Intro
Discover Augmentins uses and benefits, a broad-spectrum antibiotic treating bacterial infections, pneumonia, and skin infections, with advantages including dual-action, fast relief, and high efficacy, combating resistant strains and promoting overall health.
The world of antibiotics is vast and complex, with numerous medications available to treat a wide range of bacterial infections. Among these, Augmentin stands out as a highly effective and versatile antibiotic that has been widely used for decades. Its unique combination of amoxicillin and clavulanic acid makes it an ideal choice for treating various infections, from mild to severe. In this article, we will delve into the uses and benefits of Augmentin, exploring its mechanism of action, dosage, and potential side effects.
As we navigate the complexities of bacterial infections, it becomes clear that Augmentin plays a vital role in the treatment of various conditions. From respiratory tract infections to skin and soft tissue infections, Augmentin has proven itself to be a reliable and effective medication. Its broad-spectrum activity against both Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria makes it an excellent choice for treating infections where the causative agent is unknown or uncertain. Furthermore, Augmentin's ability to penetrate into tissues and fluids, such as bronchial secretions and middle ear fluid, makes it particularly useful for treating infections in these areas.
The importance of Augmentin in modern medicine cannot be overstated. With the rise of antibiotic resistance, it is essential to have effective medications that can combat bacterial infections. Augmentin's unique mechanism of action, which involves the inhibition of beta-lactamase enzymes, makes it an excellent choice for treating infections caused by bacteria that produce these enzymes. Additionally, Augmentin's relatively low toxicity and side effect profile make it an attractive option for patients who may be sensitive to other antibiotics. As we explore the uses and benefits of Augmentin, it becomes clear that this medication is a valuable tool in the fight against bacterial infections.
What is Augmentin?
How Does Augmentin Work?
The mechanism of action of Augmentin is complex and involves the synergistic activity of amoxicillin and clavulanic acid. Amoxicillin is able to penetrate the bacterial cell wall and inhibit the synthesis of peptidoglycan, a critical component of the bacterial cell wall. Clavulanic acid, on the other hand, inhibits the activity of beta-lactamase enzymes, which are produced by certain bacteria to inactivate amoxicillin and other penicillin-like antibiotics. By inhibiting these enzymes, clavulanic acid allows amoxicillin to reach its target and exert its antibacterial effects.Uses of Augmentin

Benefits of Augmentin
The benefits of Augmentin are numerous and well-documented. Some of the key benefits include: * Broad-spectrum activity against both Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria * Ability to penetrate into tissues and fluids, such as bronchial secretions and middle ear fluid * Effective against bacteria that produce beta-lactamase enzymes * Relatively low toxicity and side effect profile * Available in a range of formulations, including oral tablets, oral suspension, and intravenous injectionSide Effects of Augmentin

Precautions and Contraindications
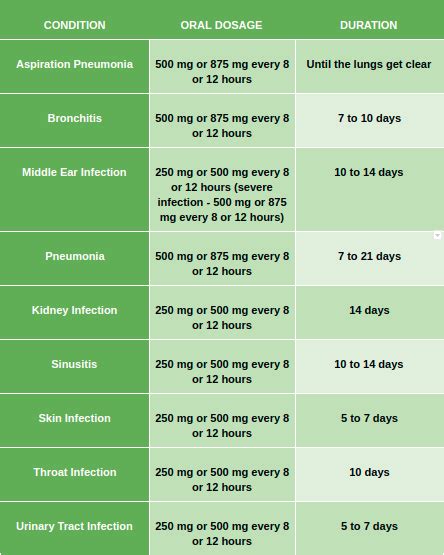
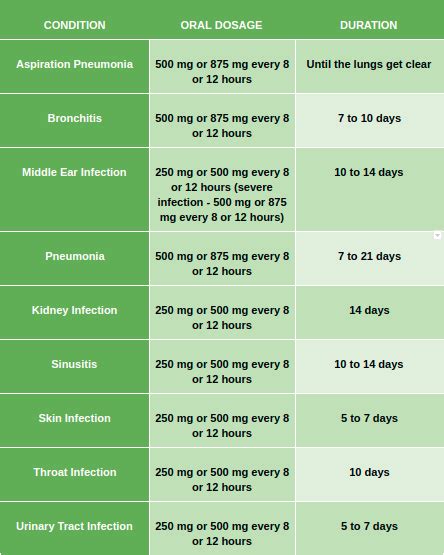
Augmentin is contraindicated in patients with a history of hypersensitivity to penicillins or other beta-lactam antibiotics. It is also contraindicated in patients with severe renal impairment or hepatic impairment. Precautions should be taken when using Augmentin in patients with: * Renal impairment, such as decreased creatinine clearance * Hepatic impairment, such as increased liver enzymes and bilirubin * Allergic reactions, such as rash, itching, and difficulty breathing * Central nervous system effects, such as dizziness, headache, and fatigueDosage and Administration
Interactions with Other Medications
Augmentin can interact with a range of medications, including: * Warfarin, which can increase the risk of bleeding * Methotrexate, which can increase the risk of toxicity * Probenecid, which can decrease the renal clearance of Augmentin * Allopurinol, which can increase the risk of rash and other allergic reactionsConclusion and Future Directions
Final Thoughts
As we reflect on the uses and benefits of Augmentin, it is clear that this medication is a valuable tool in the fight against bacterial infections. Its broad-spectrum activity, ability to penetrate into tissues and fluids, and relatively low toxicity and side effect profile make it an excellent choice for treating a wide range of infections. As we move forward in the era of antibiotic resistance, it is essential to continue to develop and refine medications like Augmentin that can effectively combat bacterial infections.What is Augmentin used for?
+Augmentin is used to treat a wide range of bacterial infections, including respiratory tract infections, skin and soft tissue infections, urinary tract infections, ear, nose, and throat infections, and infections of the gastrointestinal tract.
How does Augmentin work?
+Augmentin works by inhibiting the synthesis of the bacterial cell wall, ultimately leading to the death of the bacterial cell. The combination of amoxicillin and clavulanic acid allows Augmentin to overcome the resistance mechanisms of certain bacteria, making it a highly effective medication for treating a wide range of infections.
What are the side effects of Augmentin?
+While Augmentin is generally well-tolerated, it can cause a range of side effects, including gastrointestinal symptoms, allergic reactions, central nervous system effects, renal impairment, and hepatic impairment.
Can I take Augmentin with other medications?
+Augmentin can interact with a range of medications, including warfarin, methotrexate, probenecid, and allopurinol. It is essential to consult with a healthcare professional before taking Augmentin with other medications.
Is Augmentin effective against antibiotic-resistant bacteria?
+Augmentin is effective against a range of antibiotic-resistant bacteria, including those that produce beta-lactamase enzymes. However, the rise of antibiotic resistance continues to pose a significant threat to public health, and it is essential to use Augmentin and other antibiotics judiciously and only when necessary.
