Intro
Discover Bactrim antibiotic uses, a sulfonamide antibiotic treating bacterial infections, including UTIs, bronchitis, and pneumonia, with broad-spectrum efficacy and resistance prevention.
The world of antibiotics is vast and complex, with various medications designed to combat different types of bacterial infections. One such antibiotic that has been widely used for decades is Bactrim, a combination of two antibiotics: sulfamethoxazole and trimethoprim. Understanding the uses, benefits, and potential risks of Bactrim is crucial for both medical professionals and patients alike. In this article, we will delve into the specifics of Bactrim, exploring its applications, mechanisms, and the importance of responsible antibiotic use.
Bactrim has been a staple in the treatment of bacterial infections due to its effectiveness against a broad spectrum of bacteria. It is particularly useful in treating urinary tract infections (UTIs), which are among the most common bacterial infections affecting both men and women. The combination of sulfamethoxazole and trimethoprim in Bactrim works synergistically to inhibit the growth of bacteria, making it difficult for them to multiply and cause infection. This dual-action approach enhances the drug's efficacy and helps in reducing the development of antibiotic resistance.
The application of Bactrim extends beyond UTIs to include the treatment of other types of infections. It is used to treat acute otitis media (middle ear infections), bronchitis, and traveler's diarrhea, among others. Bactrim's broad-spectrum activity makes it a valuable option in clinical settings where the causative agent of an infection may not be immediately identified. However, it is essential to use Bactrim and other antibiotics judiciously, as the misuse or overuse of these medications can lead to the development of antibiotic-resistant bacteria, posing a significant threat to public health.
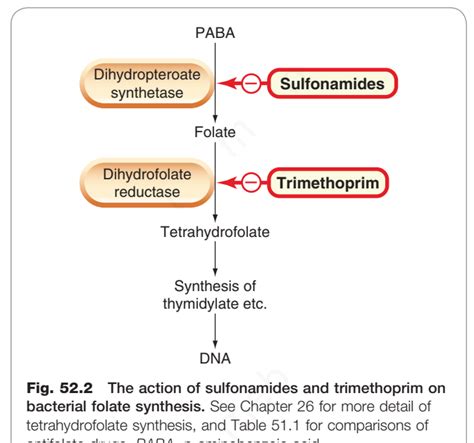
Bactrim Mechanism of Action
Benefits of Bactrim

Side Effects and Precautions

Responsible Use of Bactrim

Bactrim in Pediatric and Geriatric Populations

Interactions with Other Medications
Conclusion and Future Directions

As we move forward in the era of antibiotic resistance, it is essential for patients, healthcare professionals, and policymakers to collaborate in promoting the judicious use of antibiotics. This includes supporting research into new antimicrobial therapies, implementing infection control measures, and educating the public about the importance of antibiotic stewardship. Together, we can preserve the effectiveness of antibiotics like Bactrim for generations to come and combat the growing threat of antibiotic resistance.
What is Bactrim used for?
+Bactrim is used to treat various bacterial infections, including urinary tract infections, acute otitis media, bronchitis, and traveler's diarrhea.
How does Bactrim work?
+Bactrim works by inhibiting the synthesis of folic acid in bacteria, which is essential for bacterial DNA synthesis and cell proliferation.
What are the common side effects of Bactrim?
+Common side effects of Bactrim include nausea, vomiting, and skin rashes. More severe side effects, such as Stevens-Johnson syndrome and agranulocytosis, are rare but can be life-threatening.
Can Bactrim be used in pediatric and geriatric populations?
+Yes, Bactrim can be used in pediatric and geriatric populations, but with caution. The dosage must be carefully calculated in children, and close monitoring is necessary in geriatric patients due to the risk of adverse effects.
How can we promote the responsible use of Bactrim and other antibiotics?
+We can promote the responsible use of Bactrim and other antibiotics by using them only when necessary, completing the full course of treatment, and practicing good hygiene to prevent the spread of infections.
We hope this comprehensive guide to Bactrim has provided you with a deeper understanding of its uses, benefits, and potential risks. If you have any further questions or would like to share your experiences with Bactrim, please do not hesitate to comment below. Your insights and feedback are invaluable in helping us improve our content and serve the community better. Additionally, if you found this article informative, please consider sharing it with others who may benefit from this information. Together, let's work towards promoting antibiotic stewardship and ensuring the continued effectiveness of lifesaving medications like Bactrim.
