Intro
Discover Toradol uses and benefits, a potent NSAID for pain relief, inflammation reduction, and fever treatment, offering therapeutic advantages for various conditions, including arthritis and migraine management.
Toradol, also known as ketorolac, is a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) that has been widely used for its analgesic and anti-inflammatory properties. The medication is available in various forms, including tablets, injections, and eye drops, and is used to treat a range of conditions, from mild to moderate pain and inflammation. In this article, we will delve into the uses and benefits of Toradol, exploring its mechanisms of action, potential side effects, and practical applications.
The importance of effective pain management cannot be overstated, as it plays a crucial role in improving quality of life, reducing discomfort, and enabling individuals to engage in daily activities. Toradol has emerged as a valuable treatment option, offering a potent and rapid-acting solution for various types of pain, including post-operative pain, menstrual cramps, and migraines. By understanding the uses and benefits of Toradol, healthcare professionals and patients can make informed decisions about its use and optimize its therapeutic potential.
Toradol's versatility and efficacy have made it a popular choice among healthcare providers, who appreciate its ability to provide relief from pain and inflammation in a variety of clinical settings. From emergency departments to surgical units, Toradol has become an essential tool in the management of acute and chronic pain. Moreover, its relatively short duration of action and lack of addictive properties make it an attractive alternative to opioid-based pain medications, which are often associated with significant risks and side effects.
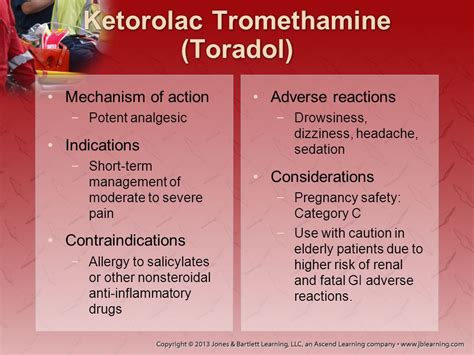
Toradol Mechanism of Action
Toradol Uses
Toradol is indicated for the short-term management of moderate to severe pain, including: * Post-operative pain * Menstrual cramps * Migraines * Dental pain * Musculoskeletal pain Its use is typically limited to a maximum of 5 days, as prolonged treatment can increase the risk of adverse effects, such as gastrointestinal bleeding and kidney damage.Toradol Benefits
Toradol Side Effects
While Toradol is generally well-tolerated, it can cause side effects, including: * Gastrointestinal bleeding * Kidney damage * Increased risk of heart attack and stroke * Allergic reactions * Dizziness and drowsiness It is essential to carefully evaluate the potential benefits and risks of Toradol before initiating treatment, particularly in patients with pre-existing medical conditions or those taking other medications that may interact with Toradol.Toradol Dosage and Administration

Toradol Interactions
Toradol can interact with other medications, including: * Blood thinners * Diuretics * Beta blockers * ACE inhibitors * Other NSAIDs These interactions can increase the risk of adverse effects or reduce the efficacy of Toradol. Therefore, it is essential to inform healthcare providers about all medications being taken before initiating Toradol treatment.Toradol Contraindications

Toradol Warnings and Precautions
Toradol should be used with caution in patients with: * History of gastrointestinal bleeding * Kidney disease * Heart disease * High blood pressure * Allergic reactions to NSAIDs Regular monitoring of kidney function, blood pressure, and gastrointestinal health is essential to minimize the risk of adverse effects and ensure optimal therapeutic outcomes.Toradol Overdose

Toradol Storage and Disposal
Toradol should be stored in a cool, dry place, away from direct sunlight and moisture. Unused medication should be disposed of properly, following local regulations and guidelines to minimize the risk of environmental contamination and ensure safe disposal.Toradol Patient Education

Toradol Clinical Trials
Numerous clinical trials have evaluated the efficacy and safety of Toradol in various clinical settings. These studies have consistently demonstrated the medication's potent analgesic and anti-inflammatory effects, as well as its relatively favorable safety profile. Ongoing research continues to explore the potential benefits and risks of Toradol, further informing its use in clinical practice.Toradol Future Directions
In conclusion, Toradol is a valuable medication that offers significant benefits in the management of moderate to severe pain and inflammation. By understanding its mechanisms of action, uses, and potential side effects, healthcare providers and patients can work together to optimize its therapeutic potential and minimize the risk of adverse effects. As research continues to uncover new insights into Toradol's clinical applications and safety profile, this medication is likely to remain an essential tool in the treatment of pain and inflammation.
We invite you to share your thoughts and experiences with Toradol in the comments section below. Have you used Toradol for pain management? What were your experiences with the medication? Do you have any questions or concerns about Toradol's uses, benefits, or potential side effects? Join the conversation and help us build a community of informed and empowered patients and healthcare providers.
What is Toradol used for?
+Toradol is used to treat moderate to severe pain and inflammation, including post-operative pain, menstrual cramps, migraines, and musculoskeletal pain.
What are the potential side effects of Toradol?
+Toradol can cause side effects, including gastrointestinal bleeding, kidney damage, increased risk of heart attack and stroke, allergic reactions, and dizziness and drowsiness.
How long can I take Toradol?
+Toradol is typically used for short-term management of pain and inflammation, with a maximum treatment duration of 5 days.
Can I take Toradol with other medications?
+Toradol can interact with other medications, including blood thinners, diuretics, beta blockers, and ACE inhibitors. It is essential to inform healthcare providers about all medications being taken before initiating Toradol treatment.
Is Toradol addictive?
+Toradol is not associated with a significant risk of addiction or dependence, unlike opioid-based pain medications.
