Intro
Thyroidectomy is a surgical procedure that involves the removal of all or part of the thyroid gland. The thyroid gland is a small, butterfly-shaped gland located in the neck, just below the Adam's apple. It plays a crucial role in regulating various bodily functions, including metabolism, growth, and development. Thyroidectomy is typically performed to treat thyroid cancer, nodules, or hyperthyroidism. The procedure can be performed using traditional open surgery or minimally invasive techniques, such as robotic or endoscopic surgery.
Thyroidectomy is a common procedure, with over 50,000 surgeries performed annually in the United States alone. The surgery can be life-changing for patients with thyroid disorders, providing relief from symptoms such as weight loss, anxiety, and fatigue. However, like any surgical procedure, thyroidectomy carries risks and complications, including damage to surrounding tissues, vocal cord paralysis, and hypocalcemia. It is essential for patients to carefully consider their treatment options and discuss any concerns with their healthcare provider.
The thyroid gland produces hormones that regulate various bodily functions, including metabolism, heart rate, and body temperature. When the thyroid gland becomes diseased or dysfunctional, it can lead to a range of symptoms, including weight loss or gain, fatigue, anxiety, and depression. Thyroidectomy can help alleviate these symptoms by removing the diseased or damaged thyroid tissue. The procedure can also help prevent the spread of thyroid cancer to other parts of the body.
Types of Thyroidectomy
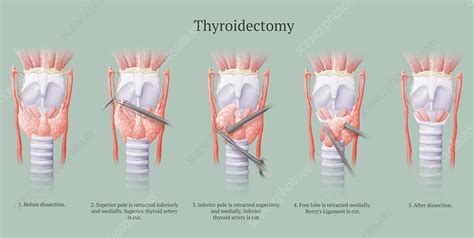
There are several types of thyroidectomy, including total thyroidectomy, subtotal thyroidectomy, and lobectomy. Total thyroidectomy involves the removal of the entire thyroid gland, while subtotal thyroidectomy involves the removal of most of the gland, leaving a small portion intact. Lobectomy involves the removal of one lobe of the thyroid gland. The type of surgery performed depends on the underlying condition, the size and location of the tumor or nodule, and the patient's overall health.
Indications for Thyroidectomy
Thyroidectomy is typically performed to treat the following conditions: * Thyroid cancer: Thyroidectomy is often the primary treatment for thyroid cancer, especially if the cancer is localized to the thyroid gland. * Thyroid nodules: Large or suspicious thyroid nodules may require surgical removal to determine if they are cancerous. * Hyperthyroidism: In some cases, thyroidectomy may be necessary to treat hyperthyroidism, especially if medication or radioactive iodine therapy is ineffective. * Goiter: A large or symptomatic goiter may require surgical removal to relieve pressure on surrounding tissues.Preparation for Thyroidectomy
Preparation for thyroidectomy typically involves a series of tests and evaluations to determine the underlying condition and overall health of the patient. These tests may include:
- Blood tests: To evaluate thyroid hormone levels and check for any underlying conditions.
- Imaging tests: Such as ultrasound, CT, or MRI scans to evaluate the size and location of the thyroid gland and any nodules or tumors.
- Fine-needle aspiration biopsy: To collect tissue samples from the thyroid gland for further evaluation.
- Vocal cord examination: To evaluate the function of the vocal cords and surrounding tissues.
Risks and Complications
As with any surgical procedure, thyroidectomy carries risks and complications, including: * Damage to surrounding tissues: Such as the vocal cords, parathyroid glands, or nerves. * Vocal cord paralysis: Which can lead to hoarseness, breathing difficulties, or swallowing problems. * Hypocalcemia: A condition characterized by low calcium levels, which can lead to muscle cramps, numbness, or tingling. * Infection: As with any surgical procedure, there is a risk of infection with thyroidectomy.Recovery from Thyroidectomy
Recovery from thyroidectomy typically takes several weeks to several months. Patients may experience pain, swelling, and bruising at the surgical site, which can be managed with pain medication and ice packs. It is essential to follow a healthy diet and lifestyle to promote healing and prevent complications. Patients may also need to take thyroid hormone replacement medication to regulate their thyroid hormone levels.
Thyroid Hormone Replacement
Thyroid hormone replacement medication is often necessary after thyroidectomy to regulate thyroid hormone levels. The medication works by replacing the hormones produced by the thyroid gland, which helps to regulate metabolism, growth, and development. The dosage and type of medication may vary depending on the individual patient's needs and underlying condition.Benefits of Thyroidectomy
Thyroidectomy can provide several benefits, including:
- Relief from symptoms: Such as weight loss, anxiety, and fatigue.
- Prevention of cancer spread: Thyroidectomy can help prevent the spread of thyroid cancer to other parts of the body.
- Improved quality of life: Thyroidectomy can help improve overall quality of life by regulating thyroid hormone levels and alleviating symptoms.
Minimally Invasive Thyroidectomy
Minimally invasive thyroidectomy is a surgical technique that uses small incisions and specialized instruments to remove the thyroid gland. This approach can provide several benefits, including: * Reduced scarring: Minimally invasive thyroidectomy typically results in smaller scars and less noticeable incisions. * Less pain: The procedure can result in less pain and discomfort compared to traditional open surgery. * Faster recovery: Minimally invasive thyroidectomy can result in a faster recovery time, with patients often returning to their normal activities within a few days.Robotic Thyroidectomy
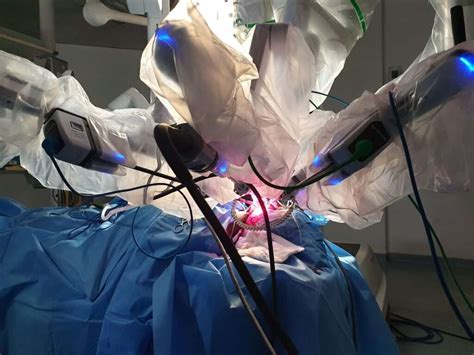
Robotic thyroidectomy is a type of minimally invasive surgery that uses a robotic system to remove the thyroid gland. The procedure involves several small incisions and specialized instruments, which are controlled by a robotic system. Robotic thyroidectomy can provide several benefits, including:
- Improved precision: The robotic system can provide improved precision and dexterity, allowing for more accurate dissection and removal of the thyroid gland.
- Reduced risk of complications: Robotic thyroidectomy can result in a reduced risk of complications, such as damage to surrounding tissues or vocal cord paralysis.
Thyroidectomy and Pregnancy
Thyroidectomy can be performed during pregnancy, but it is essential to carefully consider the risks and benefits. Thyroid disorders can affect pregnancy, and untreated conditions can lead to complications, such as miscarriage or premature birth. However, thyroidectomy can also pose risks to the fetus, such as radiation exposure or maternal hypothyroidism. It is essential to discuss any concerns with a healthcare provider and carefully weigh the risks and benefits of thyroidectomy during pregnancy.Thyroidectomy and Mental Health

Thyroidectomy can have a significant impact on mental health, particularly in patients with thyroid disorders. Thyroid disorders can lead to symptoms such as anxiety, depression, and mood swings, which can be alleviated with thyroidectomy. However, the surgery can also pose psychological challenges, such as coping with a new diagnosis or adjusting to changes in physical appearance. It is essential to discuss any concerns with a healthcare provider and seek support from mental health professionals if necessary.
Thyroidectomy and Nutrition
Thyroidectomy can affect nutrition, particularly in patients who require thyroid hormone replacement medication. A balanced diet that includes foods rich in iodine, such as seafood, dairy products, and iodized salt, can help support thyroid health. It is also essential to avoid foods that can interfere with thyroid function, such as soy products, cruciferous vegetables, and gluten. A healthcare provider can provide personalized dietary recommendations to support thyroid health and overall well-being.Future Directions
Thyroidectomy is a rapidly evolving field, with ongoing research and advancements in surgical techniques, instrumentation, and patient care. Future directions in thyroidectomy may include:
- Development of new surgical techniques: Such as single-incision thyroidectomy or transoral thyroidectomy.
- Improved instrumentation: Such as advanced robotic systems or specialized dissecting instruments.
- Personalized medicine: Tailoring treatment approaches to individual patient needs and underlying conditions.
What is thyroidectomy?
+Thyroidectomy is a surgical procedure that involves the removal of all or part of the thyroid gland.
What are the benefits of thyroidectomy?
+Thyroidectomy can provide relief from symptoms, prevent the spread of cancer, and improve overall quality of life.
What are the risks and complications of thyroidectomy?
+Thyroidectomy carries risks and complications, including damage to surrounding tissues, vocal cord paralysis, and hypocalcemia.
How long does recovery from thyroidectomy take?
+Recovery from thyroidectomy typically takes several weeks to several months, depending on the individual patient's needs and underlying condition.
Can thyroidectomy be performed during pregnancy?
+Yes, thyroidectomy can be performed during pregnancy, but it is essential to carefully consider the risks and benefits and discuss any concerns with a healthcare provider.
In conclusion, thyroidectomy is a surgical procedure that involves the removal of all or part of the thyroid gland. The procedure can provide relief from symptoms, prevent the spread of cancer, and improve overall quality of life. However, it is essential to carefully consider the risks and benefits and discuss any concerns with a healthcare provider. We invite you to share your thoughts and experiences with thyroidectomy in the comments below. If you have any questions or concerns, please do not hesitate to reach out to a healthcare professional. Share this article with others who may benefit from this information, and let's work together to promote awareness and understanding of thyroid disorders and thyroidectomy.
