Intro
Identify obstructed bowel symptoms, including abdominal pain, constipation, and vomiting. Learn about intestinal blockage causes, diagnosis, and treatment options for this serious condition.
Obstructed bowel symptoms can be a sign of a serious underlying condition that requires prompt medical attention. The bowel, also known as the intestine, plays a vital role in the digestive system by absorbing nutrients from the food we eat and eliminating waste products. When the bowel becomes obstructed, it can lead to a range of symptoms that can be uncomfortable, painful, and even life-threatening if left untreated. In this article, we will delve into the importance of recognizing obstructed bowel symptoms, their causes, and the available treatment options.
The symptoms of a bowel obstruction can vary depending on the location and severity of the blockage. Common symptoms include abdominal pain, nausea, vomiting, constipation, and bloating. In some cases, the obstruction can cause the bowel to rupture, leading to peritonitis, a potentially life-threatening infection of the abdominal cavity. It is essential to seek medical attention immediately if you experience any of these symptoms, as prompt treatment can help prevent complications and improve outcomes.
Bowel obstructions can occur in anyone, regardless of age or health status. However, certain individuals are more prone to developing this condition, including those with a history of abdominal surgery, inflammatory bowel disease, or cancer. Additionally, people who have a family history of bowel obstruction or have experienced previous episodes of bowel obstruction are at a higher risk of developing the condition again. Recognizing the symptoms of a bowel obstruction and seeking medical attention promptly can help prevent serious complications and improve treatment outcomes.
Causes of Bowel Obstruction
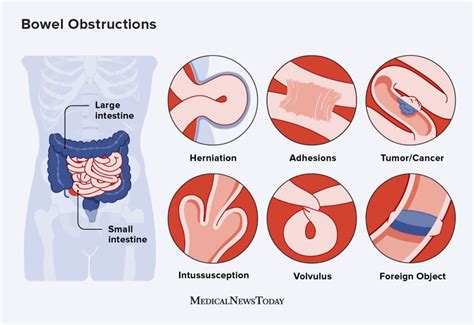
Bowel obstructions can be caused by a variety of factors, including mechanical and non-mechanical causes. Mechanical causes of bowel obstruction include adhesions, hernias, tumors, and volvulus, which can physically block the flow of food, fluid, and gas through the intestine. Non-mechanical causes, on the other hand, include conditions such as inflammatory bowel disease, intestinal pseudo-obstruction, and neurogenic bowel, which can affect the motility and function of the bowel. Understanding the underlying cause of a bowel obstruction is crucial for developing an effective treatment plan.
Types of Bowel Obstruction
Bowel obstructions can be classified into different types, depending on the location and nature of the blockage. The most common types of bowel obstruction include small bowel obstruction, large bowel obstruction, and partial bowel obstruction. Small bowel obstruction occurs when the small intestine is blocked, while large bowel obstruction occurs when the large intestine is blocked. Partial bowel obstruction, on the other hand, occurs when the bowel is only partially blocked, allowing some food, fluid, and gas to pass through.Symptoms of Bowel Obstruction
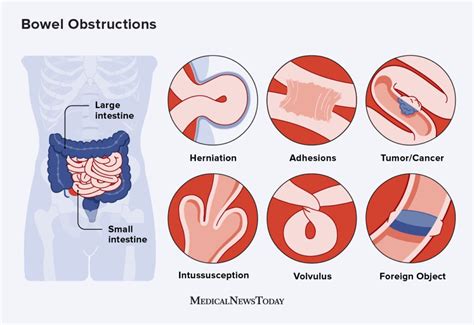
The symptoms of a bowel obstruction can vary depending on the location and severity of the blockage. Common symptoms include:
- Abdominal pain and tenderness
- Nausea and vomiting
- Constipation or inability to pass gas
- Bloating and abdominal distension
- Fever and chills
- Blood in the stool or vomit
In some cases, the symptoms of a bowel obstruction can be mild and may resemble other conditions, such as constipation or irritable bowel syndrome. However, if you experience any of the following symptoms, seek medical attention immediately:
- Severe abdominal pain that worsens over time
- Vomiting blood or black tarry stools
- Fever above 101.5°F (38.6°C)
- Signs of dehydration, such as excessive thirst, dark urine, or dizziness
Diagnosis of Bowel Obstruction
Diagnosing a bowel obstruction typically involves a combination of physical examination, medical history, and diagnostic tests. Your doctor may perform a physical examination to check for abdominal tenderness, distension, and bowel sounds. They may also ask about your medical history, including any previous surgeries, illnesses, or conditions that may have contributed to the obstruction.Diagnostic tests that may be used to diagnose a bowel obstruction include:
- X-rays: to check for any blockages or abnormalities in the bowel
- Computed Tomography (CT) scan: to provide detailed images of the bowel and surrounding tissues
- Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) scan: to provide detailed images of the bowel and surrounding tissues
- Endoscopy: to visually examine the inside of the bowel
Treatment of Bowel Obstruction
The treatment of a bowel obstruction depends on the underlying cause and severity of the condition. In some cases, the obstruction may resolve on its own with minimal treatment, while in other cases, surgery may be necessary to remove the blockage.
Conservative treatment options may include:
- Fluid replacement: to prevent dehydration and electrolyte imbalances
- Nasogastric suction: to remove fluid and gas from the stomach and intestine
- Bowel rest: to allow the bowel to heal and recover
- Medications: to manage pain, nausea, and vomiting
Surgical treatment options may include:
- Laparotomy: to remove the blockage and repair any damage to the bowel
- Bowel resection: to remove the affected portion of the bowel
- Intestinal bypass: to bypass the blocked portion of the bowel
Prevention of Bowel Obstruction
While it is not always possible to prevent a bowel obstruction, there are certain steps you can take to reduce your risk. These include: * Eating a high-fiber diet: to help prevent constipation and promote regular bowel movements * Staying hydrated: to prevent dehydration and electrolyte imbalances * Avoiding foods that can cause blockages: such as seeds, nuts, and popcorn * Managing underlying conditions: such as inflammatory bowel disease or cancer * Seeking medical attention promptly: if you experience any symptoms of a bowel obstructionComplications of Bowel Obstruction
If left untreated, a bowel obstruction can lead to serious complications, including:
- Bowel ischemia: where the bowel tissue dies due to lack of blood supply
- Bowel perforation: where the bowel ruptures, leading to peritonitis
- Sepsis: a life-threatening infection that can occur when bacteria enter the bloodstream
- Malnutrition: due to inadequate nutrition and hydration
- Death: in severe cases, a bowel obstruction can be fatal if left untreated
It is essential to seek medical attention promptly if you experience any symptoms of a bowel obstruction. With prompt treatment, it is possible to prevent complications and improve outcomes.
Living with a Bowel Obstruction
If you have been diagnosed with a bowel obstruction, it is essential to work closely with your healthcare team to manage your condition. This may involve making lifestyle changes, such as eating a high-fiber diet, staying hydrated, and avoiding foods that can cause blockages. It is also important to seek medical attention promptly if you experience any symptoms of a bowel obstruction.In addition to medical treatment, there are several things you can do to manage your condition and prevent complications. These include:
- Keeping a food diary: to track any foods that may trigger symptoms
- Avoiding strenuous activities: that can put pressure on the bowel
- Managing stress: through techniques such as meditation or deep breathing
- Getting enough rest: to allow the bowel to heal and recover
What are the symptoms of a bowel obstruction?
+The symptoms of a bowel obstruction can include abdominal pain, nausea, vomiting, constipation, and bloating. In severe cases, the obstruction can cause the bowel to rupture, leading to peritonitis, a potentially life-threatening infection of the abdominal cavity.
How is a bowel obstruction diagnosed?
+A bowel obstruction is typically diagnosed through a combination of physical examination, medical history, and diagnostic tests, such as X-rays, CT scans, and endoscopy.
What are the treatment options for a bowel obstruction?
+The treatment of a bowel obstruction depends on the underlying cause and severity of the condition. Conservative treatment options may include fluid replacement, nasogastric suction, and bowel rest, while surgical treatment options may include laparotomy, bowel resection, and intestinal bypass.
Can a bowel obstruction be prevented?
+While it is not always possible to prevent a bowel obstruction, there are certain steps you can take to reduce your risk, such as eating a high-fiber diet, staying hydrated, avoiding foods that can cause blockages, managing underlying conditions, and seeking medical attention promptly if you experience any symptoms of a bowel obstruction.
What are the complications of a bowel obstruction?
+If left untreated, a bowel obstruction can lead to serious complications, including bowel ischemia, bowel perforation, sepsis, malnutrition, and death. It is essential to seek medical attention promptly if you experience any symptoms of a bowel obstruction.
In conclusion, obstructed bowel symptoms can be a sign of a serious underlying condition that requires prompt medical attention. Recognizing the symptoms of a bowel obstruction and seeking medical attention promptly can help prevent complications and improve outcomes. By understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatment options for a bowel obstruction, you can take the necessary steps to manage your condition and prevent complications. If you have any further questions or concerns, please do not hesitate to comment below or share this article with others who may be experiencing similar symptoms.
