Intro
Discover what Tramadol is, a pain reliever medication, and learn about its uses, dosage, and side effects, including opioid addiction risks and withdrawal symptoms, for effective pain management and safety.
Tramadol is a medication that has been widely used for its analgesic properties, helping to relieve moderate to moderately severe pain. It is a synthetic opioid, meaning it is man-made and works by binding to opioid receptors in the brain, similar to natural opioids like morphine and codeine. This action changes the way the brain perceives pain, providing relief to individuals suffering from various types of pain, including chronic pain, pain after surgery, and pain caused by injuries.
The importance of understanding tramadol cannot be overstated, given its widespread use and potential for both benefits and risks. On one hand, it offers an effective solution for managing pain that might not be adequately controlled by other types of pain relievers. On the other hand, like all opioid medications, tramadol carries the risk of dependence, addiction, and side effects, some of which can be serious. Therefore, it is crucial for individuals prescribed tramadol, as well as their loved ones, to be well-informed about its use, effects, and potential risks.
Tramadol's mechanism of action is somewhat unique compared to other opioids. It not only binds to opioid receptors but also inhibits the reuptake of norepinephrine and serotonin, two neurotransmitters involved in pain regulation. This dual-action mechanism may contribute to its effectiveness in treating certain types of pain that are not responsive to other opioid analgesics. However, this complexity also means that tramadol can have a broader range of effects on the body, which can sometimes lead to unexpected side effects or interactions with other medications.
How Tramadol Works

Tramadol works by influencing the central nervous system, specifically the brain and spinal cord, to alter the perception of and response to pain. Its dual mechanism of action, involving both opioid receptor binding and the inhibition of neurotransmitter reuptake, sets it apart from some other pain medications. The opioid component directly affects the pain centers in the brain, reducing the sensation of pain. Meanwhile, the increase in norepinephrine and serotonin levels due to reduced reuptake can enhance the analgesic effect and may also contribute to its antidepressant and anxiolytic effects, although these are not its primary indications.
Benefits of Tramadol
The benefits of tramadol for pain management are significant, especially for individuals who have not found relief with non-opioid pain medications. Some of the key advantages include: - Effective pain relief: Tramadol can provide significant relief from moderate to moderately severe pain. - Versatility: It is available in various formulations, including immediate-release and extended-release tablets and capsules, which can be tailored to the individual's needs. - Dual-action mechanism: Its unique mechanism of action may make it effective for certain types of pain that are resistant to other treatments.Risks and Side Effects of Tramadol

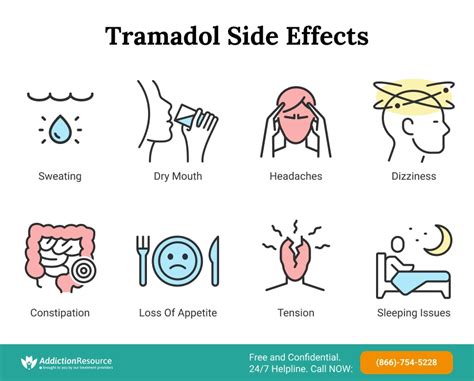
While tramadol can be an effective pain reliever, it also comes with risks and potential side effects. Common side effects include dizziness, nausea, constipation, and headache. More serious risks include the potential for addiction and dependence, as well as the risk of serotonin syndrome, a potentially life-threatening condition caused by excessive levels of serotonin in the body. The risk of respiratory depression, a condition where breathing becomes dangerously slow, is also a concern, especially when tramadol is used in high doses or combined with other central nervous system depressants.
Precautions and Contraindications
Given the potential risks, there are several precautions and contraindications to consider when using tramadol. These include: - History of substance abuse: Individuals with a history of drug or alcohol abuse may be at higher risk of developing dependence on tramadol. - Respiratory conditions: Tramadol can worsen respiratory conditions such as asthma or chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). - Pregnancy and breastfeeding: The safety of tramadol during pregnancy and breastfeeding is not well established, and its use should be approached with caution.Using Tramadol Safely
To use tramadol safely, it is essential to follow the prescribed dosage and usage instructions carefully. This includes:
- Taking the medication exactly as directed by your healthcare provider.
- Not exceeding the recommended dose or taking it for longer than prescribed.
- Being aware of potential interactions with other medications, including other opioids, benzodiazepines, and certain antidepressants.
- Monitoring for signs of dependence or addiction, such as needing to take more medication to achieve the same effect or experiencing withdrawal symptoms when attempting to stop.
Alternatives to Tramadol
For individuals who may not be candidates for tramadol due to its risks or for those who have not found it effective, there are alternative pain management strategies. These can include: - Non-opioid pain relievers: Medications like acetaminophen or NSAIDs (nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs) can be effective for mild to moderate pain. - Other opioids: In some cases, other opioid medications may be considered, although this should be done under the close supervision of a healthcare provider due to the risk of addiction and other side effects. - Non-pharmacological interventions: Techniques such as physical therapy, cognitive-behavioral therapy, and alternative therapies like acupuncture may offer relief for certain types of pain.Conclusion and Future Directions
In conclusion, tramadol is a complex medication with both benefits and risks. Its unique mechanism of action makes it a valuable option for pain management, but its potential for dependence and side effects necessitates careful use and monitoring. As research into pain management continues, it is likely that new medications and therapies will emerge, potentially offering safer alternatives or complementary treatments to tramadol. For now, it remains an important tool in the arsenal against pain, provided it is used judiciously and under medical supervision.
Final Thoughts
The decision to use tramadol should be made with a full understanding of its implications. Individuals should discuss their options thoroughly with their healthcare provider, considering their medical history, the nature of their pain, and the potential risks and benefits. By doing so, they can make an informed decision that balances the need for effective pain relief with the need to minimize risks.What is tramadol used for?
+Tramadol is used to relieve moderate to moderately severe pain.
Is tramadol an opioid?
+Yes, tramadol is a synthetic opioid.
What are the risks of taking tramadol?
+The risks include dependence, addiction, respiratory depression, and serotonin syndrome.
We hope this information has been helpful in understanding tramadol and its role in pain management. If you have any further questions or concerns about tramadol or any other medication, we encourage you to consult with a healthcare professional. Additionally, if you found this article informative, please consider sharing it with others who might benefit from this information. Your engagement and feedback are valuable to us, and we look forward to providing more insightful content in the future.
