Intro
Discover Valproic Acid uses, effects, and benefits in treating epilepsy, bipolar disorder, and migraines, with insights into its mechanisms, side effects, and interactions, for informed healthcare decisions.
Valproic acid, also known as valproate, is a medication that has been widely used in the treatment of various neurological and psychiatric disorders. Its uses and effects are diverse, and it has become an essential component in the management of conditions such as epilepsy, bipolar disorder, and migraine headaches. The importance of valproic acid lies in its ability to stabilize abnormal electrical activity in the brain, which can lead to seizures, mood swings, and other symptoms associated with these conditions.
The history of valproic acid dates back to the 1960s, when it was first introduced as an anticonvulsant medication. Since then, its uses have expanded to include the treatment of manic episodes in bipolar disorder, prevention of migraine headaches, and management of other conditions such as anxiety and insomnia. The medication works by increasing the levels of a neurotransmitter called gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) in the brain, which helps to calm down excessive electrical activity and promote a sense of relaxation.
Despite its effectiveness, valproic acid can have significant side effects, particularly when taken in high doses or for extended periods. Some common side effects include drowsiness, dizziness, nausea, and weight gain. In rare cases, valproic acid can cause more severe side effects, such as liver damage, pancreatitis, and birth defects. Therefore, it is essential to use this medication under the guidance of a healthcare professional and to carefully monitor its effects to minimize the risk of adverse reactions.
Valproic Acid Mechanism of Action
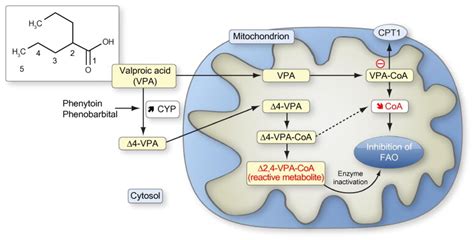
In addition to its effects on GABA and sodium channels, valproic acid has been shown to have an impact on other neurotransmitter systems, including glutamate and serotonin. The medication can also affect the expression of genes involved in the regulation of neuronal activity, which can lead to long-term changes in brain function and behavior. Overall, the mechanism of action of valproic acid is multifaceted and involves a combination of effects on neurotransmitter systems, ion channels, and gene expression.
Valproic Acid Uses

Valproic acid can be administered orally or intravenously, and it is available in various formulations, including tablets, capsules, and injectable solutions. The dosage and duration of treatment with valproic acid depend on the specific condition being treated and the individual's response to the medication.
Valproic Acid Dosage and Administration
The dosage and administration of valproic acid vary depending on the condition being treated and the individual's age, weight, and medical history. The typical dosage range for valproic acid is between 500 and 2000 mg per day, divided into two or three doses. The medication should be taken with food to minimize the risk of gastrointestinal side effects.In people with epilepsy, the dosage of valproic acid is typically adjusted based on the severity of the seizures and the individual's response to the medication. The goal is to achieve a therapeutic level of the medication in the blood, which can help to prevent seizures and minimize side effects.
Valproic Acid Side Effects
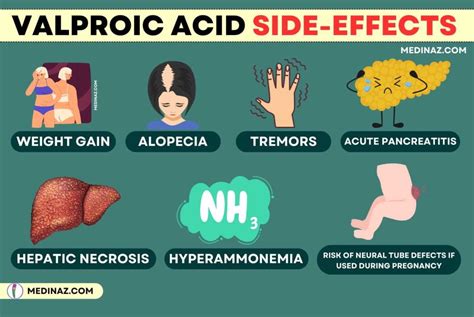
In rare cases, valproic acid can cause more severe side effects, such as:
- Liver damage and pancreatitis
- Birth defects and developmental delays *Blood dyscrasias and bone marrow suppression
- Hypersensitivity reactions and allergic reactions
It is essential to monitor the effects of valproic acid closely and to report any side effects to a healthcare professional. In some cases, the medication may need to be adjusted or discontinued to minimize the risk of adverse reactions.
Valproic Acid Interactions
Valproic acid can interact with other medications, including: * Anticonvulsants: Valproic acid can increase the levels of other anticonvulsants in the blood, which can lead to increased side effects. * Blood thinners: Valproic acid can increase the risk of bleeding when taken with blood thinners. * Antibiotics: Valproic acid can reduce the effectiveness of certain antibiotics. * Hormonal contraceptives: Valproic acid can reduce the effectiveness of hormonal contraceptives.It is essential to inform a healthcare professional about all medications being taken, including prescription and over-the-counter medications, to minimize the risk of interactions.
Valproic Acid Warnings and Precautions

It is essential to follow the instructions of a healthcare professional and to report any side effects or concerns to minimize the risk of adverse reactions.
Valproic Acid Overdose
Valproic acid overdose can occur when the medication is taken in excess or when it is combined with other medications. Symptoms of valproic acid overdose include: * Drowsiness and coma * Seizures and convulsions * Respiratory depression * Cardiac arrestIn the event of an overdose, it is essential to seek medical attention immediately. Treatment may involve supportive care, such as monitoring of vital signs and administration of activated charcoal, as well as specific treatments, such as hemodialysis and administration of antidotes.
Valproic Acid Alternatives
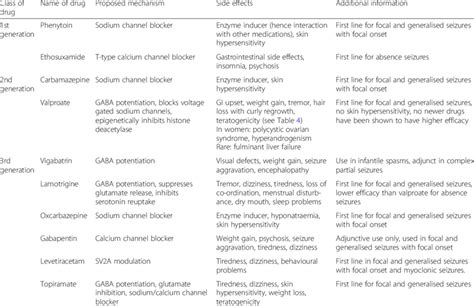
The choice of alternative medication depends on the specific condition being treated and the individual's medical history and response to treatment.
Valproic Acid Future Directions
Valproic acid has been a cornerstone in the treatment of neurological and psychiatric disorders for decades. However, there is ongoing research into the development of new treatments and therapies that can provide improved efficacy and safety. Some potential future directions for valproic acid include: * Development of new formulations: New formulations of valproic acid, such as extended-release tablets and injectable solutions, may provide improved convenience and efficacy. * Combination therapies: Combination therapies involving valproic acid and other medications may provide improved efficacy and safety in the treatment of neurological and psychiatric disorders. * Personalized medicine: The use of genetic testing and other diagnostic tools may help to identify individuals who are most likely to benefit from valproic acid treatment and to minimize the risk of adverse reactions.Overall, valproic acid remains an essential component in the treatment of neurological and psychiatric disorders. Its uses and effects are diverse, and it has become a cornerstone in the management of conditions such as epilepsy, bipolar disorder, and migraine headaches. However, it is essential to use this medication under the guidance of a healthcare professional and to carefully monitor its effects to minimize the risk of adverse reactions.
What is valproic acid used for?
+Valproic acid is used to treat various neurological and psychiatric disorders, including epilepsy, bipolar disorder, and migraine headaches.
What are the side effects of valproic acid?
+Common side effects of valproic acid include drowsiness, dizziness, nausea, and weight gain. In rare cases, the medication can cause more severe side effects, such as liver damage, pancreatitis, and birth defects.
Can valproic acid be used during pregnancy?
+Valproic acid can cause birth defects and developmental delays in children exposed to the medication in utero. It is essential to use effective contraception and to consult a healthcare professional before becoming pregnant.
What are the alternatives to valproic acid?
+There are several alternatives to valproic acid, including other anticonvulsants, mood stabilizers, and anti-anxiety medications. The choice of alternative medication depends on the specific condition being treated and the individual's medical history and response to treatment.
How long does it take for valproic acid to work?
+The time it takes for valproic acid to work can vary depending on the condition being treated and the individual's response to the medication. In general, it can take several weeks to several months to achieve the full effects of the medication.
We hope this article has provided you with a comprehensive overview of valproic acid uses and effects. If you have any further questions or concerns, please do not hesitate to comment below or share this article with others who may find it helpful. Remember to always consult a healthcare professional before starting or stopping any medication, and to carefully follow their instructions to minimize the risk of adverse reactions.
