Intro
Discover the uses and benefits of Sulfameth, an antibiotic treating bacterial infections, with advantages including anti-inflammatory properties, effective against urinary tract infections, and more, exploring its applications and advantages in medicine.
The importance of sulfameth, also known as sulfamethoxazole, cannot be overstated. This antibiotic has been a cornerstone in the treatment of various bacterial infections for decades. Its effectiveness and versatility have made it a staple in the medical world, with applications ranging from urinary tract infections to respiratory tract infections. As we delve into the world of sulfameth, it becomes clear that understanding its uses and benefits is crucial for anyone looking to make informed decisions about their health.
Sulfameth is a type of sulfonamide antibiotic, which works by inhibiting the growth and multiplication of bacteria. This mechanism of action makes it an effective treatment for a wide range of bacterial infections, including those caused by E. coli, Klebsiella, and Streptococcus. The benefits of sulfameth are numerous, with one of the most significant being its ability to target and eliminate bacteria that are resistant to other types of antibiotics. This makes it a valuable tool in the fight against antibiotic-resistant infections, which are becoming increasingly prevalent.
The versatility of sulfameth is another key aspect of its benefits. It can be used to treat a variety of infections, including urinary tract infections, respiratory tract infections, and skin and soft tissue infections. Additionally, sulfameth is often used in combination with other antibiotics, such as trimethoprim, to create a synergistic effect that enhances its effectiveness. This combination, known as co-trimoxazole, is commonly used to treat infections such as pneumonia, bronchitis, and urinary tract infections.
Sulfameth Uses

Sulfameth is used to treat a wide range of bacterial infections, including:
- Urinary tract infections (UTIs)
- Respiratory tract infections (RTIs)
- Skin and soft tissue infections
- Ear infections
- Eye infections
- Gastrointestinal infections
- Bone and joint infections
Its effectiveness against these types of infections makes it a valuable tool in the medical world. Sulfameth is often prescribed in combination with other antibiotics to create a synergistic effect that enhances its effectiveness.
Types of Infections Treated by Sulfameth
Sulfameth is effective against a variety of bacterial infections, including: * Gram-positive bacteria, such as Staphylococcus and Streptococcus * Gram-negative bacteria, such as E. coli and Klebsiella * Anaerobic bacteria, such as Bacteroides and FusobacteriumIts broad-spectrum activity makes it a useful treatment option for a wide range of infections.
Sulfameth Benefits

The benefits of sulfameth are numerous, with some of the most significant including:
- Effective against a wide range of bacterial infections
- Can be used to treat infections that are resistant to other antibiotics
- Often used in combination with other antibiotics to create a synergistic effect
- Available in a variety of formulations, including oral and injectable forms
- Generally well-tolerated, with few side effects reported
Its effectiveness and versatility make it a valuable tool in the medical world.
Advantages of Sulfameth
Some of the advantages of sulfameth include: * Broad-spectrum activity against a wide range of bacteria * Ability to target and eliminate bacteria that are resistant to other antibiotics * Can be used to treat a variety of infections, including UTIs, RTIs, and skin and soft tissue infections * Often used in combination with other antibiotics to create a synergistic effect * Generally well-tolerated, with few side effects reportedThese advantages make sulfameth a popular choice among healthcare professionals.
Sulfameth Mechanism of Action
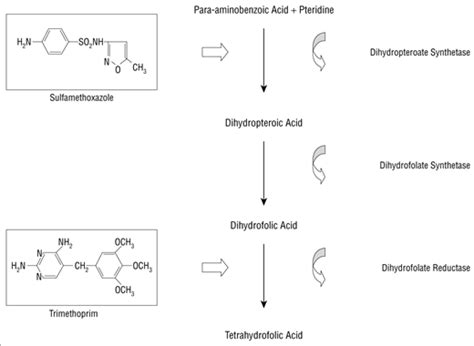
Sulfameth works by inhibiting the growth and multiplication of bacteria. It does this by:
- Inhibiting the synthesis of folic acid, which is necessary for bacterial growth and multiplication
- Interfering with the synthesis of nucleic acids, which are essential for bacterial replication
- Damaging the bacterial cell membrane, leading to the death of the bacterial cell
This mechanism of action makes sulfameth an effective treatment for a wide range of bacterial infections.
How Sulfameth Works
Sulfameth is effective against bacteria because it: * Inhibits the synthesis of folic acid, which is necessary for bacterial growth and multiplication * Interferes with the synthesis of nucleic acids, which are essential for bacterial replication * Damages the bacterial cell membrane, leading to the death of the bacterial cellIts ability to target and eliminate bacteria makes it a valuable tool in the medical world.
Sulfameth Side Effects
While sulfameth is generally well-tolerated, it can cause some side effects, including:
- Nausea and vomiting
- Diarrhea
- Abdominal pain
- Headache
- Dizziness
- Rash
These side effects are usually mild and temporary, but in some cases, they can be more severe.
Common Side Effects of Sulfameth
Some of the most common side effects of sulfameth include: * Gastrointestinal symptoms, such as nausea and vomiting * Central nervous system symptoms, such as headache and dizziness * Skin symptoms, such as rash and itching * Hematologic symptoms, such as anemia and thrombocytopeniaIt is essential to report any side effects to a healthcare professional, as they can be a sign of a more serious problem.
Sulfameth Interactions

Sulfameth can interact with other medications, including:
- Blood thinners, such as warfarin
- Diabetes medications, such as metformin
- Seizure medications, such as phenytoin
- Antacids, such as aluminum hydroxide
These interactions can increase the risk of side effects or reduce the effectiveness of sulfameth.
Medications that Interact with Sulfameth
Some of the medications that can interact with sulfameth include: * Blood thinners, such as warfarin * Diabetes medications, such as metformin * Seizure medications, such as phenytoin * Antacids, such as aluminum hydroxideIt is essential to report any medications to a healthcare professional, as they can interact with sulfameth.
Sulfameth Dosage

The dosage of sulfameth varies depending on the type and severity of the infection, as well as the age and weight of the patient. The typical dosage range is:
- 800-1600 mg per day for adults
- 20-40 mg/kg per day for children
It is essential to follow the dosage instructions provided by a healthcare professional, as taking too much or too little sulfameth can reduce its effectiveness or increase the risk of side effects.
How to Take Sulfameth
Sulfameth should be taken: * Orally, with or without food * At the same time every day * For the full duration of the treatment, even if symptoms improve before the end of the treatmentIt is essential to follow the dosage instructions provided by a healthcare professional, as taking too much or too little sulfameth can reduce its effectiveness or increase the risk of side effects.
Sulfameth Precautions

Sulfameth can cause some precautions, including:
- Allergic reactions, such as anaphylaxis
- Severe skin reactions, such as Stevens-Johnson syndrome
- Blood disorders, such as anemia and thrombocytopenia
- Liver damage, such as hepatitis
It is essential to report any precautions to a healthcare professional, as they can be a sign of a more serious problem.
Warning Signs of Sulfameth Precautions
Some of the warning signs of sulfameth precautions include: * Severe skin reactions, such as rash and itching * Blood disorders, such as anemia and thrombocytopenia * Liver damage, such as hepatitis * Allergic reactions, such as anaphylaxisIt is essential to report any precautions to a healthcare professional, as they can be a sign of a more serious problem.
What is sulfameth used for?
+Sulfameth is used to treat a wide range of bacterial infections, including urinary tract infections, respiratory tract infections, and skin and soft tissue infections.
How does sulfameth work?
+Sulfameth works by inhibiting the growth and multiplication of bacteria, making it an effective treatment for a wide range of bacterial infections.
What are the common side effects of sulfameth?
+The common side effects of sulfameth include nausea and vomiting, diarrhea, abdominal pain, headache, and dizziness.
Can sulfameth interact with other medications?
+Yes, sulfameth can interact with other medications, including blood thinners, diabetes medications, and seizure medications.
How should sulfameth be taken?
+Sulfameth should be taken orally, with or without food, at the same time every day, and for the full duration of the treatment.
As we conclude our exploration of sulfameth, it is clear that this antibiotic is a valuable tool in the medical world. Its effectiveness and versatility make it a popular choice among healthcare professionals, and its ability to target and eliminate bacteria that are resistant to other antibiotics makes it a crucial component in the fight against antibiotic-resistant infections. We encourage readers to share their thoughts and experiences with sulfameth in the comments below, and to consult with a healthcare professional before taking any medication. By working together, we can promote the responsible use of antibiotics and ensure that they remain effective for generations to come.
