Intro
Discover Lisinopril uses and benefits, including blood pressure management, heart failure treatment, and kidney protection, with its ACE inhibitor properties and cardiovascular benefits.
Lisinopril is a medication that has been widely used for several decades to treat various health conditions, particularly those related to the cardiovascular system. It belongs to a class of drugs known as angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors, which work by relaxing blood vessels and reducing blood pressure. The importance of lisinopril lies in its ability to improve the quality of life for individuals suffering from conditions such as high blood pressure, heart failure, and certain types of kidney disease. Understanding the uses and benefits of lisinopril can help patients and healthcare providers make informed decisions about its use.
The role of lisinopril in managing hypertension (high blood pressure) cannot be overstated. High blood pressure is a significant risk factor for cardiovascular diseases, including heart attacks, strokes, and kidney disease. By lowering blood pressure, lisinopril reduces the strain on the heart and blood vessels, thereby decreasing the risk of these complications. Moreover, its effectiveness in treating heart failure, a condition where the heart is unable to pump enough blood to meet the body's needs, has made it a cornerstone in the management of this condition. Lisinopril's benefits extend beyond these conditions, offering protection against diabetic nephropathy, a type of kidney damage that can occur in people with diabetes.
The mechanism of action of lisinopril involves blocking the conversion of angiotensin I to angiotensin II, a potent vasoconstrictor. By preventing this conversion, lisinopril leads to vasodilation (widening of blood vessels) and a decrease in blood pressure. This action not only reduces the workload on the heart but also decreases the amount of protein (such as albumin) lost in the urine, which is beneficial for patients with kidney disease. The drug's efficacy and relatively favorable side effect profile have made it a preferred choice among healthcare providers for the treatment of several cardiovascular and renal conditions.
Lisinopril Mechanism of Action

The mechanism of action of lisinopril is closely related to its therapeutic effects. By inhibiting the angiotensin-converting enzyme, lisinopril decreases the levels of angiotensin II, leading to decreased peripheral resistance and lowered blood pressure. This reduction in blood pressure is beneficial for patients with hypertension and heart failure, as it reduces the workload on the heart and improves cardiac output. Furthermore, the decrease in angiotensin II levels reduces the secretion of aldosterone, a hormone that promotes water and salt retention. This effect contributes to the diuretic action of lisinopril, further aiding in the reduction of blood pressure.
How Lisinopril Works
The working mechanism of lisinopril can be broken down into several key steps: - Inhibition of ACE: Lisinopril binds to the angiotensin-converting enzyme, preventing the conversion of angiotensin I to angiotensin II. - Decrease in Angiotensin II: With less angiotensin II, there is less vasoconstriction (narrowing of blood vessels) and less stimulation of the adrenal glands to release aldosterone. - Vasodilation: The decrease in angiotensin II leads to the dilation of blood vessels, reducing blood pressure. - Diuretic Effect: The reduction in aldosterone secretion results in less water and salt retention, further contributing to the lowering of blood pressure.Lisinopril Uses

Lisinopril is used for a variety of medical conditions, primarily focusing on cardiovascular and renal diseases. Its primary uses include:
- Hypertension: Lisinopril is effective in lowering blood pressure in patients with hypertension, reducing the risk of heart attack, stroke, and kidney disease.
- Heart Failure: By reducing the workload on the heart and improving cardiac output, lisinopril is beneficial for patients with heart failure, improving survival and reducing hospitalization rates.
- Diabetic Nephropathy: Lisinopril has been shown to slow the progression of kidney disease in diabetic patients, reducing proteinuria (protein in the urine) and the risk of end-stage renal disease.
Lisinopril in Hypertension Management
In the management of hypertension, lisinopril is often used as a first-line treatment due to its efficacy and safety profile. Its benefits in hypertension management include: - Effective Blood Pressure Reduction: Lisinopril has been consistently shown to lower blood pressure in a wide range of patients with hypertension. - Cardiovascular Protection: By reducing blood pressure, lisinopril decreases the risk of cardiovascular events such as heart attacks and strokes. - Renal Protection: Lisinopril's ability to reduce proteinuria makes it particularly beneficial for patients with hypertension who are at risk of kidney disease.Lisinopril Benefits

The benefits of lisinopril are multifaceted, extending beyond its ability to lower blood pressure and manage heart failure. Some of the key benefits include:
- Reduced Risk of Cardiovascular Events: By lowering blood pressure and reducing the strain on the heart, lisinopril decreases the risk of heart attacks, strokes, and other cardiovascular events.
- Improved Survival in Heart Failure: Studies have shown that lisinopril can improve survival and reduce hospitalization rates in patients with heart failure.
- Protection Against Diabetic Nephropathy: Lisinopril's ability to reduce proteinuria and slow the progression of kidney disease makes it an important medication for diabetic patients.
- Improved Quality of Life: By managing symptoms and reducing the risk of complications associated with hypertension and heart failure, lisinopril can significantly improve the quality of life for patients.
Practical Applications of Lisinopril
In practical terms, the benefits of lisinopril can be seen in its application across a wide range of clinical scenarios. For example: - In patients with hypertension, lisinopril can be used as monotherapy or in combination with other antihypertensive drugs to achieve optimal blood pressure control. - For patients with heart failure, lisinopril is often used in conjunction with other medications such as beta-blockers and diuretics to improve symptoms and reduce morbidity. - In diabetic patients, lisinopril can be used to protect against kidney disease, even in the absence of hypertension, due to its beneficial effects on proteinuria and renal function.Lisinopril Side Effects and Precautions
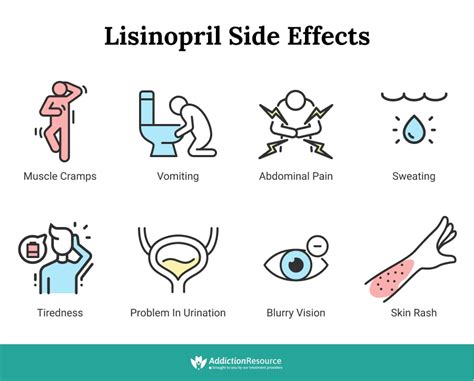
While lisinopril is generally well-tolerated, it can cause side effects and interact with other medications. Common side effects include:
- Cough: A dry, persistent cough is one of the most common side effects of lisinopril, occurring in up to 20% of patients.
- Dizziness and Lightheadedness: Due to its blood pressure-lowering effects, lisinopril can cause dizziness and lightheadedness, especially when standing up from a sitting or lying position.
- Increased Potassium Levels: Lisinopril can increase potassium levels, which can be dangerous in patients with kidney disease or those taking other medications that affect potassium levels.
Precautions and Contraindications
It is essential to use lisinopril with caution in certain patient populations and to be aware of its contraindications. For example: - Pregnancy and Breastfeeding: Lisinopril is contraindicated in pregnancy due to the risk of fetal harm and should be used with caution in breastfeeding mothers. - Kidney Disease: While lisinopril can be beneficial for patients with kidney disease, it should be used with caution, especially in those with severe renal impairment, due to the risk of hyperkalemia (high potassium levels). - Combination with Other Medications: Lisinopril can interact with other medications, such as diuretics, potassium supplements, and lithium, requiring careful monitoring and adjustment of doses.Lisinopril Dosage and Administration

The dosage of lisinopril varies depending on the condition being treated and the patient's response to the medication. For hypertension, the usual starting dose is 10 mg once daily, which can be increased to 20-40 mg daily if necessary. In heart failure, the starting dose is typically 5 mg daily, with gradual increases to achieve optimal effects. It is crucial to follow the prescribed dosage and administration instructions to maximize the benefits of lisinopril while minimizing the risk of side effects.
Monitoring and Follow-Up
Regular monitoring and follow-up are essential when taking lisinopril. This includes: - Blood Pressure Checks: Regular blood pressure monitoring to assess the effectiveness of lisinopril and adjust the dose as needed. - Kidney Function Tests: Periodic checks of kidney function, especially in patients with pre-existing kidney disease, to monitor for any adverse effects of lisinopril. - Potassium Level Monitoring: Regular monitoring of potassium levels, especially in patients at risk of hyperkalemia, to prevent complications.Conclusion and Future Directions
In conclusion, lisinopril is a versatile and effective medication that has revolutionized the management of hypertension, heart failure, and diabetic nephropathy. Its benefits extend beyond blood pressure reduction, offering protection against cardiovascular events and kidney disease. As research continues to uncover the full potential of ACE inhibitors like lisinopril, it is likely that their role in clinical practice will continue to evolve. Future studies may focus on optimizing dosing regimens, exploring new indications, and developing combination therapies that leverage the benefits of lisinopril.
Final Thoughts
As we look to the future of cardiovascular and renal care, medications like lisinopril will remain at the forefront of treatment strategies. Their ability to improve outcomes, reduce morbidity, and enhance the quality of life for patients makes them invaluable tools in the management of complex diseases. By understanding the uses, benefits, and potential limitations of lisinopril, healthcare providers can make informed decisions that improve patient care and contribute to better health outcomes.What is lisinopril used for?
+Lisinopril is used to treat high blood pressure, heart failure, and to protect the kidneys from damage due to diabetes.
How does lisinopril work?
+Lisinopril works by blocking the action of angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE), a natural chemical that narrows blood vessels and increases blood pressure. By blocking ACE, lisinopril relaxes blood vessels, reducing blood pressure and increasing the supply of blood and oxygen to the heart.
What are the common side effects of lisinopril?
+Common side effects of lisinopril include cough, dizziness, and increased potassium levels. Less common side effects can include headache, fatigue, and nausea.
Can lisinopril be used in pregnancy?
+No, lisinopril is contraindicated in pregnancy due to the risk of fetal harm. It should only be used in pregnancy if the potential benefits outweigh the risks.
How long does it take for lisinopril to start working?
+Lisinopril can start to lower blood pressure within a few hours of taking the first dose, but it may take several weeks to reach its full effect.
We hope this comprehensive overview of lisinopril has provided valuable insights into its uses, benefits, and potential side effects. Whether you are a patient, a healthcare provider, or simply someone interested in learning more about this important medication, we encourage you to share this article with others and to continue exploring the many resources available on this topic. Your engagement and feedback are crucial in helping us improve our content and provide the most accurate and helpful information possible. Thank you for reading, and we look forward to your comments and questions.
