Intro
Learn about normal blood sugar levels, glucose targets, and healthy range management to prevent diabetes and hypoglycemia, maintaining optimal blood glucose control.
Maintaining normal blood sugar levels is crucial for overall health and well-being. Blood sugar, also known as glucose, is the primary source of energy for the body's cells. When blood sugar levels are within a normal range, the body functions properly, and the risk of developing chronic diseases like diabetes, heart disease, and stroke is reduced. In this article, we will delve into the importance of normal blood sugar levels, the factors that affect them, and provide tips on how to maintain a healthy blood sugar range.
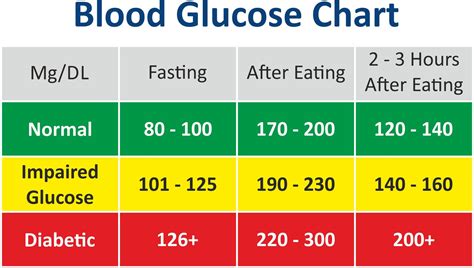
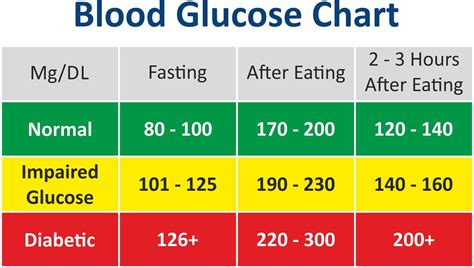
The human body is designed to regulate blood sugar levels within a narrow range, typically between 70 and 110 milligrams per deciliter (mg/dL). When blood sugar levels exceed this range, it can lead to a range of health problems. For instance, high blood sugar levels can cause damage to the blood vessels, nerves, and organs, while low blood sugar levels can lead to symptoms like dizziness, confusion, and even loss of consciousness. Therefore, it is essential to understand the factors that influence blood sugar levels and take steps to maintain a healthy range.
Understanding blood sugar levels is critical for preventing and managing chronic diseases. The body's ability to regulate blood sugar levels is influenced by a range of factors, including diet, physical activity, stress, and sleep. For example, consuming a diet high in sugar and refined carbohydrates can lead to spikes in blood sugar levels, while regular physical activity can help to improve insulin sensitivity and reduce blood sugar levels. By understanding these factors and making informed lifestyle choices, individuals can take control of their blood sugar levels and reduce their risk of developing chronic diseases.
What are Normal Blood Sugar Levels?

Factors that Affect Blood Sugar Levels
Several factors can influence blood sugar levels, including: * Diet: Consuming a diet high in sugar, refined carbohydrates, and saturated fats can lead to spikes in blood sugar levels. * Physical activity: Regular physical activity can help to improve insulin sensitivity and reduce blood sugar levels. * Stress: Chronic stress can raise blood sugar levels by stimulating the release of stress hormones like cortisol and adrenaline. * Sleep: Poor sleep quality and duration can disrupt blood sugar regulation and increase the risk of developing insulin resistance. * Medications: Certain medications, such as steroids and certain antidepressants, can affect blood sugar levels.How to Maintain Normal Blood Sugar Levels
Monitoring Blood Sugar Levels
Monitoring blood sugar levels is crucial for individuals with diabetes or those at risk of developing the condition. There are several ways to monitor blood sugar levels, including: * Fasting blood glucose test: Measures blood sugar levels after an overnight fast. * Oral glucose tolerance test: Measures blood sugar levels after consuming a sugary drink. * Random blood glucose test: Measures blood sugar levels at any time of day. * Continuous glucose monitoring: Uses a small device to track blood sugar levels throughout the day.The Benefits of Maintaining Normal Blood Sugar Levels
The Risks of Abnormal Blood Sugar Levels
Abnormal blood sugar levels can have serious consequences, including: * Diabetes: High blood sugar levels can lead to the development of diabetes, a condition characterized by insulin resistance and impaired glucose regulation. * Heart disease: High blood sugar levels can increase the risk of heart disease, including conditions like coronary artery disease and heart failure. * Kidney damage: High blood sugar levels can damage the kidneys and increase the risk of kidney disease. * Nerve damage: High blood sugar levels can damage the nerves, leading to conditions like neuropathy and nerve pain.Managing Blood Sugar Levels with Medication

Lifestyle Changes for Managing Blood Sugar Levels
In addition to medication, lifestyle changes can help to manage blood sugar levels. These include: * Eating a healthy, balanced diet: Focus on whole, unprocessed foods like vegetables, fruits, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats. * Staying hydrated: Drink plenty of water throughout the day to help regulate blood sugar levels. * Exercising regularly: Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic exercise, or 75 minutes of vigorous-intensity aerobic exercise, or a combination of both, per week. * Managing stress: Engage in stress-reducing activities like yoga, meditation, or deep breathing exercises. * Getting enough sleep: Aim for 7-9 hours of sleep per night to help regulate blood sugar levels.Conclusion and Next Steps

We invite you to share your thoughts and experiences on maintaining normal blood sugar levels in the comments section below. If you found this article informative, please share it with your friends and family on social media. By working together, we can promote healthy blood sugar levels and reduce the risk of chronic diseases.
What are the symptoms of high blood sugar levels?
+The symptoms of high blood sugar levels include increased thirst and urination, fatigue, blurred vision, and slow healing of cuts and wounds.
How often should I check my blood sugar levels?
+The frequency of checking blood sugar levels depends on individual factors, such as the type of diabetes, medication use, and lifestyle habits. It is recommended to consult with a healthcare professional for personalized guidance.
Can I manage blood sugar levels through lifestyle changes alone?
+Yes, lifestyle changes like eating a healthy, balanced diet, staying hydrated, exercising regularly, managing stress, and getting enough sleep can help to manage blood sugar levels. However, in some cases, medication may be necessary to achieve normal blood sugar levels.
What are the risks of not managing blood sugar levels?
+The risks of not managing blood sugar levels include developing chronic diseases like diabetes, heart disease, and stroke, as well as kidney damage, nerve damage, and vision problems.
How can I prevent blood sugar levels from becoming too low?
+To prevent blood sugar levels from becoming too low, it is recommended to eat regular meals, avoid skipping meals, and monitor blood sugar levels regularly. It is also essential to be aware of the signs and symptoms of low blood sugar levels, such as shakiness, dizziness, and confusion.
