Intro
Discover crucial 5 Flu Facts, including flu symptoms, vaccination, and prevention methods, to protect against influenza and seasonal flu outbreaks, promoting public health awareness.
The flu, also known as influenza, is a highly contagious respiratory illness that affects millions of people worldwide each year. It is a significant public health concern, particularly during the winter months when the virus is most active. Understanding the flu and its effects on the body is crucial for preventing its spread and mitigating its symptoms. In this article, we will delve into the world of flu facts, exploring the importance of vaccination, the differences between types of flu, and the best ways to protect yourself and your loved ones from this debilitating illness.
The flu is a serious disease that can have severe consequences, especially for vulnerable populations such as the elderly, young children, and people with certain chronic health conditions. According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), the flu results in approximately 140,000 to 720,000 hospitalizations and 12,000 to 79,000 deaths in the United States each year. These statistics highlight the need for awareness and education about the flu, its prevention, and its treatment.
As we navigate the complexities of the flu, it is essential to separate fact from fiction. Many myths and misconceptions surround this illness, which can lead to confusion and poor decision-making. By examining the latest research and expert recommendations, we can gain a deeper understanding of the flu and develop effective strategies for staying healthy during flu season. Whether you are a healthcare professional, a concerned parent, or simply someone looking to stay informed, this article will provide you with the knowledge and insights you need to make informed decisions about your health.
Understanding the Flu Virus
Types of Flu Vaccines
The flu vaccine is the most effective way to prevent the flu and its complications. There are several types of flu vaccines available, including trivalent, quadrivalent, and high-dose vaccines. Trivalent vaccines protect against three different flu viruses, while quadrivalent vaccines protect against four. High-dose vaccines are designed for people aged 65 and older, as they provide a stronger immune response. It is essential to get vaccinated every year, as the flu virus is constantly evolving, and last year's vaccine may not provide protection against this year's strains.Flu Symptoms and Diagnosis
Flu Treatment and Management
While there is no cure for the flu, there are several treatment options available to help manage its symptoms and prevent complications. Antiviral medications, such as oseltamivir (Tamiflu) and zanamivir (Relenza), can help reduce the severity and duration of the flu. These medications work best when started within 48 hours of symptom onset. In addition to antiviral medications, rest, hydration, and over-the-counter medications can help alleviate symptoms and support the body's natural recovery process.Preventing the Spread of the Flu

Flu and Vulnerable Populations
Certain populations are at higher risk for flu complications, including pregnant women, young children, older adults, and people with certain chronic health conditions. These individuals should take extra precautions to protect themselves from the flu, including getting vaccinated, practicing good hygiene, and seeking medical attention immediately if they experience any flu symptoms.Flu Season and its Impact on Public Health

Flu Surveillance and Monitoring
Flu surveillance and monitoring are critical components of public health efforts to track and respond to flu outbreaks. The CDC, in collaboration with state and local health departments, monitors flu activity through a network of laboratories, hospitals, and healthcare providers. This information is used to identify trends, detect outbreaks, and inform vaccination and treatment strategies.Conclusion and Next Steps

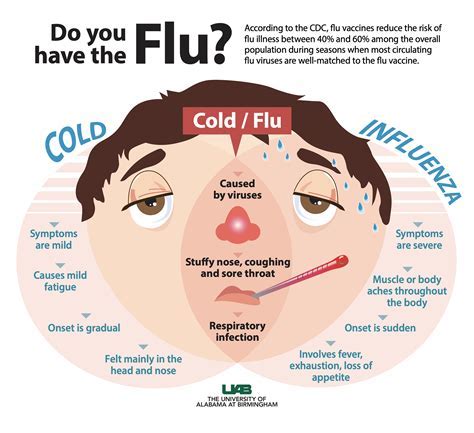
What are the most common symptoms of the flu?
+The most common symptoms of the flu include fever, chills, cough, sore throat, runny or stuffy nose, muscle or body aches, headaches, fatigue, and diarrhea or vomiting.
How can I prevent the spread of the flu?
+You can prevent the spread of the flu by getting vaccinated, washing your hands frequently, avoiding close contact with people who are sick, staying home from work or school when you are sick, and avoiding touching your eyes, nose, and mouth.
Who is at higher risk for flu complications?
+Certain populations are at higher risk for flu complications, including pregnant women, young children, older adults, and people with certain chronic health conditions.
We hope this article has provided you with a comprehensive understanding of the flu and its impact on public health. If you have any further questions or concerns, please do not hesitate to reach out. Share this article with your friends and family to help spread awareness about the flu and its prevention. Together, we can create a healthier, more informed community.
