Intro
Maintain healthy blood sugar with 5 tips for normal glucose levels, including diet, exercise, and monitoring to prevent diabetes and related health issues like hyperglycemia and hypoglycemia.
Maintaining normal glucose levels is crucial for overall health and wellbeing. Glucose, a type of sugar, is the primary source of energy for the body's cells. When glucose levels are within a normal range, the body functions optimally, and the risk of developing chronic diseases like diabetes and heart disease is minimized. Normal glucose levels are typically between 70 and 140 milligrams per deciliter (mg/dL) for individuals without diabetes, although this range may vary slightly depending on the laboratory or testing method used. For people with diabetes, the goal is often to keep glucose levels as close to the normal range as possible to prevent complications. Understanding how to manage and maintain normal glucose levels is essential for everyone, regardless of their health status.
The importance of maintaining normal glucose levels cannot be overstated. High blood glucose, or hyperglycemia, can lead to serious health issues if left unmanaged. It can cause damage to blood vessels, nerves, and organs, such as the kidneys and eyes. Conversely, low blood glucose, or hypoglycemia, can lead to immediate symptoms like shakiness, dizziness, and confusion, and if severe, can be life-threatening. Therefore, knowing how to keep glucose levels within a healthy range is vital for preventing these complications and ensuring overall health.
Achieving and maintaining normal glucose levels involves a combination of dietary changes, lifestyle modifications, and in some cases, medication. It requires understanding what factors influence glucose levels and making informed choices about diet, physical activity, and stress management. For instance, eating a balanced diet that is low in added sugars, saturated fats, and sodium, and high in fiber, vitamins, and minerals can help regulate glucose levels. Regular physical activity, such as walking, running, or swimming, also plays a critical role in glucose management by improving the body's sensitivity to insulin, the hormone that regulates glucose uptake by cells. Additionally, managing stress through techniques like meditation, yoga, or deep breathing exercises can help mitigate the impact of stress hormones, which can raise glucose levels.
Understanding Glucose Levels

Understanding glucose levels and how they are affected by different factors is the first step towards maintaining normal levels. Glucose levels are influenced by the food we eat, our physical activity levels, stress, and sleep patterns, among other factors. Foods that are high in carbohydrates, especially those with a high glycemic index, can cause a significant increase in glucose levels. Regular monitoring of glucose levels, especially for individuals with diabetes, helps in identifying patterns and making necessary adjustments to diet and lifestyle. Furthermore, understanding the role of insulin and how the body responds to different types of food can guide dietary choices that support glucose management.
Factors Influencing Glucose Levels
Several factors can influence glucose levels, including diet, physical activity, medications, stress, and sleep. Dietary choices, particularly the intake of carbohydrates, have a direct impact on glucose levels. Carbohydrates are broken down into glucose during digestion, and the amount and type of carbohydrates consumed can significantly affect blood glucose levels. Physical activity is another crucial factor; regular exercise improves insulin sensitivity, allowing glucose to enter cells more efficiently. Stress and lack of sleep can also raise glucose levels by stimulating the release of stress hormones like cortisol and adrenaline, which can cause the liver to release stored glucose into the bloodstream.Managing Diet for Normal Glucose Levels

Managing diet is a critical aspect of maintaining normal glucose levels. This involves choosing foods that are less likely to cause a spike in blood glucose. Foods with a low glycemic index, such as whole grains, non-starchy vegetables, and most fruits, are good choices because they are digested slowly and do not cause a rapid increase in glucose levels. Additionally, incorporating foods that are rich in fiber, like legumes, nuts, and seeds, can help slow down the digestion of carbohydrates and improve insulin sensitivity. Limiting the intake of added sugars, saturated fats, and refined carbohydrates is also essential for glucose management.
Benefits of a Balanced Diet
A balanced diet provides numerous benefits for glucose management and overall health. It helps in maintaining a healthy weight, reducing the risk of chronic diseases like heart disease and certain cancers, and supporting healthy blood lipid profiles. A diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins can provide essential nutrients, fiber, and antioxidants that help protect against cell damage and support immune function. Furthermore, a well-planned diet can help manage hunger and reduce cravings for unhealthy snacks, making it easier to maintain a healthy weight and support normal glucose levels.Physical Activity and Glucose Levels

Regular physical activity is another key component of maintaining normal glucose levels. Exercise improves insulin sensitivity, allowing the body to use insulin more efficiently and facilitating the uptake of glucose by cells. This can lead to lower blood glucose levels and improved glucose management. Physical activity also helps with weight management, reduces blood pressure, and improves lipid profiles, all of which are beneficial for reducing the risk of chronic diseases. Activities like brisk walking, cycling, and swimming are excellent choices because they can be done by people of all ages and fitness levels, and they provide a good balance of aerobic exercise and muscle strengthening.
Types of Physical Activity
There are various types of physical activity that can help manage glucose levels, including aerobic exercises, strength training, and high-intensity interval training (HIIT). Aerobic exercises, such as walking, jogging, and cycling, are beneficial for improving cardiovascular health and increasing insulin sensitivity. Strength training, which involves lifting weights or doing bodyweight exercises, can help build muscle mass, further improving insulin sensitivity and glucose uptake by cells. HIIT, which involves short bursts of intense exercise followed by brief periods of rest, has been shown to significantly improve insulin sensitivity and glucose management in a short amount of time.Stress Management and Glucose Levels
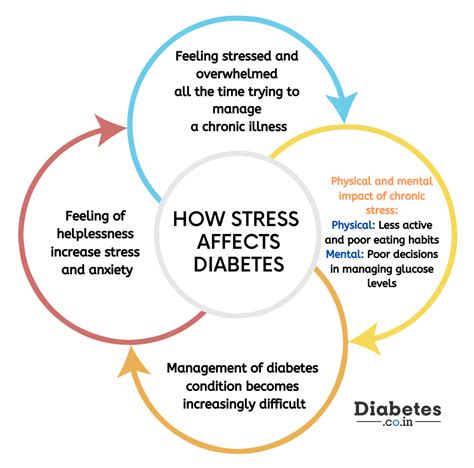
Stress management is also crucial for maintaining normal glucose levels. Chronic stress can lead to increased levels of stress hormones like cortisol, which can raise blood glucose levels by stimulating the release of glucose from stored energy sources into the bloodstream. Engaging in stress-reducing activities, such as meditation, yoga, or deep breathing exercises, can help mitigate the effects of stress on glucose levels. These activities can help reduce the production of stress hormones, improve mood, and enhance overall wellbeing. Additionally, getting enough sleep and practicing relaxation techniques can help manage stress and support glucose management.
Techniques for Stress Reduction
Several techniques can be employed for stress reduction and improved glucose management. Mindfulness meditation, which involves focusing on the present moment and letting go of worries about the past or future, has been shown to reduce stress and improve insulin sensitivity. Yoga, which combines physical movement with deep breathing and meditation techniques, can also help reduce stress and improve glucose levels. Deep breathing exercises, which involve taking slow, deep breaths in through the nose and out through the mouth, can help calm the nervous system and reduce the production of stress hormones.Monitoring and Maintaining Normal Glucose Levels

Monitoring glucose levels regularly is essential for maintaining normal levels and preventing complications. For individuals with diabetes, self-monitoring of blood glucose (SMBG) involves using a glucose meter to check blood glucose levels at different times of the day. This information can be used to adjust diet, physical activity, and medication to keep glucose levels within a target range. Regular health check-ups with a healthcare provider are also important for monitoring glucose levels and assessing the risk of developing complications.
Importance of Regular Health Check-Ups
Regular health check-ups are vital for maintaining overall health and managing glucose levels. During these check-ups, healthcare providers can monitor glucose levels, assess the risk of complications, and provide guidance on diet, physical activity, and stress management. They can also adjust medication as needed and provide referrals to specialists if necessary. Additionally, regular check-ups can help identify any potential health issues early, when they are easier to treat, reducing the risk of long-term complications.Conclusion and Next Steps

In conclusion, maintaining normal glucose levels is a multifaceted process that requires attention to diet, physical activity, stress management, and regular monitoring. By understanding the factors that influence glucose levels and making informed choices, individuals can take proactive steps towards managing their glucose levels and reducing the risk of chronic diseases. Whether through dietary changes, increased physical activity, or stress reduction techniques, there are numerous strategies available for maintaining normal glucose levels. By incorporating these strategies into daily life, individuals can improve their overall health and wellbeing.
What are normal glucose levels?
+Normal glucose levels are typically between 70 and 140 milligrams per deciliter (mg/dL) for individuals without diabetes, although this range may vary slightly depending on the laboratory or testing method used.
How does diet affect glucose levels?
+Diet has a significant impact on glucose levels. Foods high in carbohydrates, especially those with a high glycemic index, can cause a rapid increase in glucose levels. Choosing foods with a low glycemic index, such as whole grains, non-starchy vegetables, and most fruits, can help regulate glucose levels.
What role does physical activity play in glucose management?
+Regular physical activity improves insulin sensitivity, allowing the body to use insulin more efficiently and facilitating the uptake of glucose by cells. This can lead to lower blood glucose levels and improved glucose management.
We hope this article has provided you with valuable insights and practical tips for maintaining normal glucose levels. By applying these strategies and making informed choices, you can take control of your health and wellbeing. If you have any further questions or would like to share your experiences, please do not hesitate to comment below. Your feedback is invaluable, and we look forward to hearing from you. Additionally, if you found this article helpful, please consider sharing it with others who may benefit from this information. Together, we can support each other in our journey towards better health and wellbeing.
