Intro
Learn about the A1c blood test, a crucial diabetes diagnostic tool, measuring average blood sugar levels, glycated hemoglobin, and glucose control, to manage diabetes, monitor blood glucose, and prevent complications.
The A1c blood test is a crucial tool for diagnosing and managing diabetes. It provides a snapshot of a person's average blood glucose levels over the past 2-3 months. Understanding the A1c test and its results can empower individuals to take control of their health and make informed decisions about their care. In this article, we will delve into the world of A1c testing, exploring its importance, benefits, and what the results mean. Whether you are a patient or a healthcare provider, this comprehensive guide will equip you with the knowledge you need to navigate the complex world of diabetes management.
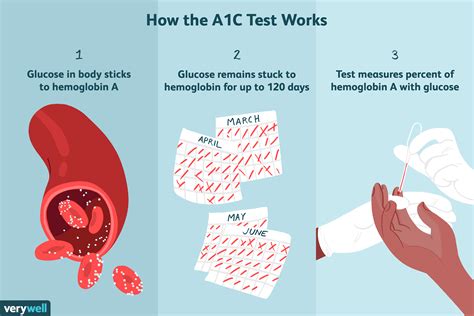
The A1c test is a simple blood test that measures the amount of glucose that has attached to hemoglobin in red blood cells. Hemoglobin is a protein in red blood cells that carries oxygen to different parts of the body. When glucose is present in the blood, it binds to hemoglobin, forming a molecule called glycated hemoglobin or HbA1c. The more glucose in the blood, the more glycated hemoglobin is formed. By measuring the amount of glycated hemoglobin, healthcare providers can determine a person's average blood glucose levels over the past 2-3 months.
The importance of A1c testing cannot be overstated. It provides a clear picture of how well diabetes is being managed, allowing healthcare providers to adjust treatment plans accordingly. For individuals with diabetes, regular A1c testing can help identify potential complications early on, reducing the risk of long-term damage to organs such as the kidneys, heart, and eyes. Moreover, A1c testing can help individuals without diabetes identify their risk of developing the condition, enabling them to make lifestyle changes to prevent or delay its onset.
A1c Test Basics

Understanding A1c Results
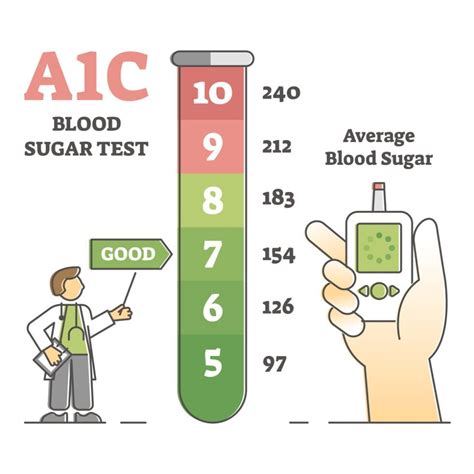
The A1c test results can be interpreted in several ways. An A1c level below 5.7% is considered normal, indicating that blood glucose levels are within a healthy range. An A1c level between 5.7% and 6.4% is considered prediabetic, meaning that blood glucose levels are higher than normal but not high enough to be classified as diabetic. An A1c level of 6.5% or higher is considered diabetic, indicating that blood glucose levels are consistently high and require medical attention.A1c Testing for Diabetes Diagnosis
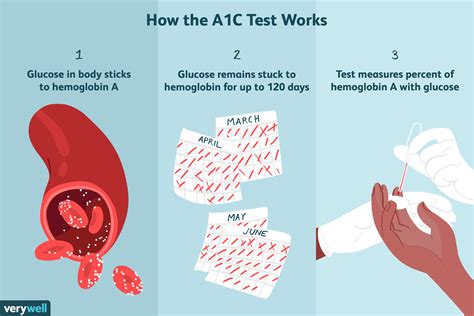
A1c Testing for Diabetes Management
In addition to its role in diagnosing diabetes, the A1c test is also an essential tool for managing the condition. Regular A1c testing can help healthcare providers monitor the effectiveness of treatment plans, making adjustments as needed to keep blood glucose levels under control. The A1c test can also help individuals with diabetes identify potential complications early on, reducing the risk of long-term damage to organs such as the kidneys, heart, and eyes.A1c Test Preparation
A1c Test Risks and Limitations
While the A1c test is a valuable tool for diagnosing and managing diabetes, it is not without risks and limitations. The test can be affected by certain medical conditions, such as anemia, kidney disease, and liver disease. Additionally, the test may not be accurate for individuals with recent blood transfusions or those taking certain medications, such as erythropoietin. Healthcare providers should be aware of these limitations and take them into account when interpreting A1c test results.A1c Testing for Prediabetes
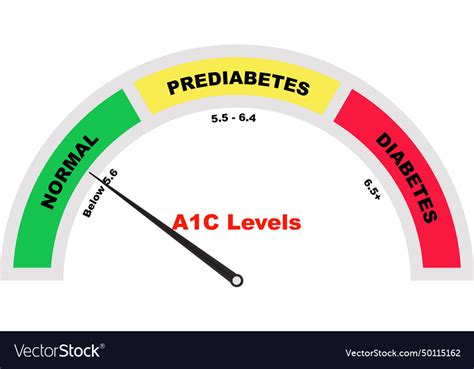
A1c Testing for Gestational Diabetes
Gestational diabetes is a type of diabetes that develops during pregnancy, typically in the second or third trimester. The A1c test can be used to diagnose gestational diabetes, although it is not the primary diagnostic tool. The ADA recommends using the oral glucose tolerance test (OGTT) to diagnose gestational diabetes, as it provides a more accurate picture of blood glucose levels during pregnancy. However, the A1c test can be used to monitor blood glucose levels and adjust treatment plans as needed.A1c Test Results Interpretation
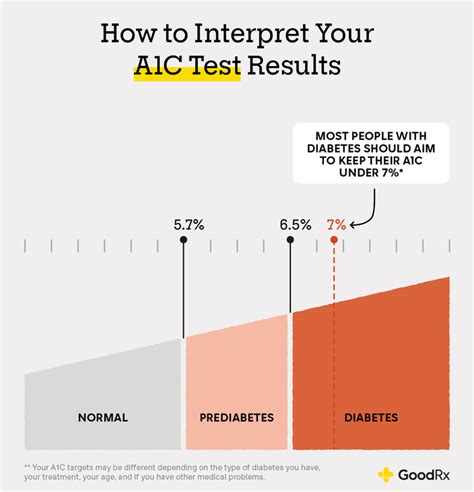
A1c Testing Frequency
The frequency of A1c testing depends on the individual's medical condition and treatment plan. The ADA recommends the following A1c testing frequency: * Individuals with type 1 diabetes: Every 3-6 months * Individuals with type 2 diabetes: Every 6 months * Individuals with prediabetes: Every 12 months * Pregnant women: Every 6-12 weeks during pregnancyA1c Test Costs and Insurance Coverage

A1c Testing at Home
There are several at-home A1c testing kits available, which can provide individuals with a convenient and affordable way to monitor their blood glucose levels. These kits typically involve a fingerstick blood sample, which is then sent to a laboratory for analysis. At-home A1c testing kits can be a useful tool for individuals with diabetes, although they should not replace regular medical care and testing.A1c Test and Lifestyle Changes
A1c Testing and Medication Adherence
Medication adherence is critical for individuals with diabetes, as it can help improve A1c test results and reduce the risk of complications. The following tips can help individuals improve their medication adherence: * Take medications as prescribed * Use a pill box or reminder to stay on track * Keep a medication log to track progress * Inform healthcare providers about any changes to medications or lifestyleA1c Test and Complications
A1c Testing and Mental Health
Mental health is a critical aspect of diabetes management, as it can affect an individual's ability to manage their condition. The following tips can help individuals with diabetes manage their mental health: * Seek support from healthcare providers, family, and friends * Engage in stress-reducing activities, such as meditation or yoga * Stay connected with others through support groups or online communities * Prioritize self-care and self-compassionWhat is the A1c test?
+The A1c test is a blood test that measures the amount of glucose that has attached to hemoglobin in red blood cells.
What is the normal range for A1c test results?
+The normal range for A1c test results is below 5.7%.
How often should I get an A1c test?
+The frequency of A1c testing depends on the individual's medical condition and treatment plan. The ADA recommends A1c testing every 3-6 months for individuals with type 1 diabetes, every 6 months for individuals with type 2 diabetes, and every 12 months for individuals with prediabetes.
Can I take the A1c test at home?
+Yes, there are several at-home A1c testing kits available that can provide individuals with a convenient and affordable way to monitor their blood glucose levels.
What can I do to improve my A1c test results?
+Individuals can improve their A1c test results by making lifestyle changes, such as eating a healthy, balanced diet, engaging in regular physical activity, maintaining a healthy weight, managing stress, and getting enough sleep.
We hope this comprehensive guide to A1c testing has provided you with a deeper understanding of the importance of this test in diagnosing and managing diabetes. By understanding the benefits, risks, and limitations of A1c testing, individuals can take control of their health and make informed decisions about their care. If you have any questions or concerns about A1c testing, we encourage you to speak with your healthcare provider or share your thoughts in the comments below. Together, we can work towards a healthier future for all.
