Intro
Understand burn differences, including degrees, types, and severity, to recognize symptoms and provide proper treatment for thermal, chemical, and electrical burns, promoting wound healing and burn care.
Burn injuries can be devastating and life-altering, affecting not only the physical health but also the emotional and psychological well-being of individuals. The severity and impact of burns depend on various factors, including the depth, size, and location of the injury. Understanding the differences between various types of burns is crucial for providing appropriate treatment and care. In this article, we will delve into the world of burns, exploring the distinct characteristics, causes, and consequences of different types of burn injuries.
Burns can occur due to various reasons, such as exposure to heat, flames, electricity, or chemicals. The severity of a burn is typically classified into four categories: first-degree, second-degree, third-degree, and fourth-degree. Each category represents a distinct level of damage to the skin and underlying tissues. First-degree burns, also known as superficial burns, affect only the outermost layer of the skin, causing redness, swelling, and pain. Second-degree burns, also known as partial-thickness burns, extend into the middle layer of the skin, resulting in blisters, swelling, and increased pain. Third-degree burns, also known as full-thickness burns, destroy both layers of the skin and can damage underlying tissues, such as muscles, tendons, and nerves. Fourth-degree burns are the most severe, extending into the deepest layers of the skin and potentially affecting internal organs.
The differences between various types of burns are not limited to their severity. Burns can also be classified based on their cause, with common types including thermal burns, electrical burns, chemical burns, and radiation burns. Thermal burns, caused by exposure to heat or flames, are the most common type of burn injury. Electrical burns, resulting from contact with electrical sources, can cause significant damage to internal tissues and organs. Chemical burns, caused by exposure to corrosive substances, can lead to severe damage to the skin and underlying tissues. Radiation burns, resulting from exposure to ionizing radiation, can cause damage to the skin and internal organs.
Burn Classifications
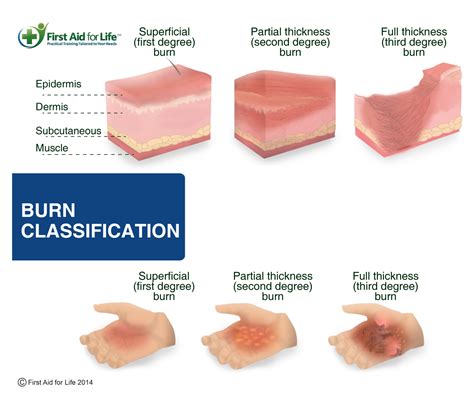
Burn classifications are essential for determining the appropriate treatment and care for burn victims. The American Burn Association (ABA) recommends a burn classification system that takes into account the severity, size, and location of the injury. The system categorizes burns into four main categories: minor, moderate, severe, and critical. Minor burns are those that affect less than 10% of the body surface area, while moderate burns affect 10-20% of the body surface area. Severe burns affect 20-30% of the body surface area, and critical burns affect more than 30% of the body surface area.
Burn Severity
Burn severity is a critical factor in determining the outcome of burn injuries. The severity of a burn is typically assessed using the Rule of Nines, which assigns a percentage value to different body parts based on their surface area. The Rule of Nines is a useful tool for estimating the total body surface area affected by a burn. However, it has its limitations, particularly in pediatric patients, where the surface area of the head and neck is proportionally larger than in adults.Burn Causes
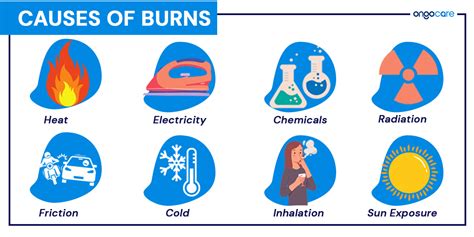
Burn causes can be diverse, ranging from accidental exposure to heat or flames to intentional acts of violence. According to the World Health Organization (WHO), burns are a leading cause of morbidity and mortality worldwide, with an estimated 180,000 deaths occurring annually. The majority of burn-related deaths occur in low- and middle-income countries, where access to medical care and emergency services may be limited.
Burn Prevention
Burn prevention is critical for reducing the incidence and severity of burn injuries. Simple measures, such as installing smoke alarms, maintaining a safe distance from heat sources, and using protective gear when handling chemicals or electrical equipment, can significantly reduce the risk of burns. Additionally, public education campaigns can raise awareness about burn prevention and promote safe practices in the community.Burn Treatment
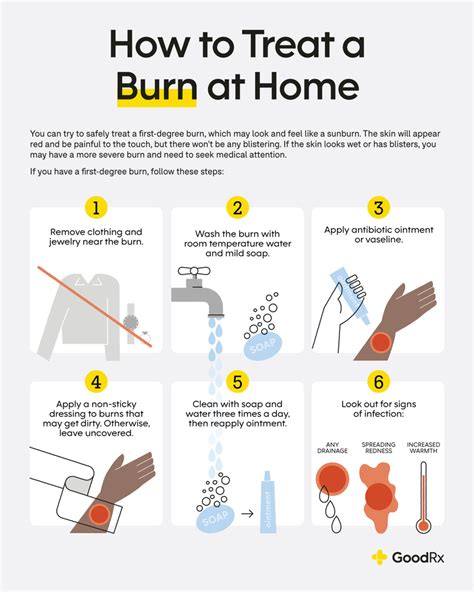
Burn treatment depends on the severity and extent of the injury. Minor burns can be treated with topical creams and dressings, while more severe burns may require surgical intervention, such as debridement or skin grafting. Electrical burns, chemical burns, and radiation burns may require specialized treatment, including cardiac monitoring, wound debridement, and administration of antidotes.
Burn Care
Burn care is a critical component of burn treatment, involving a range of activities, from wound dressing and management to pain control and psychological support. Burn care teams typically consist of multidisciplinary professionals, including nurses, doctors, physical therapists, and occupational therapists, who work together to provide comprehensive care to burn patients.Burn Complications
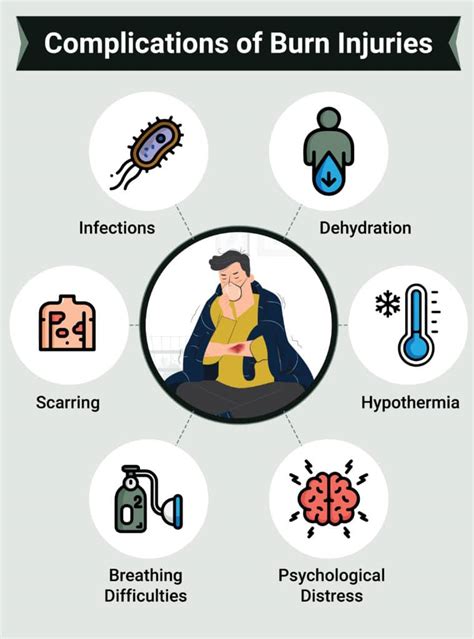
Burn complications can be severe and life-threatening, particularly in patients with extensive or deep burns. Common complications include infection, sepsis, respiratory failure, and cardiac arrest. Additionally, burn patients may experience long-term psychological and emotional trauma, including post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD), anxiety, and depression.
Burn Rehabilitation
Burn rehabilitation is a critical phase of burn care, focusing on restoring physical function, promoting wound healing, and enhancing overall quality of life. Burn rehabilitation teams work with patients to develop individualized treatment plans, incorporating physical therapy, occupational therapy, and psychological support.Burn Research

Burn research is ongoing, with scientists and clinicians exploring new treatments, technologies, and therapies to improve burn care and outcomes. Advances in burn research have led to the development of innovative treatments, such as stem cell therapy, gene therapy, and tissue engineering.
Burn Education
Burn education is essential for promoting burn prevention, improving burn care, and enhancing burn research. Burn education programs can raise awareness about burn risks, promote safe practices, and provide training for healthcare professionals.Burn Support

Burn support is critical for burn patients and their families, providing emotional, psychological, and practical assistance during the recovery process. Burn support groups can offer a sense of community, connection, and understanding, helping patients cope with the physical and emotional challenges of burn injuries.
Burn Advocacy
Burn advocacy is essential for promoting burn prevention, improving burn care, and supporting burn research. Burn advocacy efforts can raise awareness about burn risks, promote policy changes, and secure funding for burn-related initiatives.As we conclude this comprehensive overview of burn differences, we invite you to share your thoughts, experiences, and questions about burn injuries. Whether you are a burn survivor, a healthcare professional, or a concerned citizen, your input can help promote burn awareness, improve burn care, and support burn research. Please feel free to comment, share this article, or take action to make a difference in the lives of burn patients and their families.
What are the most common causes of burns?
+The most common causes of burns include thermal burns, electrical burns, chemical burns, and radiation burns.
How can I prevent burns?
+You can prevent burns by taking simple measures, such as installing smoke alarms, maintaining a safe distance from heat sources, and using protective gear when handling chemicals or electrical equipment.
What are the different types of burn classifications?
+The different types of burn classifications include minor, moderate, severe, and critical burns, which are determined based on the severity, size, and location of the injury.
What are the common complications of burns?
+The common complications of burns include infection, sepsis, respiratory failure, and cardiac arrest, as well as long-term psychological and emotional trauma.
How can I support burn patients and their families?
+You can support burn patients and their families by offering emotional, psychological, and practical assistance, such as connecting them with burn support groups, providing financial assistance, or volunteering your time and skills.
