Intro
Discover key facts about Lipitor, a statin medication, including its uses, side effects, and benefits, to manage cholesterol levels and reduce heart disease risk with effective lipid-lowering treatment.
Lipitor, also known as atorvastatin, is a widely prescribed medication used to lower cholesterol levels in the blood. It belongs to a group of drugs called statins, which work by inhibiting the production of cholesterol in the liver. With its widespread use, it's essential to understand the facts about Lipitor to make informed decisions about your health. In this article, we'll delve into the world of Lipitor, exploring its benefits, side effects, and usage guidelines.
The importance of managing cholesterol levels cannot be overstated. High levels of low-density lipoprotein (LDL) cholesterol, also known as "bad" cholesterol, can increase the risk of heart disease, heart attacks, and strokes. Lipitor has been proven to be effective in reducing LDL cholesterol levels, thereby decreasing the risk of cardiovascular events. However, like any medication, Lipitor has its pros and cons, and it's crucial to be aware of them to ensure safe and effective use.
As we navigate the complexities of Lipitor, it's essential to consider the various factors that influence its effectiveness and potential side effects. From dosage and administration to interactions with other medications, understanding the intricacies of Lipitor is vital for maximizing its benefits while minimizing its risks. In the following sections, we'll provide an in-depth examination of Lipitor, covering its mechanism of action, benefits, and potential drawbacks.
What is Lipitor?

How Does Lipitor Work?
Lipitor's mechanism of action is complex, involving multiple pathways and interactions with other molecules. In simple terms, Lipitor works by: * Inhibiting the production of cholesterol in the liver * Increasing the uptake of LDL cholesterol from the bloodstream * Reducing the amount of LDL cholesterol available for deposition in the walls of arteries * Increasing the levels of high-density lipoprotein (HDL) cholesterol, also known as "good" cholesterolBenefits of Lipitor

Who Should Take Lipitor?
Lipitor is typically prescribed for individuals with high levels of LDL cholesterol, particularly those who are at increased risk of cardiovascular events. This includes: * Individuals with a family history of high cholesterol or cardiovascular disease * Those who are overweight or obese * Individuals with diabetes or high blood pressure * Those who smoke or have a history of smokingSide Effects of Lipitor
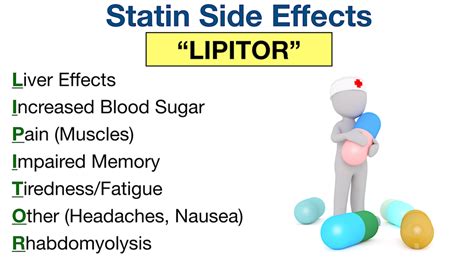
Interactions with Other Medications
Lipitor can interact with other medications, including: * Blood thinners, such as warfarin * Diabetes medications, such as metformin * Certain antibiotics, such as erythromycin * Grapefruit or grapefruit juice, which can increase the levels of Lipitor in the bloodstreamDosage and Administration
Monitoring and Follow-up
Regular monitoring and follow-up are crucial when taking Lipitor. This includes: * Regular blood tests to check liver function and lipid profiles * Monitoring for side effects, such as muscle pain or joint pain * Adjusting the dosage or discontinuing the medication if side effects occurAlternatives to Lipitor
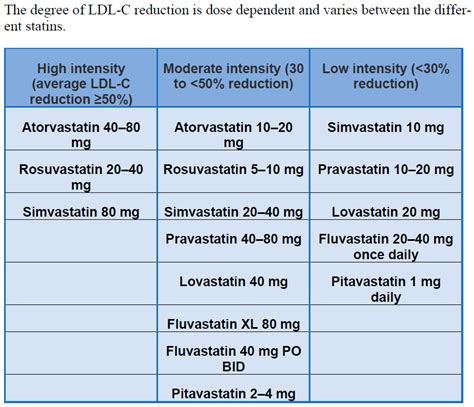
Lifestyle Modifications
Lifestyle modifications can play a significant role in managing high cholesterol and reducing the risk of cardiovascular events. This includes: * Eating a healthy, balanced diet low in saturated and trans fats * Engaging in regular physical activity, such as walking or jogging * Maintaining a healthy weight * Quitting smoking or avoiding secondhand smokeWhat is the typical dosage of Lipitor?
+The typical dosage of Lipitor ranges from 10 to 80 milligrams per day, taken orally once daily.
Can I take Lipitor with other medications?
+Lipitor can interact with other medications, including blood thinners, diabetes medications, and certain antibiotics. It's essential to consult with your doctor before taking Lipitor with other medications.
What are the common side effects of Lipitor?
+Common side effects of Lipitor include muscle pain or weakness, joint pain or swelling, abdominal pain or nausea, headache or dizziness, and increased risk of liver damage or liver enzyme elevations.
As we conclude our exploration of Lipitor, it's essential to remember that managing high cholesterol requires a comprehensive approach that incorporates medication, lifestyle modifications, and regular monitoring. By understanding the benefits and potential drawbacks of Lipitor, individuals can make informed decisions about their health and work with their healthcare providers to develop effective treatment plans. We invite you to share your thoughts and questions about Lipitor in the comments section below, and we encourage you to share this article with others who may benefit from this information. Together, we can work towards a healthier and more informed community.
