Intro
Discover key 5 Z Pack facts, including its antibiotic uses, azithromycin benefits, and common side effects, to understand this popular medications role in treating bacterial infections effectively.
The 5 Z Pack, also known as azithromycin, has been a widely prescribed antibiotic for various bacterial infections. Its efficacy and convenience have made it a popular choice among healthcare providers and patients alike. However, there is more to this medication than meets the eye. In this article, we will delve into the world of 5 Z Pack facts, exploring its benefits, working mechanisms, and key information that every patient should know.
The importance of understanding antibiotics like the 5 Z Pack cannot be overstated. With the rise of antibiotic resistance, it is crucial that patients are educated on the proper use and potential risks associated with these medications. By doing so, we can promote responsible antibiotic use and mitigate the development of resistant bacterial strains. Moreover, being informed about the 5 Z Pack can help patients make the most out of their treatment, ensuring they recover quickly and effectively from their infections.
As we navigate the complexities of the 5 Z Pack, it is essential to consider the broader context of antibiotic therapy. The discovery of antibiotics has revolutionized the field of medicine, saving countless lives and transforming the way we approach infectious diseases. However, with great power comes great responsibility, and it is our duty to use these medications wisely. By exploring the intricacies of the 5 Z Pack, we can gain a deeper appreciation for the importance of antibiotic stewardship and the role that patients play in promoting responsible antibiotic use.
What is the 5 Z Pack?
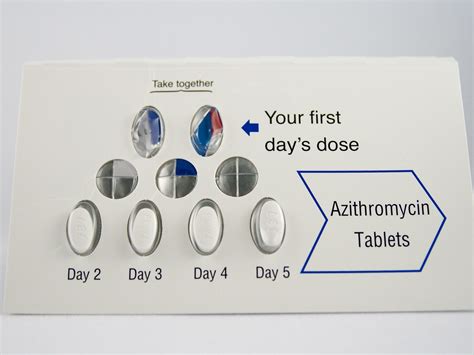
How Does the 5 Z Pack Work?
The 5 Z Pack works by binding to the bacterial ribosome, which is responsible for protein synthesis. This binding process inhibits the translation of messenger RNA into proteins, effectively stopping the growth of the bacteria. As a result, the bacteria are unable to multiply and eventually die, allowing the patient's immune system to clear the infection. The 5 Z Pack is particularly effective against gram-positive bacteria, although it also has activity against some gram-negative bacteria.Benefits of the 5 Z Pack
Common Uses of the 5 Z Pack
The 5 Z Pack is commonly used to treat a range of bacterial infections, including: * Respiratory tract infections: The medication is effective against infections such as pneumonia, bronchitis, and sinusitis. * Skin infections: The 5 Z Pack can be used to treat skin infections such as acne, impetigo, and cellulitis. * Sexually transmitted infections: The medication is used to treat infections such as chlamydia and gonorrhea. * Other infections: The 5 Z Pack may also be used to treat other bacterial infections, such as urinary tract infections and gastrointestinal infections.Side Effects and Risks
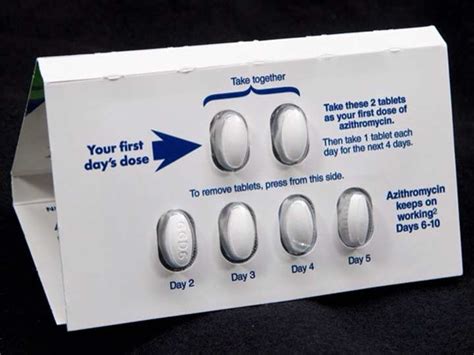
Precautions and Contraindications
The 5 Z Pack is not suitable for all patients, and certain precautions and contraindications should be considered. These include: * Pregnancy and breastfeeding: The medication should be used with caution in pregnant and breastfeeding women, as it may affect the developing fetus or baby. * Allergic reactions: Patients with a history of allergic reactions to azithromycin or other macrolide antibiotics should avoid using the 5 Z Pack. * Liver and kidney disease: Patients with liver or kidney disease should use the medication with caution, as it may affect the liver or kidneys. * Interactions with other medications: The 5 Z Pack may interact with other medications, such as warfarin, digoxin, and phenytoin.Interactions with Other Medications
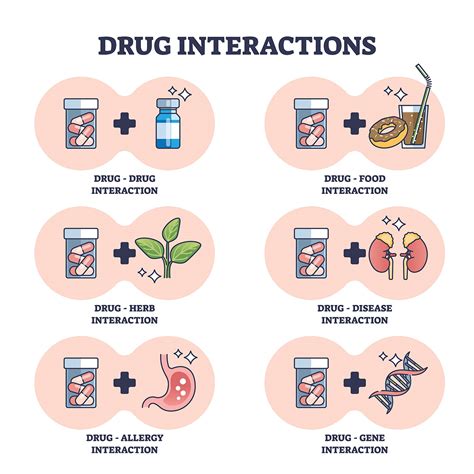
Dosage and Administration
The dosage and administration of the 5 Z Pack may vary depending on the patient's age, weight, and medical condition. The typical dosage is: * Adults: 500mg as a single dose or 250mg daily for 5 days. * Children: 10-20mg/kg daily for 3-5 days. * Patients with renal impairment: The dosage may need to be adjusted in patients with renal impairment.Resistance and Antibiotic Stewardship

Future Directions
The development of new antibiotics and alternative therapies is crucial to addressing the issue of antibiotic resistance. Some potential future directions include: * Novel antibiotic compounds: Researchers are exploring new antibiotic compounds that target different mechanisms of bacterial growth and survival. * Alternative therapies: Alternative therapies, such as phage therapy and antimicrobial peptides, may offer new approaches to treating bacterial infections. * Vaccines: Vaccines may play a critical role in preventing bacterial infections and reducing the need for antibiotics.What is the 5 Z Pack used for?
+The 5 Z Pack is used to treat a range of bacterial infections, including respiratory tract infections, skin infections, and sexually transmitted infections.
How does the 5 Z Pack work?
+The 5 Z Pack works by inhibiting the growth of bacteria, ultimately leading to their death. This is achieved through the inhibition of protein synthesis, which is essential for bacterial growth and survival.
What are the common side effects of the 5 Z Pack?
+Common side effects of the 5 Z Pack include gastrointestinal symptoms, allergic reactions, cardiac effects, and other side effects such as dizziness, headache, and fatigue.
Can I take the 5 Z Pack with other medications?
+The 5 Z Pack may interact with other medications, which can affect its efficacy or increase the risk of side effects. It is essential to consult with a healthcare provider before taking the medication with other drugs.
How can I promote antibiotic stewardship?
+Promoting antibiotic stewardship involves responsible prescribing, patient education, and surveillance. Patients should only take antibiotics when necessary and in accordance with guidelines, and healthcare providers should educate patients on the proper use of antibiotics and the risks associated with their misuse.
As we conclude our exploration of the 5 Z Pack, it is essential to remember that antibiotics are powerful medications that should be used responsibly. By understanding the benefits, working mechanisms, and potential risks associated with the 5 Z Pack, patients can make informed decisions about their treatment and promote antibiotic stewardship. We encourage readers to share their thoughts and experiences with the 5 Z Pack, and to take an active role in promoting responsible antibiotic use. Together, we can work towards a future where antibiotics are used effectively and safely, and where the development of antibiotic resistance is slowed.
