Intro
Discover optimal A1c targets by age, including diabetes management, blood sugar control, and glycemic goals for adults, children, and seniors, to achieve healthy hemoglobin levels and prevent complications.
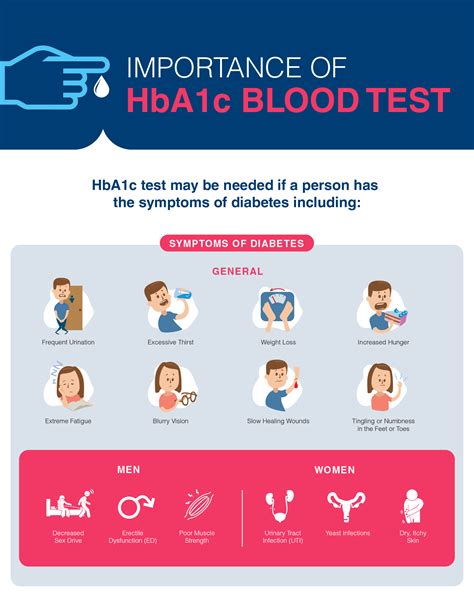
Managing blood sugar levels is crucial for individuals with diabetes, and one key metric used to assess long-term glucose control is the hemoglobin A1c (HbA1c) level. The HbA1c test measures the average blood glucose levels over the past 2 to 3 months, providing valuable insights into how well diabetes is being managed. The importance of understanding and achieving appropriate HbA1c targets cannot be overstated, as it directly impacts the risk of developing diabetes-related complications. For healthcare providers and patients alike, knowing the recommended HbA1c targets by age is essential for tailoring diabetes care to meet individual needs.
The management of diabetes is multifaceted, involving lifestyle modifications, medication, and regular monitoring of blood glucose levels. Among the various factors that influence diabetes management, age plays a significant role. As individuals age, their risk of developing diabetes and related complications can increase, making it critical to have age-specific guidelines for HbA1c targets. These targets are designed to balance the benefits of tight glucose control with the potential risks and challenges associated with achieving very low HbA1c levels, especially in older adults or those with certain comorbidities.
Understanding the nuances of HbA1c targets by age requires considering the latest clinical guidelines and research findings. Professional organizations such as the American Diabetes Association (ADA) and the American Association of Clinical Endocrinologists (AACE) provide recommendations on HbA1c targets, taking into account factors such as the individual's risk of hypoglycemia, disease duration, life expectancy, and the presence of comorbid conditions. These guidelines are not static; they evolve based on new evidence, underscoring the importance of staying updated on the best practices in diabetes management.
HbA1c Targets for Different Age Groups

The HbA1c targets vary by age, reflecting the different needs and risks associated with diabetes management across the lifespan. For younger individuals, including children and adolescents, tighter control is often recommended to minimize the risk of long-term complications. In contrast, for older adults, the targets may be less stringent, considering the potential for increased risk of hypoglycemia and other age-related factors.
Children and Adolescents
For children and adolescents with diabetes, the goal is to achieve HbA1c levels as close to the normal range as possible (<6.5%) without causing significant hypoglycemia. This approach is aimed at reducing the risk of long-term diabetes-related complications, such as diabetic retinopathy, nephropathy, and neuropathy, which can have a profound impact on quality of life.Adults and Older Adults
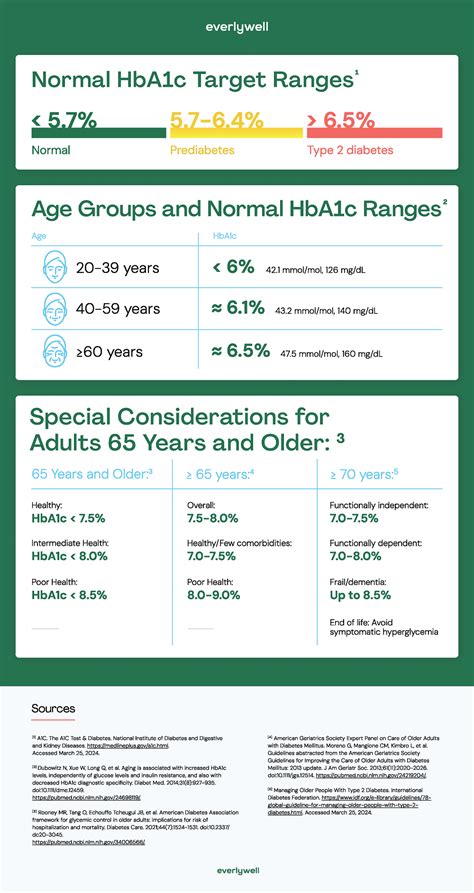
For adults, the recommended HbA1c target is generally <7%, though this can be adjusted based on individual factors such as the risk of hypoglycemia, disease duration, and the presence of cardiovascular disease. In older adults, particularly those with limited life expectancy, comorbidities, or a history of severe hypoglycemia, less stringent HbA1c targets (e.g., <8%) may be appropriate, prioritizing the avoidance of hypoglycemia and maintaining quality of life.
Pregnancy and Diabetes
During pregnancy, tight blood glucose control is crucial to minimize the risks of complications for both the mother and the fetus. For women with pre-existing diabetes, the HbA1c target before conception is <6.5%, and during pregnancy, it is <6%. Achieving these targets requires careful management and close monitoring, as the risks of hypoglycemia and other complications can increase during this period.Benefits of Achieving HbA1c Targets
Achieving the recommended HbA1c targets offers numerous benefits, including reduced risks of microvascular complications (such as diabetic retinopathy, nephropathy, and neuropathy) and macrovascular complications (including heart disease and stroke). Additionally, good glycemic control can improve quality of life, reduce the risk of diabetes-related infections, and decrease the likelihood of cognitive decline in older adults.
Challenges in Achieving HbA1c Targets
Despite the benefits, achieving and maintaining HbA1c targets can be challenging. Barriers include the complexity of diabetes management, the cost of medications and supplies, access to healthcare services, and psychological factors such as diabetes distress and fear of hypoglycemia. Addressing these challenges requires a multifaceted approach, including patient education, support from healthcare providers, and the development of personalized treatment plans that consider the individual's unique circumstances and preferences.Strategies for Improving HbA1c Levels
Improving HbA1c levels involves a combination of lifestyle modifications and, when necessary, adjustments to medication regimens. Key strategies include:
- Dietary Changes: Following a balanced diet that is low in added sugars, saturated fats, and sodium, and high in fiber, fruits, vegetables, and whole grains.
- Physical Activity: Engaging in regular physical activity, such as walking, to improve insulin sensitivity and glucose uptake by muscles.
- Weight Management: Achieving and maintaining a healthy weight to reduce insulin resistance and improve glycemic control.
- Medication Adherence: Taking medications as prescribed and attending regular follow-up appointments with healthcare providers to monitor progress and adjust treatment plans as needed.
Role of Technology in Diabetes Management
The use of technology, including continuous glucose monitoring systems, insulin pumps, and mobile health applications, can significantly enhance diabetes management. These tools provide real-time data on glucose levels, facilitate more precise dosing of insulin, and offer educational resources and support, making it easier for individuals to achieve their HbA1c targets.Future Directions in HbA1c Management
The future of HbA1c management holds promise with ongoing research into new medications, technologies, and therapeutic approaches. Personalized medicine, which involves tailoring treatment to an individual's unique genetic, environmental, and lifestyle factors, is expected to play a growing role in optimizing diabetes care. Additionally, advancements in artificial intelligence and machine learning may lead to more sophisticated predictive models for diabetes management, enabling earlier interventions and better outcomes.
Conclusion and Next Steps
In conclusion, understanding and achieving appropriate HbA1c targets by age is fundamental to effective diabetes management. By recognizing the importance of these targets and implementing strategies to improve glycemic control, individuals with diabetes can reduce their risk of complications and improve their quality of life. As research and technology continue to evolve, it is essential for patients, healthcare providers, and policymakers to stay informed and work together to address the challenges and opportunities in diabetes care.What is the significance of HbA1c in diabetes management?
+HbA1c is a critical metric for assessing long-term glucose control, providing insights into the average blood glucose levels over the past 2 to 3 months.
How do HbA1c targets vary by age?
+HbA1c targets are age-specific, with tighter control recommended for younger individuals and less stringent targets for older adults, considering factors such as the risk of hypoglycemia and life expectancy.
What strategies can improve HbA1c levels?
+Improving HbA1c levels involves dietary changes, regular physical activity, weight management, medication adherence, and the use of technology such as continuous glucose monitoring systems and insulin pumps.
We invite readers to share their experiences and insights into managing diabetes and achieving HbA1c targets. Your comments and questions can help others navigate the complexities of diabetes care and inspire new discussions on this critical topic. Whether you are a patient, a healthcare provider, or simply someone interested in learning more about diabetes management, your engagement is invaluable. Let's work together to promote better understanding, support, and outcomes for individuals with diabetes.
