Intro
Discover key facts about Sulfameth, an antibiotic used to treat infections, including its mechanism, side effects, and interactions, exploring sulfamethoxazole uses, sulfonamide resistance, and more.
Sulfamethoxazole, commonly referred to as sulfameth, is a sulfonamide antibiotic used in combination with trimethoprim to treat various bacterial infections. The importance of understanding sulfamethoxazole cannot be overstated, as it is a crucial component in the treatment of many diseases. In this article, we will delve into the world of sulfamethoxazole, exploring its uses, benefits, and potential side effects. Whether you are a medical professional or simply someone looking to learn more about this antibiotic, this article aims to provide you with a comprehensive understanding of sulfamethoxazole.
The use of sulfamethoxazole in medicine has been widespread due to its effectiveness against a broad range of bacterial infections. It is often prescribed in combination with trimethoprim, another antibiotic, to create a synergistic effect that enhances its bactericidal activity. This combination is particularly useful in treating urinary tract infections, respiratory tract infections, and gastrointestinal infections, among others. Understanding the mechanism of action, benefits, and potential drawbacks of sulfamethoxazole is essential for both healthcare providers and patients to ensure its safe and effective use.
Sulfamethoxazole works by inhibiting the synthesis of folic acid in bacteria, which is essential for their growth and replication. When used in combination with trimethoprim, it creates a double blockade in the folic acid synthesis pathway, leading to a potent bactericidal effect. This unique mechanism of action makes sulfamethoxazole and trimethoprim a preferred choice for treating certain bacterial infections. However, like all medications, sulfamethoxazole can cause side effects, and its use must be carefully considered, especially in patients with certain medical conditions or those taking specific medications.
Introduction to Sulfamethoxazole
Pharmacokinetics of Sulfamethoxazole
The pharmacokinetics of sulfamethoxazole involves its absorption, distribution, metabolism, and excretion. After oral administration, sulfamethoxazole is well absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract, with peak plasma concentrations achieved within 1 to 4 hours. It is widely distributed throughout the body, with high concentrations found in the urine, which makes it particularly effective for treating urinary tract infections. Sulfamethoxazole is metabolized in the liver and excreted primarily through the kidneys. Its half-life is approximately 10 hours, which allows for once or twice daily dosing in many cases.Benefits of Sulfamethoxazole
Common Uses of Sulfamethoxazole
Sulfamethoxazole is commonly used to treat urinary tract infections, such as cystitis and pyelonephritis, due to its high concentration in the urine. It is also effective against respiratory tract infections, including bronchitis and pneumonia, and gastrointestinal infections, such as traveler's diarrhea. Additionally, sulfamethoxazole is used to treat and prevent Pneumocystis jirovecii pneumonia in patients with HIV/AIDS, showcasing its versatility in different clinical scenarios.Potential Side Effects of Sulfamethoxazole

Precautions and Contraindications
The use of sulfamethoxazole requires careful consideration in certain patient populations. It is contraindicated in patients with a known hypersensitivity to sulfonamides or trimethoprim. Caution is advised in patients with renal or hepatic impairment, as well as in those with glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase (G6PD) deficiency, due to the risk of hemolysis. Pregnant women, especially those in the third trimester, and breastfeeding mothers should use sulfamethoxazole with caution, as it can displace bilirubin from plasma protein binding sites, potentially leading to kernicterus in the newborn.Drug Interactions with Sulfamethoxazole
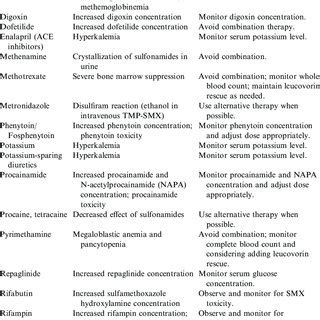
Resistance and Stewardship
The increasing resistance to sulfamethoxazole and other antibiotics highlights the need for antibiotic stewardship. This involves the appropriate selection of antibiotics, dosing, and duration of therapy to minimize the development of resistance. Healthcare providers must balance the need for effective treatment with the risk of promoting antibiotic resistance, ensuring that sulfamethoxazole and other antibiotics remain effective for future generations.Conclusion and Future Perspectives

Final Thoughts
As we reflect on the importance of sulfamethoxazole, it is clear that this antibiotic plays a critical role in modern medicine. Its benefits, mechanism of action, and potential side effects must be understood to ensure its safe and effective use. By doing so, we can continue to rely on sulfamethoxazole as a valuable component in the treatment of bacterial infections, improving patient outcomes and contributing to the broader goal of combating antibiotic resistance.What is sulfamethoxazole used for?
+Sulfamethoxazole is used to treat various bacterial infections, including urinary tract infections, respiratory tract infections, and gastrointestinal infections, often in combination with trimethoprim.
How does sulfamethoxazole work?
+Sulfamethoxazole works by inhibiting the synthesis of folic acid in bacteria, which is essential for their growth and replication. When used with trimethoprim, it creates a synergistic effect that enhances its bactericidal activity.
What are the common side effects of sulfamethoxazole?
+Common side effects include nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, and rash. More severe but rare side effects can include Stevens-Johnson syndrome, toxic epidermal necrolysis, and agranulocytosis.
We invite you to share your thoughts and questions about sulfamethoxazole in the comments below. Whether you are a healthcare professional or someone who has been prescribed this antibiotic, your insights can help others better understand its role in treating bacterial infections. Let's work together to promote antibiotic stewardship and ensure that sulfamethoxazole and other antibiotics remain effective for years to come.
