Intro
Discover normal albumin levels and their importance in health. Learn about albumin tests, low albumin symptoms, and high albumin causes, understanding its role in liver and kidney function, and overall well-being.
Albumin is a type of protein that is found in the blood, and it plays a crucial role in maintaining various bodily functions. Normal albumin levels are essential for overall health, and any deviations from the normal range can indicate underlying health issues. In this article, we will delve into the world of albumin, exploring its importance, functions, and the factors that influence its levels in the blood.
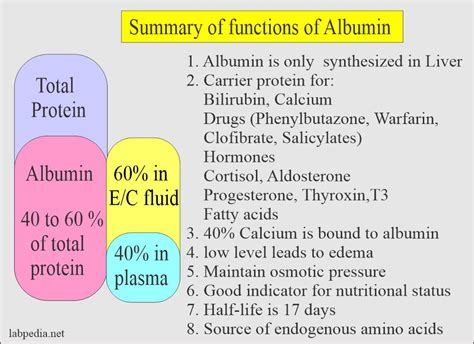
Albumin is produced by the liver and is the most abundant protein in the blood, making up about 50-60% of the total protein content. It is a small, water-soluble protein that is rich in amino acids, which are the building blocks of proteins. Albumin has several important functions, including maintaining blood volume, regulating blood pressure, and transporting various substances such as hormones, vitamins, and minerals throughout the body. Additionally, albumin helps to maintain the balance of fluids between the blood and tissues, which is essential for proper bodily functions.
The importance of normal albumin levels cannot be overstated. Abnormal albumin levels can indicate a range of health issues, including liver disease, kidney disease, and malnutrition. For example, low albumin levels can indicate liver damage or disease, as the liver is responsible for producing albumin. On the other hand, high albumin levels can indicate dehydration or other conditions that cause an increase in blood volume. Therefore, it is essential to maintain normal albumin levels to ensure overall health and well-being.
What are Normal Albumin Levels?
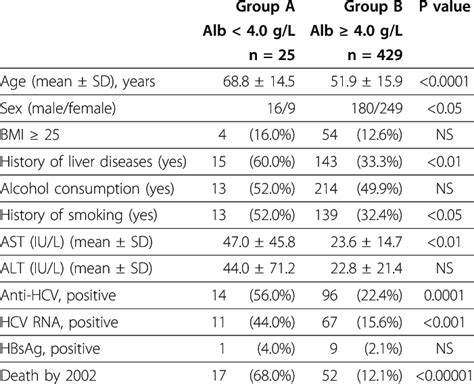
Factors that Influence Albumin Levels
Several factors can influence albumin levels, including: * Liver function: The liver produces albumin, so any liver damage or disease can affect albumin levels. * Kidney function: The kidneys help to regulate albumin levels by removing excess albumin from the blood. * Nutrition: Malnutrition or a diet lacking essential amino acids can affect albumin production. * Age: Albumin levels tend to decrease with age. * Sex: Albumin levels are generally higher in men than in women. * Body mass index (BMI): Albumin levels tend to be lower in individuals with a higher BMI.How are Albumin Levels Measured?
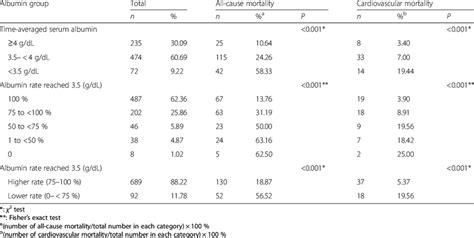
Interpreting Albumin Levels
Interpreting albumin levels requires careful consideration of various factors, including the individual's overall health, medical history, and any underlying conditions. For example, low albumin levels may indicate liver disease or malnutrition, while high albumin levels may indicate dehydration or other conditions that cause an increase in blood volume. It is essential to consult with a healthcare professional to interpret albumin levels and determine the underlying cause of any abnormalities.Consequences of Abnormal Albumin Levels
On the other hand, high albumin levels can lead to:
- Dehydration: High albumin levels can indicate dehydration, which can cause a range of health problems.
- Blood clots: High albumin levels can increase the risk of blood clots, which can lead to serious health problems such as stroke and heart attack.
- Kidney disease: High albumin levels can indicate kidney disease, which can lead to a range of health problems.
Treatment Options for Abnormal Albumin Levels
Treatment options for abnormal albumin levels depend on the underlying cause of the abnormality. For example, if low albumin levels are caused by liver disease, treatment may involve medications to manage liver function, as well as dietary changes to support liver health. If high albumin levels are caused by dehydration, treatment may involve increasing fluid intake and addressing any underlying conditions that may be contributing to dehydration.Prevention and Management of Abnormal Albumin Levels
Lifestyle Changes to Support Healthy Albumin Levels
Lifestyle changes can play a significant role in supporting healthy albumin levels. Some strategies include: * Eating a plant-based diet that is rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains. * Incorporating lean protein sources such as poultry, fish, and legumes into the diet. * Avoiding processed and packaged foods that are high in salt, sugar, and unhealthy fats. * Staying physically active through regular exercise, such as walking, jogging, or swimming. * Managing stress through techniques such as meditation, yoga, or deep breathing exercises.Conclusion and Final Thoughts
We invite you to share your thoughts and experiences with albumin levels in the comments section below. Have you or a loved one experienced abnormal albumin levels? What strategies have you used to prevent and manage abnormal albumin levels? Share your story and help others understand the importance of maintaining healthy albumin levels.
What is the normal range for albumin levels?
+Normal albumin levels typically range from 3.5 to 5.5 grams per deciliter (g/dL) of blood.
What are the consequences of low albumin levels?
+Low albumin levels can lead to edema, fatigue, malnutrition, and increased risk of infection.
How can I prevent and manage abnormal albumin levels?
+Preventing and managing abnormal albumin levels requires a comprehensive approach that incorporates lifestyle changes, dietary modifications, and medical treatment. This may include eating a balanced diet, staying hydrated, managing underlying conditions, and getting regular blood tests.
