Intro
Discover the Losartan Medication Guide, covering dosage, side effects, and interactions. Learn about blood pressure management, hypertension treatment, and angiotensin II receptor blockers for a healthy lifestyle.
Losartan is a medication that has been widely used to treat high blood pressure and protect the kidneys from damage due to diabetes. It belongs to a class of drugs known as angiotensin II receptor blockers (ARBs), which work by blocking the action of a natural chemical that narrows blood vessels, allowing blood vessels to widen and improve blood flow. This medication has been a cornerstone in the management of cardiovascular diseases and has been prescribed to millions of patients worldwide. Understanding how losartan works, its benefits, potential side effects, and proper usage is essential for patients who are taking or considering this medication.
The importance of managing high blood pressure cannot be overstated. Hypertension is a major risk factor for heart disease, stroke, and kidney disease. If left uncontrolled, high blood pressure can lead to serious complications, including heart failure, vision loss, and kidney failure. Losartan, by effectively lowering blood pressure, plays a critical role in reducing the risk of these complications. Moreover, for patients with diabetes, losartan has been shown to slow the progression of kidney disease, a common and serious complication of diabetes. This dual benefit makes losartan a valuable medication for a wide range of patients.
The mechanism of action of losartan is complex but essentially involves the blockade of angiotensin II, a potent vasoconstrictor, from binding to its receptor. By preventing this interaction, losartan leads to vasodilation, which reduces blood pressure. This action also has protective effects on the kidneys by reducing the pressure inside the kidneys and decreasing proteinuria, the presence of excess proteins in the urine, which is a marker of kidney damage. The efficacy of losartan in lowering blood pressure and its protective effects on the kidneys have been well-documented in numerous clinical trials, making it a trusted medication among healthcare providers.
Benefits of Losartan
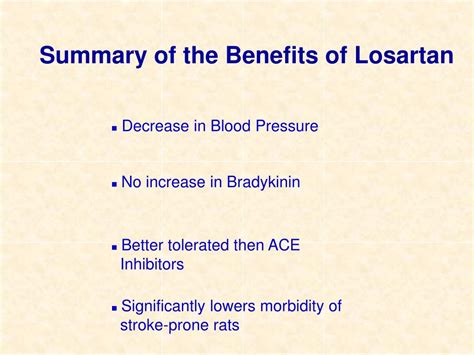
Key Benefits for Patients
The benefits of losartan can be summarized as follows: - Effective in lowering blood pressure and controlling hypertension. - Offers renal protection, particularly in patients with diabetes. - Generally well-tolerated with a favorable side effect profile. - Can be used in combination with other medications for additive effects. - Available in various formulations, including generic versions, making it more accessible to a wider range of patients.Working Mechanism of Losartan
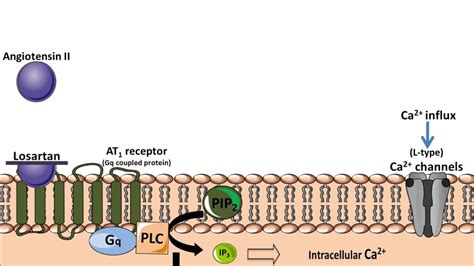
Steps Involved in Losartan’s Action
The steps involved in losartan’s action can be outlined as follows: 1. **Inhibition of Angiotensin II**: Losartan binds to the AT1 receptor, preventing angiotensin II from exerting its effects. 2. **Vasodilation**: The blockade of angiotensin II’s vasoconstrictive effects leads to the dilation of blood vessels. 3. **Blood Pressure Reduction**: The combined effect of vasodilation and reduced aldosterone secretion leads to a decrease in blood pressure. 4. **Renal Protection**: Reduced intraglomerular pressure and decreased aldosterone levels contribute to the protective effects on the kidneys.Side Effects and Precautions

Precautions and Warnings
- **Pregnancy and Breastfeeding**: Losartan is contraindicated in pregnancy due to the potential for fetal harm and should be used with caution in breastfeeding mothers. - **Kidney Disease**: Patients with kidney disease should have their renal function monitored closely while on losartan. - **Hyperkalemia**: Patients at risk of hyperkalemia should have their potassium levels monitored.Practical Examples and Statistical Data
Statistical Overview
- **Reduction in Blood Pressure**: Clinical trials have shown that losartan can reduce systolic blood pressure by an average of 10-15 mmHg and diastolic blood pressure by 5-10 mmHg. - **Kidney Protection**: Studies in patients with diabetic nephropathy have demonstrated a 20-30% reduction in the risk of kidney disease progression with losartan treatment.FAQs

What is the primary use of losartan?
+Losartan is primarily used to treat high blood pressure and protect the kidneys from damage due to diabetes.
Can losartan be used in patients with kidney disease?
+Yes, losartan can be used in patients with kidney disease, but their renal function should be closely monitored, especially if they have pre-existing kidney disease.
Is losartan safe during pregnancy?
+No, losartan is contraindicated in pregnancy due to the potential for fetal harm.
In conclusion, losartan is a valuable medication for the management of hypertension and the protection of the kidneys in patients with diabetes. Its efficacy, safety profile, and benefits make it a preferred choice among healthcare providers. By understanding how losartan works, its potential side effects, and the precautions that need to be taken, patients can work closely with their healthcare providers to manage their condition effectively. We invite readers to share their experiences or ask questions about losartan and its use in the comments section below, and to share this article with others who may benefit from this information.
