Intro
Treat 2nd degree burns with our comprehensive guide, covering wound care, blister management, and pain relief, to promote healing and minimize scarring, using topical creams and home remedies for effective burn treatment and recovery.
Burns are a common type of injury that can occur in various settings, including at home, in the workplace, or as a result of an accident. Among the different types of burns, second-degree burns are particularly prevalent and require proper treatment to prevent infection and promote healing. In this article, we will delve into the world of 2 degree burn treatment, exploring the causes, symptoms, and treatment options available for individuals who have suffered from this type of injury.
Second-degree burns, also known as partial-thickness burns, affect both the epidermis and dermis layers of the skin. They can be further divided into two subcategories: superficial second-degree burns, which affect the upper portion of the dermis, and deep second-degree burns, which extend deeper into the dermis. Understanding the severity of the burn is crucial in determining the best course of treatment. If left untreated or improperly managed, second-degree burns can lead to serious complications, including infection, scarring, and even long-term damage to the affected area.
The importance of proper 2 degree burn treatment cannot be overstated. Not only can it help alleviate pain and discomfort, but it can also prevent infection and promote faster healing. In addition, proper treatment can reduce the risk of scarring and minimize the likelihood of long-term damage to the affected area. With the right approach, individuals can recover from second-degree burns and regain full use of the affected area. In the following sections, we will explore the various aspects of 2 degree burn treatment, including causes, symptoms, treatment options, and prevention strategies.
Causes and Risk Factors of Second-Degree Burns
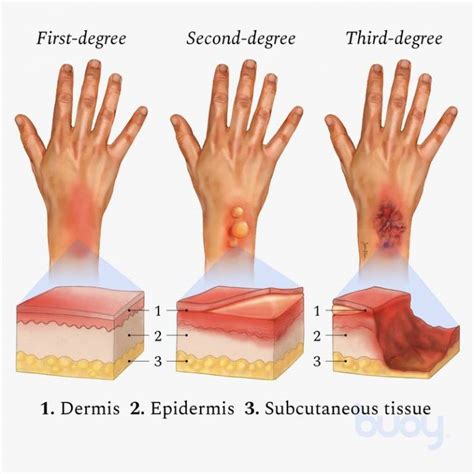
Risk Factors for Second-Degree Burns
Several risk factors can increase an individual's likelihood of suffering from a second-degree burn. These include: * Age: Children and older adults are more prone to burns due to their sensitive skin and decreased mobility. * Occupation: Individuals who work with heat, flames, or chemicals are at a higher risk of suffering from burns. * Medical conditions: Certain medical conditions, such as diabetes or peripheral artery disease, can increase the risk of burns due to decreased sensation or circulation.Symptoms of Second-Degree Burns
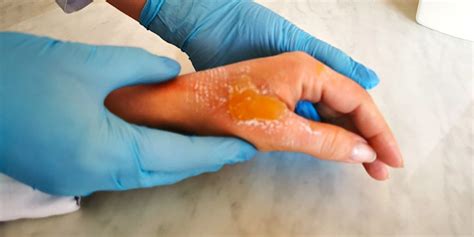
Diagnosing Second-Degree Burns
Diagnosing second-degree burns typically involves a visual examination of the affected area. A healthcare professional may also perform a thorough medical history to determine the cause and severity of the burn. In some cases, additional tests, such as a biopsy or imaging studies, may be necessary to assess the extent of the damage.Treatment Options for Second-Degree Burns
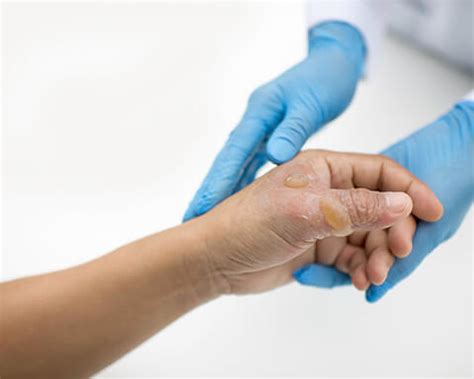
Home Remedies for Second-Degree Burns
In addition to medical treatment, several home remedies can help alleviate symptoms and promote healing. These include: * Aloe vera gel to soothe and calm the skin * Honey to promote wound healing and prevent infection * Tea tree oil to reduce inflammation and prevent infection * Cool baths or showers to reduce pain and discomfortPrevention Strategies for Second-Degree Burns

Complications of Second-Degree Burns
If left untreated or improperly managed, second-degree burns can lead to serious complications, including: * Infection: Bacteria can enter the wound and cause infection, which can spread to other parts of the body. * Scarring: Second-degree burns can result in significant scarring, which can be permanent. * Contractures: The formation of scar tissue can cause contractures, or tightening of the skin, which can limit mobility.Recovery and Rehabilitation for Second-Degree Burns
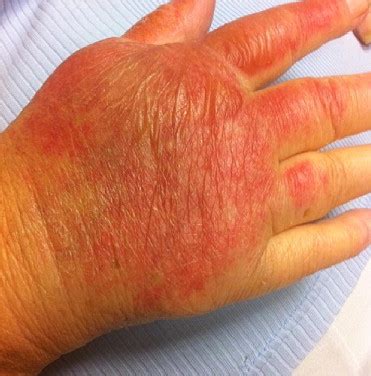
Coping with Emotional Trauma
In addition to physical recovery, individuals who have suffered from second-degree burns may also experience emotional trauma. It is essential to: * Seek support from family, friends, or a mental health professional * Engage in stress-reducing activities, such as meditation or deep breathing * Focus on positive outcomes and celebrate small victories during the recovery processWhat are the most common causes of second-degree burns?
+Second-degree burns can be caused by exposure to heat, flames, or hot liquids. Common causes include scalds from hot water or coffee, contact with open flames, electrical burns, and chemical burns.
How can I prevent second-degree burns?
+Preventing second-degree burns involves taking simple precautions, such as using protective gear, keeping children and pets away from hot surfaces or open flames, and being cautious when handling hot liquids or objects.
What are the symptoms of second-degree burns?
+The symptoms of second-degree burns include redness and swelling of the affected area, blisters or bubbles on the skin, pain or discomfort, and increased sensitivity to touch or temperature.
How can I treat second-degree burns at home?
+Mild second-degree burns can often be treated at home with basic first aid, including cool compresses, topical antibiotics, and pain medication. However, it is essential to seek medical attention if the burn is severe or if symptoms persist.
What are the potential complications of second-degree burns?
+If left untreated or improperly managed, second-degree burns can lead to serious complications, including infection, scarring, and contractures. It is essential to seek medical attention if symptoms persist or worsen over time.
In conclusion, second-degree burns are a common type of injury that requires proper treatment to prevent infection and promote healing. By understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatment options available, individuals can take the necessary steps to recover from second-degree burns and regain full use of the affected area. We encourage readers to share their experiences and ask questions in the comments section below. Additionally, we invite you to explore our other articles on burn care and prevention to learn more about this important topic.
