Intro
Understand your White Blood Cell test results, including normal ranges, high and low counts, and what they mean for your immune system, infection risk, and overall health, with expert explanations of WBC differential and absolute counts.
The importance of understanding white blood cell test results cannot be overstated, as it plays a crucial role in diagnosing and managing various health conditions. White blood cells, also known as leukocytes, are a vital part of the immune system, helping to fight off infections and diseases. A white blood cell test, also known as a complete blood count (CBC), measures the levels of different types of white blood cells in the blood. This test is commonly used to diagnose and monitor conditions such as infections, inflammation, and blood disorders. In this article, we will delve into the world of white blood cell test results, exploring what they mean, how they are interpreted, and what factors can influence them.
A white blood cell test is typically performed as part of a routine medical checkup or when a patient is experiencing symptoms such as fever, fatigue, or weakness. The test involves taking a blood sample from a vein in the arm, which is then sent to a laboratory for analysis. The results of the test can provide valuable insights into the patient's immune system and help healthcare providers diagnose and manage a range of conditions. From a medical perspective, understanding white blood cell test results is essential for developing effective treatment plans and monitoring patient progress. Moreover, being aware of the importance of white blood cells can empower individuals to take a more proactive approach to their health, making informed decisions about their lifestyle and wellness.
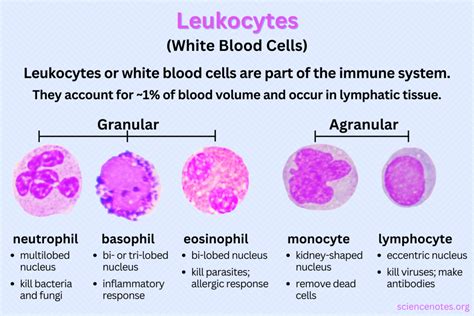
The human body is equipped with an intricate immune system, comprising various types of white blood cells, each with unique functions and characteristics. There are five main types of white blood cells: neutrophils, lymphocytes, monocytes, eosinophils, and basophils. Neutrophils are the most abundant type, accounting for approximately 50-70% of all white blood cells. They play a crucial role in fighting off bacterial and fungal infections. Lymphocytes, on the other hand, are responsible for immune responses, such as producing antibodies to fight off viruses and other pathogens. Monocytes are large white blood cells that mature into macrophages, which engulf and digest foreign particles and microorganisms. Eosinophils and basophils are less abundant but still play important roles in fighting off parasites and allergic reactions.
Understanding White Blood Cell Test Results

When interpreting white blood cell test results, healthcare providers look at the overall white blood cell count, as well as the levels of each individual type of white blood cell. The normal range for white blood cell count is typically between 4,000 and 11,000 cells per microliter (µL) of blood. However, this range can vary slightly depending on the laboratory and the individual's age, sex, and other factors. Abnormal white blood cell counts can indicate a range of conditions, including infections, inflammation, and blood disorders.
High White Blood Cell Count
A high white blood cell count, also known as leukocytosis, can indicate the presence of an infection, inflammation, or other conditions such as leukemia or lymphoma. A high white blood cell count can also be caused by factors such as stress, exercise, or certain medications. On the other hand, a low white blood cell count, also known as leukopenia, can indicate a weakened immune system, making the individual more susceptible to infections.Types of White Blood Cells
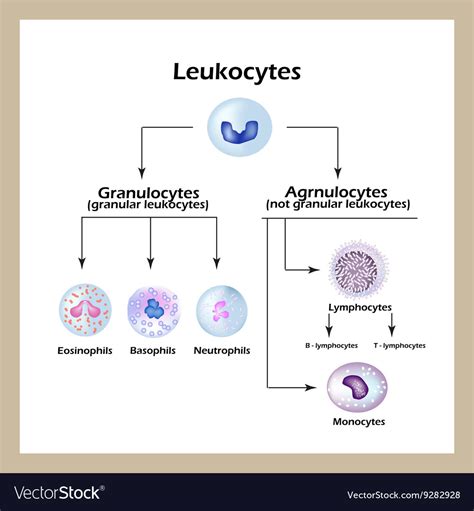
Each type of white blood cell has a unique function and characteristics. Neutrophils, for example, are highly motile and can migrate to sites of infection, where they engulf and digest foreign particles and microorganisms. Lymphocytes, on the other hand, are responsible for immune responses, such as producing antibodies to fight off viruses and other pathogens. Monocytes are large white blood cells that mature into macrophages, which play a crucial role in cleaning up debris and foreign particles from the body.
Neutrophils
Neutrophils are the most abundant type of white blood cell, accounting for approximately 50-70% of all white blood cells. They are highly motile and can migrate to sites of infection, where they engulf and digest foreign particles and microorganisms. Neutrophils are also involved in the inflammatory response, helping to clean up debris and promote healing.Lymphocytes
Lymphocytes are responsible for immune responses, such as producing antibodies to fight off viruses and other pathogens. There are two main types of lymphocytes: B cells and T cells. B cells produce antibodies, while T cells directly attack and kill infected cells or produce chemical signals that activate the immune response.Factors That Influence White Blood Cell Test Results
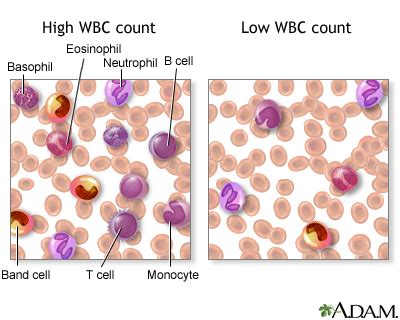
Several factors can influence white blood cell test results, including age, sex, and certain medical conditions. For example, newborns and young children tend to have higher white blood cell counts than adults. Additionally, women tend to have higher white blood cell counts than men, particularly during pregnancy. Certain medical conditions, such as anemia or blood disorders, can also affect white blood cell counts.
Aging and White Blood Cell Count
As we age, our immune system undergoes natural changes that can affect white blood cell counts. Older adults may experience a decline in immune function, making them more susceptible to infections. Additionally, certain age-related medical conditions, such as arthritis or diabetes, can also impact white blood cell counts.Medications and White Blood Cell Count
Certain medications, such as corticosteroids or chemotherapy, can suppress the immune system and affect white blood cell counts. On the other hand, some medications, such as antibiotics or antivirals, can stimulate the immune system and increase white blood cell counts.Interpreting White Blood Cell Test Results

Interpreting white blood cell test results requires a comprehensive understanding of the individual's medical history, symptoms, and laboratory results. Healthcare providers consider factors such as the overall white blood cell count, the levels of each individual type of white blood cell, and the presence of any abnormal cells or conditions.
White Blood Cell Differential Count
A white blood cell differential count is a laboratory test that measures the levels of each individual type of white blood cell. This test can help healthcare providers diagnose and monitor conditions such as infections, inflammation, and blood disorders.Automated White Blood Cell Count
Automated white blood cell count is a laboratory test that uses specialized equipment to count the number of white blood cells in a blood sample. This test is faster and more accurate than manual counting methods and can provide valuable insights into the individual's immune system.Common Conditions Diagnosed with White Blood Cell Tests
White blood cell tests are commonly used to diagnose and monitor a range of conditions, including infections, inflammation, and blood disorders. Some common conditions diagnosed with white blood cell tests include:
- Infections such as pneumonia, tuberculosis, or sepsis
- Inflammatory conditions such as arthritis, lupus, or rheumatoid arthritis
- Blood disorders such as leukemia, lymphoma, or anemia
- Immune system disorders such as HIV/AIDS or autoimmune disorders
Infections and White Blood Cell Count
Infections can cause a significant increase in white blood cell count, as the body responds to the presence of foreign particles or microorganisms. The type and severity of the infection can affect the level of increase in white blood cell count.Inflammatory Conditions and White Blood Cell Count
Inflammatory conditions such as arthritis or lupus can cause a chronic increase in white blood cell count, as the body responds to the presence of inflammation. The severity and duration of the inflammatory condition can affect the level of increase in white blood cell count.Limitations and Potential Risks of White Blood Cell Tests

While white blood cell tests are a valuable diagnostic tool, they have limitations and potential risks. For example, white blood cell counts can be affected by various factors, such as age, sex, and certain medical conditions. Additionally, white blood cell tests may not always detect underlying conditions, and abnormal results may require further testing or evaluation.
False Negative Results
False negative results can occur when a white blood cell test fails to detect an underlying condition. This can happen when the condition is in its early stages or when the individual has a weakened immune system.False Positive Results
False positive results can occur when a white blood cell test indicates an underlying condition that is not present. This can happen when the individual has a viral infection or when the test is affected by certain medications or laboratory errors.What is a normal white blood cell count?
+A normal white blood cell count is typically between 4,000 and 11,000 cells per microliter (µL) of blood.
What does a high white blood cell count indicate?
+A high white blood cell count can indicate the presence of an infection, inflammation, or other conditions such as leukemia or lymphoma.
What is the difference between a white blood cell count and a white blood cell differential count?
+A white blood cell count measures the total number of white blood cells in a blood sample, while a white blood cell differential count measures the levels of each individual type of white blood cell.
In
