Intro
Discover AIDS symptoms, signs, and stages. Learn about HIV infection, diagnosis, and treatment options, managing opportunistic infections and related health issues.
The human immunodeficiency virus, commonly known as HIV, is a serious health concern that affects millions of people worldwide. One of the most significant consequences of HIV infection is the development of acquired immunodeficiency syndrome, or AIDS. Understanding the symptoms of AIDS is crucial for early detection, treatment, and management of the disease. In this article, we will delve into the world of AIDS symptoms, exploring the various signs and indicators that can help individuals and healthcare professionals identify and address the condition.
The importance of recognizing AIDS symptoms cannot be overstated. As the disease progresses, the immune system becomes increasingly compromised, making it more challenging for the body to fight off infections and diseases. By being aware of the symptoms of AIDS, individuals can seek medical attention promptly, reducing the risk of complications and improving treatment outcomes. Furthermore, early detection and treatment can significantly slow down the progression of the disease, enabling people living with HIV to lead longer, healthier lives.
AIDS symptoms can vary widely from person to person, and not everyone will experience all of the signs and indicators. However, there are several common symptoms that are often associated with the disease. These include recurring fevers, night sweats, and unexplained weight loss, as well as skin rashes, sores, and lesions. Additionally, people with AIDS may experience persistent diarrhea, coughing, and shortness of breath, as well as neurological problems such as confusion, memory loss, and difficulty concentrating.
AIDS Symptoms Overview
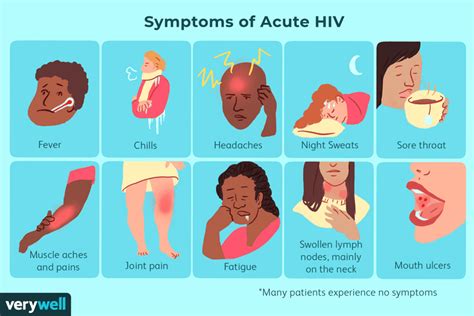
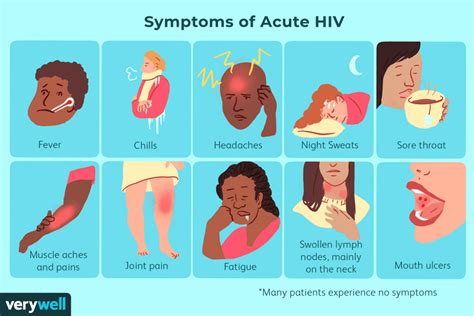
To better understand the symptoms of AIDS, it's essential to consider the various stages of the disease. The initial stage, known as acute HIV infection, typically occurs within 2-4 weeks after exposure to the virus. During this stage, individuals may experience flu-like symptoms, such as fever, headache, and fatigue, as well as swollen lymph nodes and a rash. As the disease progresses to the clinical latency stage, the symptoms may subside, and the individual may not exhibit any noticeable signs of illness. However, this stage can last for many years, during which time the virus is still active and can be transmitted to others.
Early Signs Of AIDS
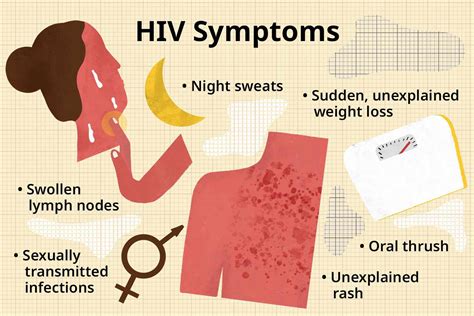
The early signs of AIDS can be subtle and may resemble those of other illnesses. Some common early symptoms include persistent fatigue, unexplained weight loss, and recurring fevers. Individuals may also experience skin problems, such as rashes, sores, and lesions, as well as hair loss and nail changes. Additionally, people with AIDS may develop respiratory issues, such as coughing, shortness of breath, and pneumonia, as well as gastrointestinal problems, including diarrhea, nausea, and vomiting.
AIDS Symptoms In Women
AIDS symptoms in women can be similar to those experienced by men, but there are some key differences. Women with AIDS may be more likely to experience vaginal yeast infections, pelvic inflammatory disease, and cervical cancer. They may also be at higher risk for pregnancy complications, such as miscarriage, premature birth, and low birth weight. Furthermore, women with AIDS may experience changes in their menstrual cycle, including irregular periods, heavy bleeding, and amenorrhea.AIDS Symptoms In Children
AIDS symptoms in children can be particularly challenging to diagnose, as they may not always exhibit noticeable signs of illness. However, some common symptoms in children with AIDS include recurring infections, such as pneumonia and ear infections, as well as developmental delays and growth problems. Children with AIDS may also experience neurological issues, such as seizures, developmental delays, and learning disabilities. Additionally, they may be at higher risk for opportunistic infections, such as tuberculosis and toxoplasmosis.
Treatment And Management Of AIDS Symptoms
The treatment and management of AIDS symptoms typically involve a combination of antiretroviral therapy (ART) and other medications. ART helps to slow down the progression of the disease by reducing the viral load and boosting the immune system. Other medications may be prescribed to treat specific symptoms, such as opportunistic infections, skin problems, and gastrointestinal issues. Additionally, lifestyle changes, such as maintaining a healthy diet, exercising regularly, and getting enough sleep, can help to manage AIDS symptoms and improve overall health.Living With AIDS

Living with AIDS requires a comprehensive approach that incorporates medical treatment, lifestyle changes, and emotional support. Individuals with AIDS must work closely with their healthcare providers to manage their symptoms, prevent complications, and maintain their overall health. This may involve regular blood tests, medication adherence, and lifestyle modifications, such as quitting smoking, reducing stress, and getting enough exercise. Furthermore, people with AIDS may benefit from counseling, support groups, and other resources that can help them cope with the emotional and psychological aspects of the disease.
Prevention And Education
Prevention and education are critical components of AIDS management. By understanding the risks and consequences of HIV infection, individuals can take steps to protect themselves and others. This includes practicing safe sex, using condoms, and avoiding shared needles and other equipment. Additionally, getting tested for HIV and knowing one's status can help to prevent the transmission of the disease. Education and awareness campaigns can also help to reduce stigma and promote a better understanding of AIDS and HIV.AIDS Research And Developments

AIDS research and developments are ongoing, with scientists and healthcare professionals working tirelessly to improve our understanding of the disease and develop more effective treatments. Recent advances in antiretroviral therapy have significantly improved the management of AIDS, enabling people with HIV to live longer, healthier lives. Additionally, researchers are exploring new approaches to HIV prevention, including vaccines, microbicides, and pre-exposure prophylaxis (PrEP). These developments offer hope for a future where AIDS is no longer a life-threatening disease.
Global Efforts To Combat AIDS
Global efforts to combat AIDS are crucial for reducing the spread of the disease and improving the lives of people affected by it. International organizations, governments, and non-profit groups are working together to provide access to HIV testing, treatment, and care, as well as to promote education, awareness, and prevention. These efforts include initiatives to reduce stigma, increase funding for AIDS research and programs, and improve access to healthcare services, particularly in low- and middle-income countries.AIDS Awareness And Education

AIDS awareness and education are essential for preventing the spread of the disease and promoting a better understanding of HIV and AIDS. By educating individuals about the risks and consequences of HIV infection, we can empower them to make informed decisions about their health and well-being. Additionally, awareness campaigns can help to reduce stigma and promote a more supportive and inclusive environment for people living with HIV and AIDS.
Conclusion And Final Thoughts
In conclusion, AIDS symptoms are a critical aspect of the disease that requires attention, understanding, and management. By recognizing the signs and indicators of AIDS, individuals can seek medical attention promptly, reducing the risk of complications and improving treatment outcomes. Furthermore, education, awareness, and prevention are essential for combating the spread of HIV and promoting a better understanding of AIDS. As we continue to work towards a future where AIDS is no longer a life-threatening disease, it's essential that we prioritize research, development, and global efforts to combat the disease.What are the early signs of AIDS?
+The early signs of AIDS can include recurring fevers, night sweats, and unexplained weight loss, as well as skin rashes, sores, and lesions.
How is AIDS treated and managed?
+AIDS is typically treated and managed with a combination of antiretroviral therapy (ART) and other medications, as well as lifestyle changes, such as maintaining a healthy diet and exercising regularly.
Can AIDS be prevented?
+Yes, AIDS can be prevented by practicing safe sex, using condoms, and avoiding shared needles and other equipment. Additionally, getting tested for HIV and knowing one's status can help to prevent the transmission of the disease.
We hope that this article has provided you with a comprehensive understanding of AIDS symptoms and the importance of early detection, treatment, and management. If you have any questions or concerns, please don't hesitate to reach out to us. Share this article with your friends and family to help raise awareness about AIDS and promote a better understanding of the disease. Together, we can work towards a future where AIDS is no longer a life-threatening disease.
