Intro
Discover the normal triglyceride level range and learn how to manage healthy lipid profiles, reducing risk of hypertriglyceridemia and cardiovascular disease through diet and lifestyle changes.
Triglycerides are a type of fat found in the blood, and they play a crucial role in the body's energy production. Having normal triglyceride levels is essential for maintaining overall health and preventing various diseases. In this article, we will delve into the world of triglycerides, exploring their importance, the normal triglyceride level range, and how to maintain healthy levels.
Triglycerides are the most common type of fat in the body, and they are composed of three fatty acid chains attached to a glycerol molecule. They are produced in the liver and intestines and are transported through the bloodstream to various tissues, where they are used as energy or stored for later use. High triglyceride levels can increase the risk of heart disease, stroke, and other cardiovascular conditions, making it essential to monitor and maintain normal levels.
The normal triglyceride level range varies depending on factors such as age, sex, and overall health. Generally, a normal triglyceride level is considered to be below 150 milligrams per deciliter (mg/dL) of blood. However, levels between 150-199 mg/dL are considered borderline high, while levels above 200 mg/dL are considered high. It is essential to note that triglyceride levels can fluctuate throughout the day, and it is recommended to have a fasting lipid profile test to get an accurate reading.
Understanding Triglycerides
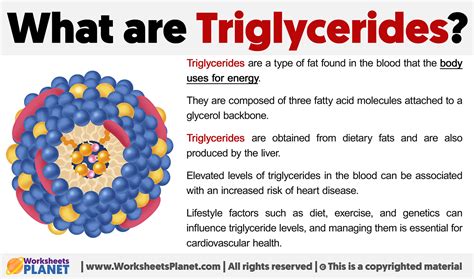
To understand triglycerides, it is essential to know how they are produced and transported in the body. Triglycerides are produced in the liver and intestines from the food we eat, particularly from carbohydrates and fats. They are then transported through the bloodstream to various tissues, where they are used as energy or stored for later use. The liver plays a crucial role in regulating triglyceride levels, and any disruption in liver function can lead to abnormal triglyceride levels.
Factors Affecting Triglyceride Levels
Several factors can affect triglyceride levels, including diet, lifestyle, and underlying medical conditions. A diet high in saturated and trans fats, carbohydrates, and sugar can increase triglyceride levels. Lack of physical activity, smoking, and excessive alcohol consumption can also contribute to high triglyceride levels. Certain medical conditions, such as diabetes, kidney disease, and hypothyroidism, can also affect triglyceride levels.Normal Triglyceride Level Range
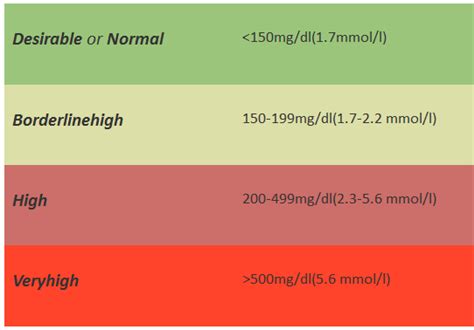
The normal triglyceride level range varies depending on factors such as age, sex, and overall health. Generally, a normal triglyceride level is considered to be below 150 mg/dL of blood. However, levels between 150-199 mg/dL are considered borderline high, while levels above 200 mg/dL are considered high. The following are the normal triglyceride level ranges for different age groups and sexes:
- Adult men: below 150 mg/dL
- Adult women: below 150 mg/dL
- Children and adolescents: below 75 mg/dL
- Older adults (65 years and above): below 150 mg/dL
Triglyceride Level Categories
Triglyceride levels can be categorized into several ranges, including: * Normal: below 150 mg/dL * Borderline high: 150-199 mg/dL * High: 200-499 mg/dL * Very high: 500 mg/dL or aboveHealth Risks Associated with High Triglyceride Levels

High triglyceride levels can increase the risk of various health conditions, including:
- Heart disease: High triglyceride levels can increase the risk of heart disease, including heart attacks, strokes, and peripheral artery disease.
- Pancreatitis: Very high triglyceride levels can increase the risk of pancreatitis, a condition characterized by inflammation of the pancreas.
- Kidney disease: High triglyceride levels can increase the risk of kidney disease, particularly in people with diabetes.
- Stroke: High triglyceride levels can increase the risk of stroke, particularly in people with high blood pressure and diabetes.
Diagnosis and Treatment of High Triglyceride Levels
High triglyceride levels can be diagnosed with a fasting lipid profile test, which measures the levels of triglycerides, cholesterol, and other lipids in the blood. Treatment for high triglyceride levels typically involves lifestyle changes, such as diet and exercise, as well as medication. The following are some common treatments for high triglyceride levels: * Statins: Statins are a type of medication that can help lower triglyceride levels by reducing the production of cholesterol in the liver. * Fibrates: Fibrates are a type of medication that can help lower triglyceride levels by increasing the breakdown of triglycerides in the blood. * Omega-3 fatty acids: Omega-3 fatty acids, particularly EPA and DHA, can help lower triglyceride levels by reducing inflammation and improving blood lipid profiles. * Lifestyle changes: Lifestyle changes, such as diet and exercise, can help lower triglyceride levels by reducing the intake of saturated and trans fats, carbohydrates, and sugar, and increasing physical activity.Maintaining Normal Triglyceride Levels
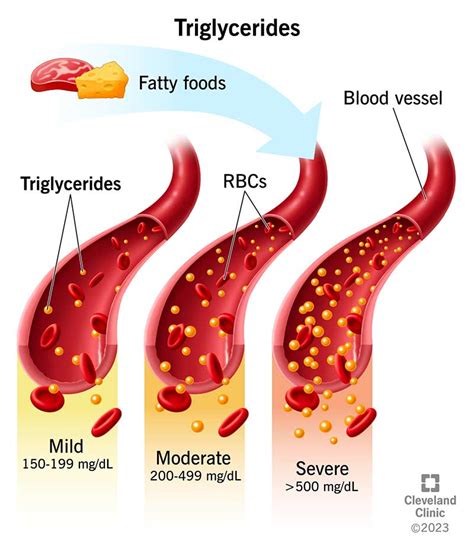
Maintaining normal triglyceride levels is essential for overall health and preventing various diseases. The following are some tips for maintaining normal triglyceride levels:
- Eat a healthy diet: Eating a healthy diet that is low in saturated and trans fats, carbohydrates, and sugar can help maintain normal triglyceride levels.
- Exercise regularly: Regular exercise can help maintain normal triglyceride levels by increasing the breakdown of triglycerides in the blood.
- Maintain a healthy weight: Maintaining a healthy weight can help maintain normal triglyceride levels by reducing the production of triglycerides in the liver.
- Don't smoke: Smoking can increase triglyceride levels, so quitting smoking can help maintain normal triglyceride levels.
- Limit alcohol consumption: Excessive alcohol consumption can increase triglyceride levels, so limiting alcohol consumption can help maintain normal triglyceride levels.
Practical Tips for Maintaining Normal Triglyceride Levels
The following are some practical tips for maintaining normal triglyceride levels: * Choose healthy fats: Choose healthy fats, such as monounsaturated and polyunsaturated fats, instead of saturated and trans fats. * Eat more fiber: Eating more fiber can help maintain normal triglyceride levels by reducing the absorption of cholesterol and triglycerides in the gut. * Drink plenty of water: Drinking plenty of water can help maintain normal triglyceride levels by increasing the breakdown of triglycerides in the blood. * Get enough sleep: Getting enough sleep can help maintain normal triglyceride levels by reducing stress and inflammation.Conclusion and Final Thoughts

In conclusion, maintaining normal triglyceride levels is essential for overall health and preventing various diseases. By understanding the normal triglyceride level range, the factors that affect triglyceride levels, and the health risks associated with high triglyceride levels, individuals can take steps to maintain normal triglyceride levels. By following the tips outlined in this article, individuals can reduce their risk of heart disease, stroke, and other cardiovascular conditions, and maintain overall health and well-being.
We invite you to share your thoughts and experiences with maintaining normal triglyceride levels. Have you struggled with high triglyceride levels in the past? What lifestyle changes have you made to maintain normal triglyceride levels? Share your story with us, and let's work together to promote healthy living and disease prevention.
What are triglycerides?
+Triglycerides are a type of fat found in the blood, and they play a crucial role in the body's energy production.
What is the normal triglyceride level range?
+The normal triglyceride level range varies depending on factors such as age, sex, and overall health, but generally, a normal triglyceride level is considered to be below 150 mg/dL of blood.
What are the health risks associated with high triglyceride levels?
+High triglyceride levels can increase the risk of heart disease, stroke, and other cardiovascular conditions, as well as pancreatitis and kidney disease.
