Intro
Treat Afib with ablation, a minimally invasive procedure using catheter ablation, pulmonary vein isolation, and radiofrequency energy to restore heart rhythm, reducing arrhythmia symptoms and improving cardiac health.
Atrial fibrillation, commonly referred to as Afib, is a type of irregular heartbeat that can lead to serious health complications if left untreated. It occurs when the upper chambers of the heart beat too quickly or irregularly, preventing the heart from pumping blood effectively. Over the years, various treatments have been developed to manage Afib, with catheter ablation being one of the most effective procedures. In this article, we will delve into the world of ablation and explore how it treats Afib, its benefits, and what patients can expect from the procedure.
Ablation has become a popular treatment option for Afib due to its minimally invasive nature and high success rates. The procedure involves using catheters to destroy the abnormal electrical pathways in the heart that cause the irregular heartbeat. By eliminating these pathways, the heart can return to its normal rhythm, reducing the risk of complications such as stroke and heart failure. With the advancement of technology, ablation has become a safer and more effective treatment option for patients with Afib.
The importance of treating Afib cannot be overstated. If left untreated, Afib can lead to serious health complications, including stroke, heart failure, and other heart-related problems. According to the American Heart Association, Afib increases the risk of stroke by five times and can also lead to heart failure and other heart-related complications. Furthermore, Afib can significantly impact a patient's quality of life, causing symptoms such as palpitations, shortness of breath, and fatigue. By treating Afib with ablation, patients can reduce their risk of complications and improve their overall quality of life.
What is Ablation?
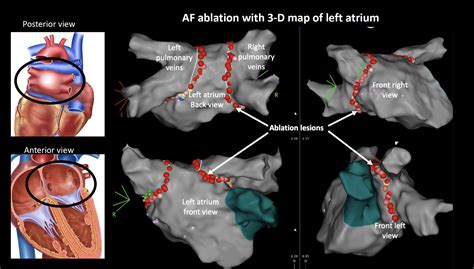
Types of Ablation
There are several types of ablation procedures, including radiofrequency ablation, cryoablation, and laser ablation. Radiofrequency ablation uses heat to destroy the abnormal electrical pathways, while cryoablation uses extreme cold. Laser ablation, on the other hand, uses high-energy light to destroy the abnormal tissue. Each type of ablation has its own advantages and disadvantages, and the choice of procedure depends on the individual patient's needs and medical history.Benefits of Ablation
Risks and Complications
While ablation is generally a safe procedure, there are some risks and complications to be aware of. These include bleeding, infection, and damage to the heart or surrounding tissues. In rare cases, ablation can also cause complications such as stroke or heart attack. However, these risks are relatively low, and most patients can expect a safe and effective procedure.Preparing for Ablation
What to Expect During the Procedure
During the procedure, patients can expect to be given anesthesia to minimize discomfort. The doctor will then insert a catheter through a vein in the leg and guide it to the heart using imaging technology. The procedure can take several hours to complete, and patients may be required to stay in the hospital overnight for observation.Recovery and Follow-Up

Long-Term Results
The long-term results of ablation can vary depending on the individual patient and the type of procedure used. According to a study published in the Journal of Cardiovascular Electrophysiology, ablation can provide long-term relief from Afib symptoms in up to 70% of patients. However, some patients may require repeat procedures or ongoing medication to manage their condition.Conclusion and Next Steps

Final Thoughts
Ablation has revolutionized the treatment of Afib, providing a safe and effective solution for patients. With its high success rate and minimal risks, ablation has become a popular treatment option for patients with Afib. As medical technology continues to evolve, we can expect even more innovative treatments to emerge, providing hope for patients with Afib and other heart-related conditions.What is Afib and how is it treated?
+Afib, or atrial fibrillation, is a type of irregular heartbeat that can be treated with ablation, medication, or lifestyle changes. Ablation is a minimally invasive procedure that uses catheters to destroy the abnormal electrical pathways in the heart that cause Afib.
What are the benefits of ablation for Afib?
+Ablation has several benefits, including a high success rate, minimal scarring, and a quick recovery time. According to a study published in the Journal of the American College of Cardiology, ablation has a success rate of up to 80% in treating Afib.
What are the risks and complications of ablation?
+While ablation is generally a safe procedure, there are some risks and complications to be aware of, including bleeding, infection, and damage to the heart or surrounding tissues. In rare cases, ablation can also cause complications such as stroke or heart attack.
How do I prepare for ablation?
+Preparing for ablation involves several steps, including stopping certain medications, avoiding food and drink, and undergoing imaging tests. Patients should also inform their doctor about any medical conditions or allergies they may have.
What can I expect during the ablation procedure?
+During the procedure, patients can expect to be given anesthesia to minimize discomfort. The doctor will then insert a catheter through a vein in the leg and guide it to the heart using imaging technology. The procedure can take several hours to complete, and patients may be required to stay in the hospital overnight for observation.
