Intro
Identify early signs of preeclampsia, a pregnancy complication, including high blood pressure, proteinuria, and swelling, to ensure timely treatment and prevent eclampsia, placental abruption, and other complications, promoting a healthy pregnancy and fetal well-being.
Preeclampsia is a pregnancy complication characterized by high blood pressure and often accompanied by significant amounts of protein in the urine. This condition can lead to serious complications for both the mother and the baby if left untreated. It is essential for pregnant women to be aware of the early signs of preeclampsia to seek medical attention promptly. The importance of recognizing these signs cannot be overstated, as early detection and treatment can significantly improve outcomes for both the mother and the baby.
The condition affects a significant number of pregnancies worldwide, and its impact can be severe. Preeclampsia is a leading cause of maternal and fetal morbidity and mortality, making it a critical area of focus for prenatal care. Understanding the risk factors, symptoms, and management strategies for preeclampsia is vital for healthcare providers and pregnant women alike. By being informed, individuals can take proactive steps to minimize risks and ensure the best possible health outcomes.
Preeclampsia can develop at any stage of pregnancy, but it typically occurs after 20 weeks of gestation. In some cases, it may develop earlier, especially in women with pre-existing medical conditions. The condition can progress rapidly, which is why regular prenatal check-ups are crucial. These check-ups allow healthcare providers to monitor blood pressure and urine protein levels, enabling early detection and intervention. With the advancements in medical science and the emphasis on prenatal care, the management and outcomes of preeclampsia have improved significantly over the years.
Understanding Preeclampsia
Understanding preeclampsia involves recognizing its causes, symptoms, and effects on pregnancy. While the exact cause of preeclampsia is not fully understood, research suggests that it is related to the development of the placenta. In a normal pregnancy, the placenta develops properly, allowing for adequate blood flow and nutrient exchange between the mother and the fetus. However, in preeclampsia, the placenta does not develop as it should, leading to reduced blood flow and increased blood pressure.
Risk Factors for Preeclampsia
Several risk factors increase a woman's likelihood of developing preeclampsia. These include: - First pregnancy: Women having their first baby are at a higher risk. - Age: Women under 20 or over 35 years old are at increased risk. - Pre-existing medical conditions: Conditions like high blood pressure, diabetes, and kidney disease can increase the risk. - Carrying twins or other multiples: The risk is higher in multiple pregnancies. - Family history: Having a family history of preeclampsia can increase the risk. - Obesity: Being overweight or obese can increase the risk of developing preeclampsia.Symptoms of Preeclampsia
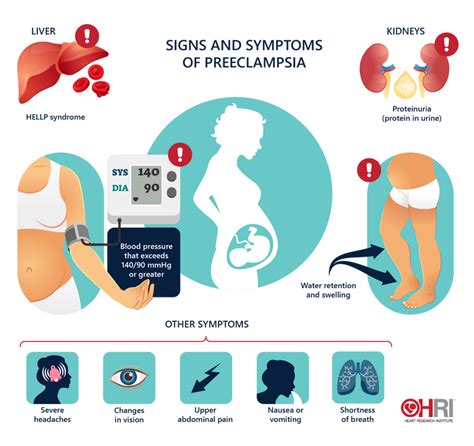
The symptoms of preeclampsia can vary, but they often include:
- High blood pressure: This is the most common symptom, detected during prenatal check-ups.
- Protein in the urine: Significant amounts of protein in the urine (proteinuria) are a hallmark of preeclampsia.
- Severe headaches: These can be a sign of preeclampsia, especially if they are persistent and severe.
- Vision changes: Blurred vision, double vision, or sensitivity to light can occur.
- Nausea and vomiting: While common in early pregnancy, severe nausea and vomiting late in pregnancy can be a sign of preeclampsia.
- Abdominal pain: Upper abdominal pain, especially if severe and persistent, can be a symptom.
- Decreased urine output: Producing less urine than usual can indicate preeclampsia.
- Sudden weight gain: A sudden increase in weight due to fluid retention can be a sign.
Diagnosing Preeclampsia
Diagnosing preeclampsia involves a combination of physical examination, medical history, and laboratory tests. Healthcare providers look for high blood pressure and significant protein in the urine. Other tests may include blood tests to check for signs of kidney or liver damage and ultrasound scans to assess the baby's growth and well-being.Treatment and Management
The treatment and management of preeclampsia depend on the severity of the condition and the gestational age of the baby. For mild cases, close monitoring of blood pressure and urine protein levels may be sufficient. This often involves more frequent prenatal visits and, in some cases, bed rest. In more severe cases, hospitalization may be necessary to closely monitor the mother and the baby. The primary goal is to prevent the condition from progressing to eclampsia, which involves seizures and can be life-threatening.
Severe Preeclampsia
Severe preeclampsia requires immediate medical attention. It is characterized by very high blood pressure and significant protein in the urine, along with other symptoms such as vision changes, severe headache, and abdominal pain. In these cases, delivery is often the best course of action, regardless of the gestational age, to protect the health of both the mother and the baby.Prevention Strategies

While there is no guaranteed way to prevent preeclampsia, certain strategies can reduce the risk. These include:
- Maintaining a healthy weight before and during pregnancy.
- Following a balanced diet that is rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains.
- Staying hydrated by drinking plenty of water.
- Engaging in regular physical activity, as recommended by a healthcare provider.
- Managing stress through techniques like meditation or yoga.
- Avoiding tobacco and alcohol use.
Lifestyle Modifications
Lifestyle modifications play a crucial role in managing preeclampsia. Women with preeclampsia may need to make changes to their daily activities, such as getting plenty of rest and avoiding strenuous activities. Monitoring blood pressure at home and reporting any changes or concerns to a healthcare provider is also important.Support and Resources

Having a support system is vital for women dealing with preeclampsia. This can include family, friends, and support groups. Online resources and healthcare providers can also offer valuable information and guidance. It's essential to stay informed and connected to manage the condition effectively and ensure the best possible outcomes.
Coping with Preeclampsia
Coping with preeclampsia involves emotional support as well as physical care. The diagnosis can be stressful and overwhelming, and women may experience anxiety or depression. Seeking help from mental health professionals and joining support groups can provide emotional support and help women cope with the challenges of preeclampsia.Future Perspectives

Research into preeclampsia is ongoing, with scientists exploring new diagnostic tools, treatments, and prevention strategies. Understanding the underlying causes of preeclampsia is crucial for developing effective interventions. As medical science advances, the management and outcomes of preeclampsia are likely to improve, offering better health prospects for mothers and babies.
Advancements in Preeclampsia Research
Advancements in preeclampsia research hold promise for improved diagnosis and treatment. Studies are focusing on the role of genetics, the placenta's development, and the immune system's response. These findings could lead to the development of new therapies and better management strategies, ultimately reducing the risks associated with preeclampsia.Conclusion and Next Steps

In conclusion, preeclampsia is a significant pregnancy complication that requires awareness, understanding, and prompt medical attention. By recognizing the early signs, understanding the risk factors, and following prevention strategies, women can reduce their risk and ensure the best possible health outcomes for themselves and their babies. It's crucial for pregnant women and their families to stay informed and engaged with healthcare providers throughout the pregnancy journey.
We invite you to share your thoughts, questions, or experiences with preeclampsia in the comments below. Your insights can help others understand this condition better and encourage open discussions about pregnancy health. If you found this article informative, please consider sharing it with others who might benefit from this information.
What are the primary symptoms of preeclampsia?
+The primary symptoms include high blood pressure, significant protein in the urine, severe headaches, vision changes, nausea and vomiting, abdominal pain, and sudden weight gain.
How is preeclampsia diagnosed?
+Preeclampsia is diagnosed through a combination of physical examination, medical history, and laboratory tests, including blood pressure checks and urine tests for protein.
Can preeclampsia be prevented?
+While there is no guaranteed way to prevent preeclampsia, maintaining a healthy weight, following a balanced diet, staying hydrated, engaging in regular physical activity, and managing stress can reduce the risk.
