Intro
The discovery of Helicobacter pylori (H. pylori) has revolutionized our understanding of gastrointestinal diseases. This bacterium, which infects the stomach and duodenum, has been linked to various health issues, including peptic ulcers, gastritis, and even stomach cancer. The importance of H. pylori cannot be overstated, as it affects millions of people worldwide, causing significant morbidity and mortality. In this article, we will delve into the world of H. pylori, exploring its effects on the body, diagnosis, treatment, and prevention.
H. pylori infection is a common problem, affecting up to 50% of the global population. The bacterium is usually acquired during childhood, and once infected, it can persist for life if left untreated. The infection can cause a range of symptoms, from mild discomfort to severe abdominal pain, and can increase the risk of developing more serious conditions. Understanding the ways in which H. pylori affects the body is crucial for developing effective treatment and prevention strategies.
As research into H. pylori continues to evolve, it has become clear that this bacterium is a complex and multifaceted organism. Its ability to adapt to the harsh environment of the stomach, evade the immune system, and manipulate the host's cellular processes has fascinated scientists and clinicians alike. The study of H. pylori has also led to a greater understanding of the importance of the gut microbiome and its role in maintaining overall health. In this article, we will explore five key ways in which H. pylori affects the body, and what can be done to prevent and treat this infection.
Introduction to H Pylori
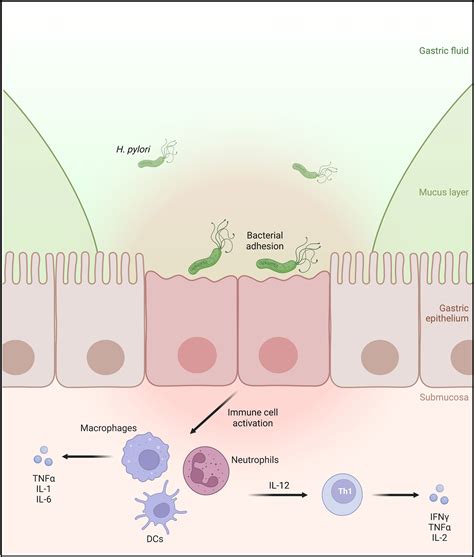
H. pylori is a type of bacteria that infects the stomach and duodenum, causing inflammation and damage to the lining of these organs. The bacterium produces various virulence factors, including enzymes and toxins, which enable it to survive and thrive in the harsh environment of the stomach. H. pylori infection is usually acquired during childhood, and once infected, it can persist for life if left untreated.
Transmission and Risk Factors
The exact mechanisms of H. pylori transmission are not fully understood, but it is thought to be spread through contaminated food, water, and close contact with infected individuals. Certain risk factors, such as poor sanitation, crowded living conditions, and low socioeconomic status, increase the likelihood of acquiring the infection. Understanding the transmission and risk factors of H. pylori is crucial for developing effective prevention strategies.Diagnosis and Treatment of H Pylori
Diagnosing H. pylori infection typically involves a combination of tests, including endoscopy, biopsy, and non-invasive methods such as breath tests and stool antigen tests. Treatment usually involves a combination of antibiotics and acid-suppressing medications, which aim to eradicate the infection and reduce symptoms. However, antibiotic resistance is a growing concern, and alternative treatments, such as probiotics and natural compounds, are being explored.
Antibiotic Resistance and Alternative Treatments
The increasing prevalence of antibiotic-resistant H. pylori strains has led to a growing interest in alternative treatments. Probiotics, prebiotics, and natural compounds, such as cranberry extract and green tea, have been shown to have antimicrobial properties and may be useful in treating H. pylori infection. Further research is needed to fully understand the potential of these alternative treatments and to develop effective strategies for combating antibiotic resistance.Prevention and Management of H Pylori

Preventing H. pylori infection is crucial, as it can reduce the risk of developing associated diseases. Good hygiene practices, such as frequent handwashing and proper food handling, can help prevent the spread of the infection. Additionally, a healthy diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains may help reduce the risk of infection. Managing H. pylori infection involves a combination of treatment, lifestyle modifications, and regular monitoring to prevent complications.
Lifestyle Modifications and Dietary Changes
Lifestyle modifications, such as quitting smoking, reducing stress, and getting regular exercise, can help manage H. pylori infection. Dietary changes, such as increasing consumption of antioxidant-rich foods and avoiding spicy or acidic foods, may also be beneficial. Further research is needed to fully understand the impact of lifestyle and dietary changes on H. pylori infection and to develop effective management strategies.Complications and Long-Term Effects of H Pylori

H. pylori infection can lead to various complications, including peptic ulcers, gastritis, and stomach cancer. The long-term effects of the infection can be severe, and it is essential to seek medical attention if symptoms persist or worsen over time. Understanding the complications and long-term effects of H. pylori is crucial for developing effective treatment and prevention strategies.
Peptic Ulcers and Gastritis
Peptic ulcers and gastritis are common complications of H. pylori infection. These conditions can cause significant morbidity and mortality, and it is essential to seek medical attention if symptoms persist or worsen over time. Treatment usually involves a combination of antibiotics and acid-suppressing medications, which aim to eradicate the infection and reduce symptoms.Current Research and Future Directions
Current research into H. pylori is focused on developing effective treatment and prevention strategies. The discovery of new virulence factors and the development of novel diagnostic tests are crucial for improving our understanding of the infection. Future directions for research include the development of vaccines, the exploration of alternative treatments, and the investigation of the role of H. pylori in other diseases.
Vaccines and Alternative Treatments
The development of vaccines against H. pylori is a promising area of research. Vaccines could provide a safe and effective way to prevent infection, reducing the risk of associated diseases. Alternative treatments, such as probiotics and natural compounds, are also being explored, and further research is needed to fully understand their potential.What is H. pylori?
+H. pylori is a type of bacteria that infects the stomach and duodenum, causing inflammation and damage to the lining of these organs.
How is H. pylori transmitted?
+The exact mechanisms of H. pylori transmission are not fully understood, but it is thought to be spread through contaminated food, water, and close contact with infected individuals.
What are the symptoms of H. pylori infection?
+Symptoms of H. pylori infection can range from mild discomfort to severe abdominal pain, and can include nausea, vomiting, and bloating.
How is H. pylori diagnosed?
+Diagnosing H. pylori infection typically involves a combination of tests, including endoscopy, biopsy, and non-invasive methods such as breath tests and stool antigen tests.
What is the treatment for H. pylori infection?
+Treatment usually involves a combination of antibiotics and acid-suppressing medications, which aim to eradicate the infection and reduce symptoms.
In conclusion, H. pylori is a complex and multifaceted organism that affects millions of people worldwide. Understanding the ways in which H. pylori affects the body, and developing effective treatment and prevention strategies, is crucial for reducing the risk of associated diseases. We hope that this article has provided you with a comprehensive overview of H. pylori, and we invite you to share your thoughts and questions in the comments below. If you have any further questions or would like to learn more about H. pylori, please do not hesitate to reach out to us.
