Intro
Identify 7 heart attack signs, including chest pain, shortness of breath, and fatigue, to prevent cardiac arrest and ensure timely medical attention for cardiovascular health.
Recognizing the signs of a heart attack is crucial for prompt medical attention and saving lives. A heart attack, also known as myocardial infarction, occurs when the blood flow to the heart is severely blocked, causing damage to the heart muscle. The importance of understanding these signs cannot be overstated, as timely intervention can significantly improve outcomes and reduce the risk of death. Over the years, awareness campaigns have highlighted the common signs of a heart attack, but there is still a need for education, especially among high-risk groups.
The impact of heart attacks on individuals and families is profound, making prevention and early detection critical. By being informed about the signs and symptoms, individuals can take proactive steps to protect their heart health and seek medical help when needed. Moreover, understanding the mechanisms behind heart attacks and the factors that increase the risk can empower people to make lifestyle changes and manage their health more effectively.
Heart health is a topic of increasing interest, with research continuously unveiling new insights into the causes, prevention, and treatment of heart diseases. As the leading cause of death worldwide, heart attacks necessitate a comprehensive approach that includes public awareness, preventive measures, and advanced medical care. The signs of a heart attack can vary from person to person, and not everyone experiences the classic symptoms depicted in media and popular culture. Therefore, it is essential to delve into the specifics of heart attack signs, their variations, and what actions to take upon recognizing them.
Introduction to Heart Attack Signs
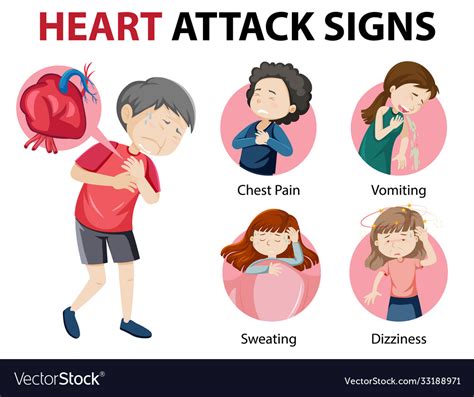
Understanding Chest Pain
Chest pain is the most recognized symptom of a heart attack, but it's crucial to understand that not all chest pain is the same. The pain associated with a heart attack can be persistent or may come and go. It's also important to note that women, older adults, and people with diabetes might experience heart attack symptoms differently, such as having no chest pain at all.Recognizing the Signs in Different Groups

Atypical Symptoms
Atypical symptoms of a heart attack include discomfort in the arms, back, neck, jaw, or stomach, which can be mistaken for other conditions. These symptoms can be particularly misleading for women and older adults, leading to delays in seeking medical help. Furthermore, some individuals might experience mild symptoms that they attribute to indigestion, stress, or other less severe conditions, further complicating timely diagnosis.The Importance of Prompt Medical Attention

Steps to Take Upon Recognizing Signs
Upon recognizing the signs of a heart attack, whether in oneself or someone else, it's crucial to act quickly. The first step is to call emergency services or the local equivalent. If the person is unconscious, not breathing, or not breathing normally, starting CPR (if trained to do so) can be lifesaving. Providing as much information as possible to the emergency operator, including the location and any symptoms observed, can help ensure a rapid and appropriate response.Prevention and Risk Reduction

Lifestyle Changes for Heart Health
Making lifestyle changes is a proactive step towards reducing the risk of heart disease. This includes adopting a heart-healthy diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean protein sources, while limiting intake of saturated fats, trans fats, and sodium. Regular physical activity, such as walking, can also significantly reduce risk. Quitting smoking and limiting alcohol consumption are also crucial steps. Managing stress through techniques like meditation or yoga can further contribute to heart health.Advanced Medical Care and Treatment Options
Future Directions in Heart Health
The future of heart health looks promising, with ongoing research focusing on prevention, early detection, and innovative treatments. Personalized medicine, which tailors treatment to the individual's genetic profile and health status, is becoming increasingly important. Additionally, public health initiatives aimed at reducing risk factors on a population level are critical for decreasing the global burden of heart disease.Conclusion and Call to Action

As we move forward in the fight against heart disease, it's vital to stay informed, engaged, and proactive. Share this article with someone you care about, and together, let's work towards a future where heart attacks are less common and more survivable. Your actions today can make a difference tomorrow.
What are the most common signs of a heart attack?
+The most common signs include chest pain or discomfort, shortness of breath, and cold sweats, among others. It's also important to recognize that symptoms can vary, especially among different demographic groups.
How can I reduce my risk of having a heart attack?
+Reducing your risk involves managing modifiable risk factors through lifestyle changes, such as adopting a heart-healthy diet, exercising regularly, quitting smoking, and limiting alcohol consumption. Managing stress and ensuring good sleep are also beneficial.
What should I do if I think someone is having a heart attack?
+If you suspect someone is having a heart attack, call emergency services immediately. If the person is unconscious, not breathing, or not breathing normally, and you are trained to do so, start CPR. Provide as much information as possible to the emergency operator.
