Intro
Reflux, commonly known as acid reflux, is a condition where stomach acid flows back into the esophagus, causing discomfort and pain. While it is often associated with heartburn, reflux can also be a sign of a more serious condition, such as a heart attack. Recognizing the signs of a reflux-related heart attack is crucial for prompt medical attention and treatment. In this article, we will explore the importance of identifying reflux heart attack signs, the relationship between reflux and heart health, and provide guidance on what to do if you experience these symptoms.
The connection between reflux and heart health is complex, and research suggests that there may be a link between the two. Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD), a chronic form of reflux, has been linked to an increased risk of heart disease, including heart attacks. This may be due to the fact that GERD can cause inflammation and damage to the esophagus, which can lead to the release of chemicals that narrow blood vessels and increase blood pressure, both of which can contribute to heart disease.
Understanding the signs of a reflux-related heart attack is essential for seeking medical help quickly. Unlike traditional heart attack symptoms, such as chest pain and shortness of breath, reflux heart attack signs can be more subtle and may be mistaken for other conditions. It is crucial to be aware of these signs and take them seriously, as prompt medical attention can significantly improve outcomes.
Introduction to Reflux Heart Attack Signs
Understanding the Relationship Between Reflux and Heart Health
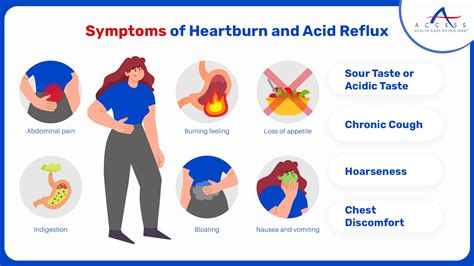
The relationship between reflux and heart health is complex, and research is ongoing to understand the link between the two. Studies have shown that people with GERD are more likely to develop heart disease, including heart attacks, than those without the condition. This may be due to the chronic inflammation and damage caused by GERD, which can lead to the release of chemicals that narrow blood vessels and increase blood pressure.Common Reflux Heart Attack Signs
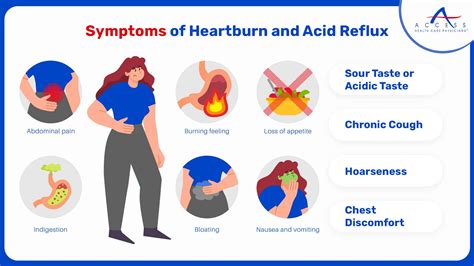
Less Common Reflux Heart Attack Signs
There are also some less common reflux heart attack signs to look out for. These may include: * Pain or discomfort in the arms, back, neck, jaw, or stomach: This can be a symptom of a heart attack, especially if it is accompanied by chest pain or discomfort. * Feeling weak, lightheaded, or faint: These symptoms can be caused by a variety of conditions, including GERD, but they can also be a sign of a heart attack. * Cold sweats: This can be a symptom of a heart attack, especially if it is accompanied by chest pain or discomfort.Risk Factors for Reflux Heart Attack
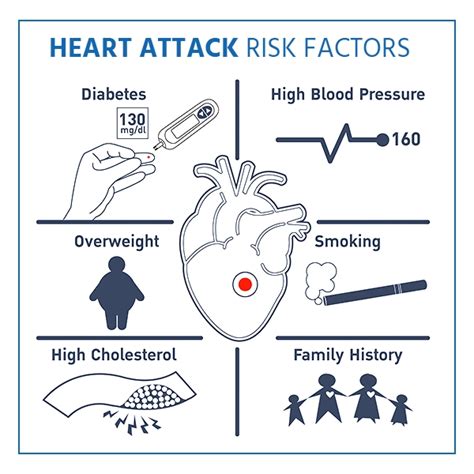
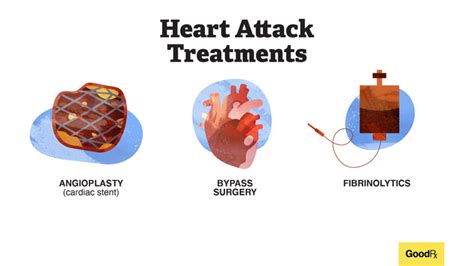
Reducing the Risk of Reflux Heart Attack
There are several ways to reduce the risk of reflux heart attack, including: * Maintaining a healthy weight: Excess weight can increase the risk of heart disease, and it can also increase the risk of a heart attack. * Eating a healthy diet: A diet that is low in saturated fats, trans fats, and cholesterol can help reduce the risk of heart disease, and it can also reduce the risk of a heart attack. * Getting regular exercise: Regular exercise can help reduce the risk of heart disease, and it can also reduce the risk of a heart attack. * Managing stress: Stress can increase the risk of heart disease, and it can also increase the risk of a heart attack.Treatment Options for Reflux Heart Attack
Seeking Medical Attention
If you experience any of the symptoms of a reflux heart attack, it is essential to seek medical attention immediately. Call emergency services or go to the emergency room if you experience: * Chest pain or discomfort that lasts for more than a few minutes * Pain or discomfort in the arms, back, neck, jaw, or stomach * Shortness of breath or difficulty breathing * Feeling weak, lightheaded, or faint * Cold sweatsConclusion and Next Steps

We encourage you to share your thoughts and experiences with reflux heart attack signs in the comments below. If you have any questions or concerns, please don't hesitate to ask. By working together, we can raise awareness about the importance of recognizing reflux heart attack signs and promote heart health.
What are the common symptoms of a reflux heart attack?
+The common symptoms of a reflux heart attack include chest pain or discomfort, nausea and vomiting, difficulty swallowing, and shortness of breath.
How can I reduce the risk of a reflux heart attack?
+You can reduce the risk of a reflux heart attack by maintaining a healthy weight, eating a healthy diet, getting regular exercise, and managing stress.
What should I do if I experience symptoms of a reflux heart attack?
+If you experience symptoms of a reflux heart attack, seek medical attention immediately. Call emergency services or go to the emergency room if you experience chest pain or discomfort, pain or discomfort in the arms, back, neck, jaw, or stomach, shortness of breath or difficulty breathing, feeling weak, lightheaded, or faint, or cold sweats.
