Intro
Discover the ultimate Bone Marrow Biopsy Guide, covering preparation, procedure, and recovery. Learn about bone marrow aspiration, biopsy results, and understand related terms like myeloma, leukemia, and lymphoma diagnosis and treatment.
Bone marrow is the spongy tissue inside some of your bones, such as your hips and thighbones, which produces blood cells. A bone marrow biopsy is a procedure that involves removing a small sample of bone marrow from your body for examination. This test can help diagnose and monitor various blood disorders, such as anemia, leukemia, and lymphoma. Understanding the importance of bone marrow biopsies can help you prepare for the procedure and make informed decisions about your health.
The process of a bone marrow biopsy can seem intimidating, but it's a relatively common and safe procedure. The test is usually performed on an outpatient basis, and you can typically go home the same day. Your doctor may recommend a bone marrow biopsy if you have symptoms such as fatigue, weight loss, or frequent infections, which could indicate a blood disorder. The results of the biopsy can provide valuable information about the condition of your bone marrow and help your doctor develop an effective treatment plan.
A bone marrow biopsy can also help monitor the progression of a disease or the effectiveness of treatment. For example, if you have a history of cancer, a bone marrow biopsy can help determine if the cancer has spread to your bone marrow. Additionally, the test can help diagnose other conditions, such as bone marrow failure or inflammation. With the help of a bone marrow biopsy, your doctor can gain a better understanding of your overall health and develop a personalized treatment plan to address any underlying conditions.
What to Expect During a Bone Marrow Biopsy
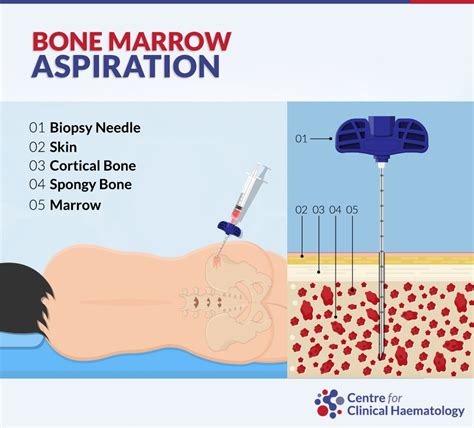
During a bone marrow biopsy, you'll typically lie on your side or sit on the edge of a table. The doctor will clean the area where the biopsy will be performed, usually the hip or pelvic bone, and inject a local anesthetic to numb the skin and bone. You may feel some pressure or discomfort during the procedure, but the anesthetic should help minimize any pain. The doctor will then insert a needle into the bone and remove a small sample of bone marrow. The sample will be sent to a laboratory for examination.
Types of Bone Marrow Biopsies
There are two main types of bone marrow biopsies: aspiration and core biopsy. A bone marrow aspiration involves removing a sample of the liquid portion of the bone marrow, while a core biopsy involves removing a small sample of bone tissue and marrow. In some cases, both types of biopsies may be performed at the same time. The type of biopsy you'll need will depend on your specific condition and the information your doctor needs to diagnose or monitor your condition.Preparing for a Bone Marrow Biopsy
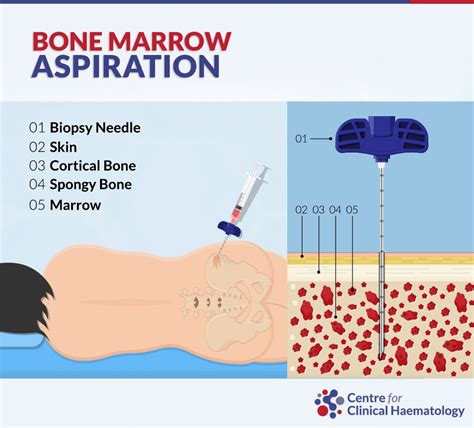
To prepare for a bone marrow biopsy, your doctor may ask you to stop taking certain medications, such as blood thinners, for a few days before the procedure. You should also inform your doctor about any medications you're currently taking, including over-the-counter medications and supplements. On the day of the procedure, wear loose, comfortable clothing and avoid eating or drinking anything for a few hours beforehand. You may also want to bring a friend or family member to drive you home after the procedure, as you may feel drowsy or uncomfortable.
Risks and Complications
As with any medical procedure, there are some risks and complications associated with bone marrow biopsies. These may include bleeding, infection, or nerve damage. In rare cases, the procedure may also cause a bone fracture or other complications. However, these risks are generally low, and the benefits of the procedure usually outweigh the potential risks. Your doctor will discuss the potential risks and complications with you before the procedure and answer any questions you may have.Understanding the Results of a Bone Marrow Biopsy
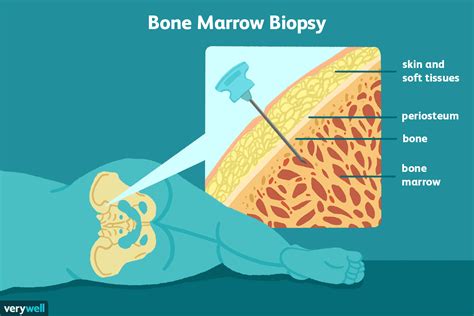
The results of a bone marrow biopsy can provide valuable information about the condition of your bone marrow and help your doctor diagnose or monitor a blood disorder. The results may show abnormal cells, such as cancer cells, or other conditions, such as bone marrow failure or inflammation. Your doctor will discuss the results with you and explain what they mean in the context of your overall health. In some cases, additional tests or procedures may be needed to confirm the diagnosis or monitor the progression of a disease.
Common Conditions Diagnosed with Bone Marrow Biopsies
Bone marrow biopsies can help diagnose a range of conditions, including: * Leukemia: a type of blood cancer that affects the bone marrow * Lymphoma: a type of cancer that affects the immune system * Anemia: a condition characterized by a lack of red blood cells * Bone marrow failure: a condition in which the bone marrow fails to produce enough blood cells * Infection: a bacterial, viral, or fungal infection that affects the bone marrowRecovery and Aftercare
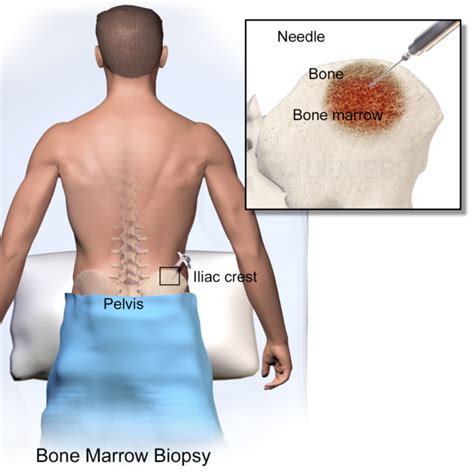
After a bone marrow biopsy, you may feel some discomfort or pain at the site of the procedure. Your doctor may recommend over-the-counter pain medication to help manage any discomfort. You should also avoid strenuous activities, such as heavy lifting or bending, for a few days after the procedure. In most cases, you can return to your normal activities within a few days. Your doctor will provide you with specific instructions on how to care for the site of the biopsy and manage any potential side effects.
Follow-up Care
After a bone marrow biopsy, you'll typically need to follow up with your doctor to discuss the results and any further treatment or testing that may be needed. Your doctor may also recommend additional tests or procedures to monitor the progression of a disease or the effectiveness of treatment. Be sure to ask your doctor any questions you may have about the procedure, the results, or any further treatment or testing.Conclusion and Next Steps

A bone marrow biopsy is a valuable diagnostic tool that can help diagnose and monitor various blood disorders. By understanding the procedure, the risks and complications, and the results, you can make informed decisions about your health. If you have any questions or concerns about bone marrow biopsies, be sure to discuss them with your doctor. With the right information and care, you can take control of your health and make informed decisions about your treatment.
What is a bone marrow biopsy?
+A bone marrow biopsy is a procedure that involves removing a small sample of bone marrow from your body for examination.
Why do I need a bone marrow biopsy?
+Your doctor may recommend a bone marrow biopsy to diagnose or monitor a blood disorder, such as anemia, leukemia, or lymphoma.
What are the risks and complications of a bone marrow biopsy?
+The risks and complications of a bone marrow biopsy include bleeding, infection, and nerve damage. However, these risks are generally low, and the benefits of the procedure usually outweigh the potential risks.
We hope this article has provided you with a comprehensive understanding of bone marrow biopsies. If you have any further questions or concerns, please don't hesitate to reach out to your doctor or a medical professional. Share this article with friends and family who may be interested in learning more about bone marrow biopsies, and take the first step towards taking control of your health.
