Intro
Discover 5 ways subclinical hypothyroidism affects health, from fatigue to weight gain, and learn how to manage symptoms with natural remedies and thyroid support, alleviating hypothyroidism symptoms and promoting overall well-being.
Subclinical hypothyroidism, also known as mild thyroid failure, is a condition where the thyroid gland doesn't produce enough thyroid hormones to meet the body's needs, but not to the extent of causing overt hypothyroidism. This condition can have a significant impact on one's quality of life, and it's essential to understand its effects and how to manage it. In this article, we'll delve into the world of subclinical hypothyroidism, exploring its causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment options.
The thyroid gland plays a vital role in regulating various bodily functions, such as metabolism, growth, and development. When the thyroid gland is underactive, it can lead to a range of symptoms, including fatigue, weight gain, and dry skin. Subclinical hypothyroidism is often referred to as a "gray area" between normal thyroid function and overt hypothyroidism. It's estimated that approximately 4-10% of the general population suffers from subclinical hypothyroidism, with women being more likely to be affected than men.
Subclinical hypothyroidism can be caused by various factors, including autoimmune disorders, such as Hashimoto's thyroiditis, radiation therapy, and certain medications. In some cases, the condition can be asymptomatic, making it challenging to diagnose. However, if left untreated, subclinical hypothyroidism can increase the risk of developing cardiovascular disease, osteoporosis, and other health problems. It's crucial to understand the causes, symptoms, and treatment options available to manage this condition effectively.
Understanding Subclinical Hypothyroidism
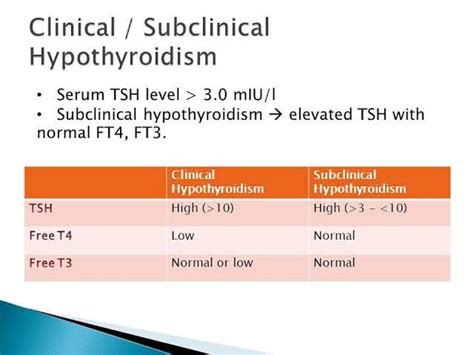
Causes of Subclinical Hypothyroidism
The causes of subclinical hypothyroidism can be divided into two main categories: autoimmune and non-autoimmune. Autoimmune disorders, such as Hashimoto's thyroiditis, are the most common cause of subclinical hypothyroidism. This condition occurs when the immune system mistakenly attacks the thyroid gland, leading to inflammation and damage. Non-autoimmune causes of subclinical hypothyroidism include radiation therapy, thyroid surgery, and certain medications.Diagnosis and Treatment of Subclinical Hypothyroidism
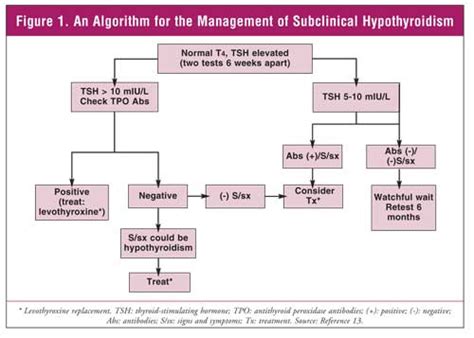
Treatment Options for Subclinical Hypothyroidism
The treatment of subclinical hypothyroidism depends on the underlying cause and the severity of the condition. In some cases, treatment may not be necessary, and the condition can be monitored with regular laboratory tests. However, if the condition is caused by an autoimmune disorder or other underlying condition, treatment may be necessary to manage the condition and prevent complications.5 Ways Subclinical Hypothyroidism Affects the Body
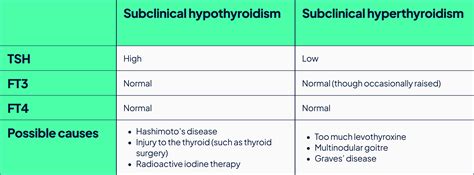
- Fatigue and weakness: Subclinical hypothyroidism can cause fatigue and weakness, making it challenging to perform daily activities.
- Weight gain: Subclinical hypothyroidism can cause weight gain, particularly around the midsection, due to a decrease in metabolism.
- Dry skin and hair loss: Subclinical hypothyroidism can cause dry skin and hair loss, due to a decrease in the production of thyroid hormones.
- Increased risk of cardiovascular disease: Subclinical hypothyroidism can increase the risk of developing cardiovascular disease, due to an increase in LDL cholesterol and triglycerides.
- Osteoporosis: Subclinical hypothyroidism can increase the risk of developing osteoporosis, due to a decrease in bone density.
Managing Subclinical Hypothyroidism
Managing subclinical hypothyroidism requires a comprehensive approach, including lifestyle modifications, dietary changes, and treatment. Lifestyle modifications, such as regular exercise and stress management, can help manage the condition and prevent complications. Dietary changes, such as increasing the intake of iodine and selenium, can also help manage the condition.Lifestyle Modifications for Subclinical Hypothyroidism
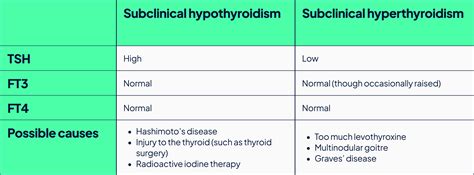
Dietary Changes for Subclinical Hypothyroidism
Dietary changes can also help manage subclinical hypothyroidism. Increasing the intake of iodine and selenium, essential nutrients for thyroid function, can help manage the condition. Foods rich in iodine, such as seaweed and dairy products, and foods rich in selenium, such as Brazil nuts and fish, can help support thyroid function.Conclusion and Next Steps

We invite you to share your thoughts and experiences with subclinical hypothyroidism in the comments section below. If you have any questions or concerns, please don't hesitate to reach out. Share this article with friends and family who may be affected by subclinical hypothyroidism, and let's work together to raise awareness about this important health topic.
What is subclinical hypothyroidism?
+Subclinical hypothyroidism is a condition where the thyroid gland doesn't produce enough thyroid hormones to meet the body's needs, but not to the extent of causing overt hypothyroidism.
What are the symptoms of subclinical hypothyroidism?
+The symptoms of subclinical hypothyroidism can include fatigue, weight gain, dry skin, and hair loss.
How is subclinical hypothyroidism diagnosed?
+Subclinical hypothyroidism is diagnosed using a combination of physical examination, medical history, and laboratory tests, including the TSH test.
What are the treatment options for subclinical hypothyroidism?
+The treatment options for subclinical hypothyroidism depend on the underlying cause and severity of the condition, and may include lifestyle modifications, dietary changes, and medication.
Can subclinical hypothyroidism increase the risk of other health problems?
+Yes, subclinical hypothyroidism can increase the risk of other health problems, including cardiovascular disease, osteoporosis, and infertility.
