Intro
Discover how A1c tests help manage diabetes, improving blood sugar control and reducing complications through regular monitoring, insulin therapy, and healthy lifestyle changes, for better glucose management and overall health.
The importance of monitoring and managing diabetes cannot be overstated, given the significant impact this condition has on the lives of millions of people worldwide. Diabetes, a chronic health condition that affects how your body turns food into energy, can lead to various complications if not properly managed. One crucial tool in the management of diabetes is the Hemoglobin A1c (HbA1c) test, which provides a snapshot of a person's average blood glucose levels over the past 2 to 3 months. Understanding the role of A1c in diabetes care is essential for both healthcare providers and individuals living with diabetes.
Effective diabetes management involves a combination of lifestyle changes, medication (if prescribed), and regular monitoring of blood glucose levels. The A1c test is a key component of this monitoring process, offering valuable insights into how well diabetes is being controlled. By measuring the percentage of glucose that has bound to hemoglobin in red blood cells, the A1c test gives healthcare providers a clear picture of a patient's blood glucose control over time. This information is critical for making informed decisions about treatment plans, including adjustments to diet, exercise, and medication.
For individuals living with diabetes, the A1c test serves as a motivator and a guide. It helps in setting realistic goals for blood glucose control and encourages adherence to treatment plans. Moreover, understanding A1c results empowers individuals to make informed decisions about their health, fostering a sense of control and responsibility over their condition. The test results can also highlight areas for improvement, whether it's adjusting eating habits, increasing physical activity, or improving adherence to medication regimens. By leveraging the information provided by A1c tests, individuals can work closely with their healthcare providers to optimize their diabetes management strategies.
A1c and Diabetes Management
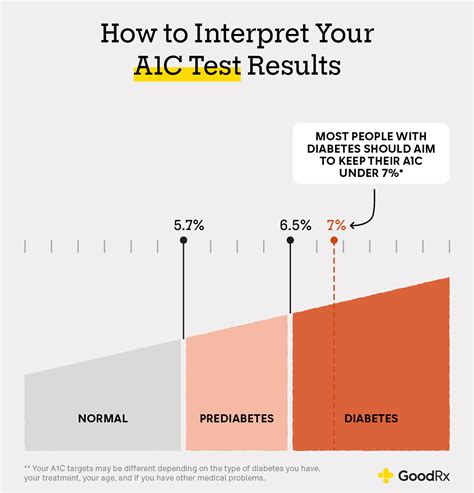
Benefits of Regular A1c Testing
Regular A1c testing offers several benefits for individuals with diabetes. It helps in: - **Early Detection of Complications:** By monitoring A1c levels, healthcare providers can identify potential complications early, allowing for timely interventions. - **Personalized Treatment Plans:** A1c results enable healthcare providers to tailor treatment plans to the individual's needs, improving the likelihood of achieving target blood glucose levels. - **Motivation and Engagement:** Seeing the impact of lifestyle changes and treatment adherence through A1c results can motivate individuals to maintain or improve their diabetes management strategies.Understanding A1c Results
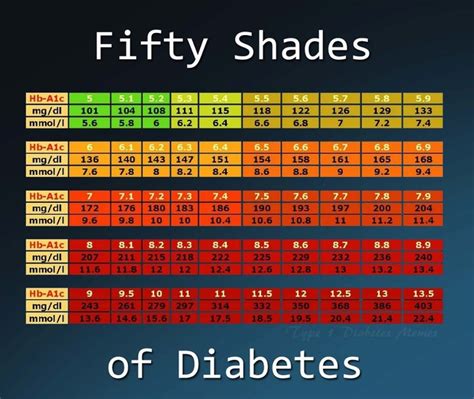
Achieving Target A1c Levels
Achieving and maintaining target A1c levels requires a multifaceted approach that includes: - **Healthy Eating:** Focusing on a balanced diet that is rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats. - **Regular Physical Activity:** Engaging in at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic exercise, or 75 minutes of vigorous-intensity aerobic exercise, or a combination of both, per week. - **Medication Adherence:** Taking diabetes medications as prescribed by your healthcare provider. - **Regular Monitoring:** Checking blood glucose levels as recommended by your healthcare provider and attending regular health check-ups.A1c and Lifestyle Changes
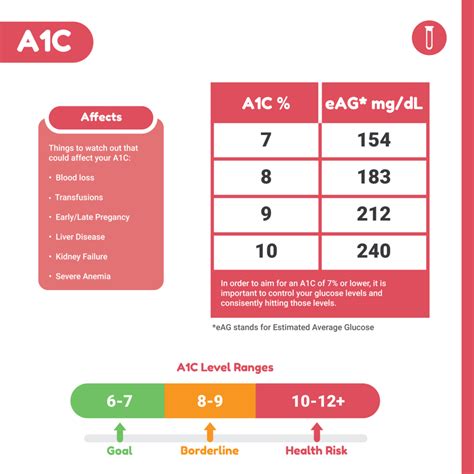
Practical Tips for Lifestyle Modification
- **Keep a Food Diary:** Tracking what you eat can help identify patterns and areas for improvement in your diet. - **Find Enjoyable Physical Activities:** Engaging in physical activities that you enjoy can make it easier to stick to an exercise routine. - **Set Realistic Goals:** Break down larger goals into smaller, achievable steps to maintain motivation and track progress.A1c in Preventing Diabetes Complications
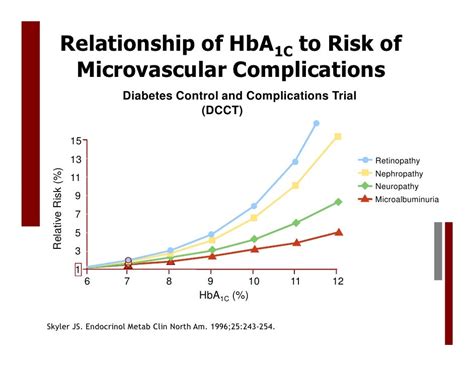
Common Diabetes Complications
- **Cardiovascular Disease:** High blood pressure and high cholesterol, which are common in people with diabetes, increase the risk of heart disease and stroke. - **Diabetic Retinopathy:** Damage to the blood vessels in the retina can lead to vision problems and even blindness. - **Diabetic Neuropathy:** Nerve damage can cause numbness, pain, and weakness in the hands and feet.A1c and Mental Health
Coping Mechanisms for Diabetes-Related Stress
- **Support Groups:** Joining a support group can provide a sense of community and understanding. - **Mindfulness and Meditation:** Practicing mindfulness and meditation can help reduce stress and improve mood. - **Professional Help:** Seeking help from a mental health professional is important for addressing diabetes-related stress and anxiety.A1c Testing in Different Populations
Considerations for Special Populations
- **Pregnant Women:** Tighter blood glucose control is crucial to prevent complications. - **Older Adults:** Less stringent A1c targets may be appropriate due to the risk of hypoglycemia and other health considerations. - **Children and Adolescents:** A1c targets may need to be adjusted based on age and the presence of other health conditions.What is the normal range for A1c levels?
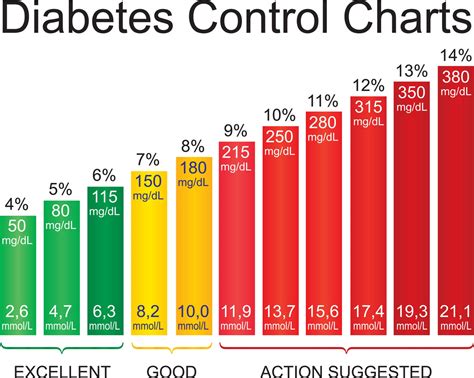
+For people without diabetes, the normal range for A1c levels is less than 5.7%. For individuals with diabetes, the target A1c level is typically less than 7%, though this can vary based on individual factors.
How often should I get an A1c test?
+The frequency of A1c testing depends on the type of diabetes and how well the condition is being managed. Generally, individuals with diabetes should have an A1c test at least twice a year, but it may be recommended more frequently if blood glucose levels are not well controlled or if there are changes in treatment.
Can A1c levels be affected by factors other than blood glucose control?
+Yes, several factors can affect A1c levels, including the lifespan of red blood cells, hemoglobin variants, and certain medical conditions. It's essential to discuss any unusual A1c results with your healthcare provider to understand the underlying causes.
In conclusion, A1c testing is a powerful tool in the management of diabetes, offering insights into blood glucose control over time. By understanding the role of A1c in diabetes care, individuals can work more effectively with their healthcare providers to achieve better blood glucose control, reduce the risk of complications, and improve their overall quality of life. We invite readers to share their experiences with A1c testing and diabetes management, and to ask any questions they may have about this critical aspect of diabetes care. By engaging in this conversation, we hope to foster a community that supports and empowers individuals living with diabetes.
