosis and monitoring has never been more critical. By understanding how the sedimentation rate works, we can better appreciate the complexities of the human body and the innovative solutions that medical science has to offer. In the following sections, we will examine the mechanisms, benefits, and applications of sedimentation rates in greater detail, providing a comprehensive overview of this vital medical test.
What is Sedimentation Rate?
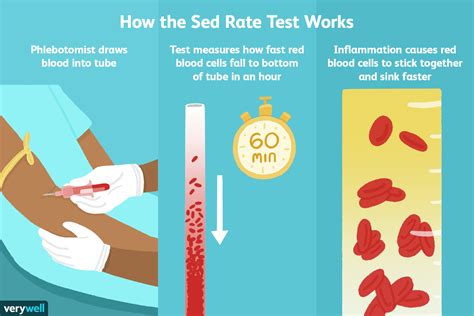
How Sedimentation Rate Works
The sedimentation rate works by measuring the rate at which red blood cells settle due to gravity. In a normal blood sample, the red blood cells are evenly distributed throughout the sample. However, when there is inflammation in the body, the red blood cells tend to clump together, forming stacks called rouleaux. These stacks of red blood cells are heavier than individual cells, causing them to settle more quickly to the bottom of the test tube. The sedimentation rate is therefore an indirect measure of the amount of inflammation in the body.Benefits of Sedimentation Rate
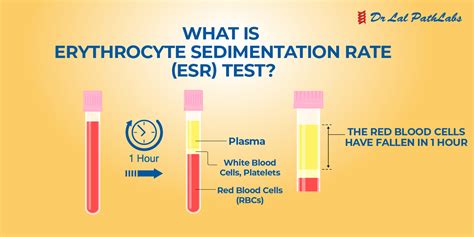
Steps Involved in Sedimentation Rate Test
The steps involved in the sedimentation rate test are: 1. Blood sample collection: A blood sample is collected from the patient's vein using a needle and syringe. 2. Anticoagulant treatment: The blood sample is treated with an anticoagulant to prevent clotting. 3. Test tube preparation: The blood sample is placed in a test tube, and the test tube is prepared for the sedimentation rate test. 4. Sedimentation rate measurement: The rate at which the red blood cells settle is measured over a specified period, usually one hour. 5. Result interpretation: The sedimentation rate is calculated and interpreted by a healthcare professional.Practical Applications of Sedimentation Rate

Limitations of Sedimentation Rate
The sedimentation rate has several limitations, including: * Non-specificity: The sedimentation rate is a non-specific test, meaning that it can be elevated in a variety of conditions, not just inflammatory diseases. * Variability: The sedimentation rate can vary depending on the individual and the laboratory performing the test. * Lack of standardization: There is a lack of standardization in the performance and interpretation of the sedimentation rate test.Five Ways Sedimentation Rate Works
Statistical Data
According to the American College of Rheumatology, the sedimentation rate is elevated in approximately 70% of patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Additionally, a study published in the Journal of Clinical Rheumatology found that the sedimentation rate was a significant predictor of disease activity in patients with lupus.Conclusion and Future Directions

Final Thoughts
The sedimentation rate is a fascinating topic that has the potential to revolutionize the field of medicine. By understanding how the sedimentation rate works, we can better appreciate the complexities of the human body and the innovative solutions that medical science has to offer. As we continue to explore the intricacies of the sedimentation rate, we may uncover new and exciting applications for this test, leading to improved patient outcomes and a better understanding of the human body.What is the sedimentation rate used for?
+The sedimentation rate is used to detect and monitor inflammatory diseases, infections, and cancers. It is a non-invasive and relatively inexpensive diagnostic tool that measures the rate at which red blood cells settle at the bottom of a test tube.
How is the sedimentation rate performed?
+The sedimentation rate is performed by collecting a blood sample from the patient's vein, treating it with an anticoagulant, and placing it in a test tube. The rate at which the red blood cells settle is then measured over a specified period, usually one hour.
What are the limitations of the sedimentation rate?
+The sedimentation rate has several limitations, including non-specificity, variability, and lack of standardization. It is a non-specific test, meaning that it can be elevated in a variety of conditions, not just inflammatory diseases.
Can the sedimentation rate be used to monitor treatment effectiveness?
+Yes, the sedimentation rate can be used to monitor treatment effectiveness. By measuring the level of inflammatory markers in the blood, the sedimentation rate can provide valuable information on the effectiveness of treatments for inflammatory diseases.
What is the future of the sedimentation rate?
+The future of the sedimentation rate includes the development of more standardized and sensitive tests, as well as the exploration of new applications for this test. With ongoing research and advancements in medical technology, the sedimentation rate is likely to remain a valuable diagnostic tool in the field of medicine.
