Intro
Learn about alcohol withdrawal symptoms, including tremors, seizures, and delirium tremens, and understand the treatment options for managing withdrawal syndrome and alcohol dependence.
Alcohol withdrawal symptoms are a common occurrence for individuals who have been consuming alcohol heavily over a prolonged period and then suddenly stop or significantly reduce their intake. The symptoms can range from mild to severe and can be life-threatening in extreme cases. It is essential to understand the importance of addressing alcohol withdrawal symptoms to ensure a safe and successful recovery.
The severity and duration of alcohol withdrawal symptoms depend on various factors, including the amount and frequency of alcohol consumption, the duration of alcohol use, and the individual's overall health. Some people may experience mild symptoms, while others may face more severe and potentially life-threatening complications. It is crucial to recognize the signs and symptoms of alcohol withdrawal to provide timely and appropriate medical attention.
Alcohol withdrawal symptoms can be a significant obstacle to overcoming alcohol addiction. The fear of experiencing these symptoms can prevent individuals from seeking help and quitting drinking. However, with the right treatment and support, it is possible to manage alcohol withdrawal symptoms and achieve long-term sobriety. In this article, we will delve into the world of alcohol withdrawal symptoms, exploring their causes, symptoms, treatment options, and recovery strategies.
Causes of Alcohol Withdrawal Symptoms
The causes of alcohol withdrawal symptoms can be attributed to several factors, including:
- Prolonged and heavy alcohol consumption
- Sudden cessation or reduction of alcohol intake
- Individual tolerance and sensitivity to alcohol
- Underlying medical conditions, such as liver disease or mental health disorders
- Genetic predisposition to alcohol addiction
Factors Influencing Alcohol Withdrawal Symptoms
The severity and duration of alcohol withdrawal symptoms can be influenced by various factors, including: * Age: Older individuals may experience more severe symptoms due to decreased liver function and increased sensitivity to alcohol. * Sex: Women may be more susceptible to severe withdrawal symptoms due to differences in body composition and hormone levels. * Medical history: Pre-existing medical conditions, such as liver disease or mental health disorders, can exacerbate withdrawal symptoms. * Alcohol consumption patterns: The amount, frequency, and duration of alcohol consumption can impact the severity of withdrawal symptoms.Symptoms of Alcohol Withdrawal
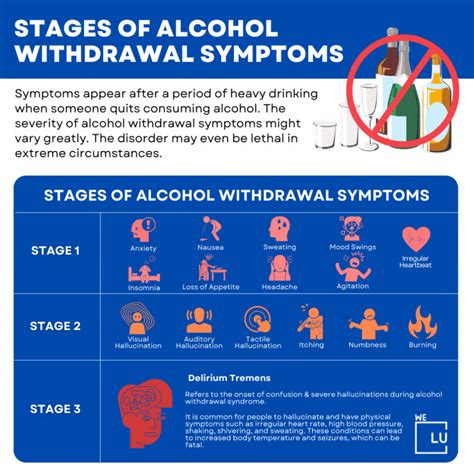
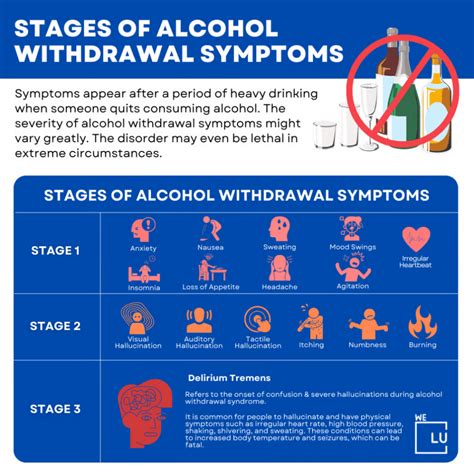
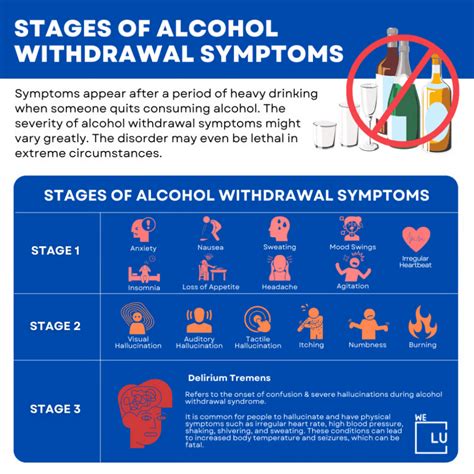
Mild symptoms of alcohol withdrawal may include:
- Anxiety and restlessness
- Insomnia and vivid dreams
- Tremors and shakiness
- Nausea and vomiting
- Headaches and fatigue
Moderate symptoms of alcohol withdrawal may include:
- Increased heart rate and blood pressure
- Sweating and fever
- Irritability and mood swings
- Confusion and disorientation
- Hallucinations and delusions
Severe symptoms of alcohol withdrawal may include:
- Seizures and convulsions
- Delirium tremens (DTs), characterized by severe confusion, hallucinations, and agitation
- Cardiovascular complications, such as heart attack or stroke
- Respiratory failure
- Death
Treatment Options for Alcohol Withdrawal
Treatment for alcohol withdrawal symptoms typically involves a combination of medical and therapeutic interventions. The primary goal of treatment is to manage symptoms, prevent complications, and support long-term recovery.Medical treatment for alcohol withdrawal may include:
- Benzodiazepines, such as diazepam or lorazepam, to manage symptoms and prevent seizures
- Anti-seizure medications, such as carbamazepine or valproate, to prevent seizures
- Beta blockers, such as propranolol, to manage cardiovascular symptoms
- Clonidine, an alpha-2 adrenergic agonist, to manage hypertension and anxiety
Therapeutic interventions for alcohol withdrawal may include:
- Counseling and psychotherapy to address underlying issues and promote coping skills
- Support groups, such as Alcoholics Anonymous (AA), to provide social support and encouragement
- Cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) to address negative thought patterns and behaviors
- Family therapy to educate and support loved ones
Recovery Strategies for Alcohol Withdrawal

- Seek medical attention: Consult a healthcare professional for guidance and support throughout the recovery process.
- Join a support group: Participate in support groups, such as AA, to connect with others who have experienced similar challenges.
- Practice self-care: Engage in activities that promote relaxation and stress reduction, such as meditation, yoga, or deep breathing exercises.
- Develop a relapse prevention plan: Identify triggers and develop strategies to manage cravings and prevent relapse.
- Build a support network: Surround yourself with positive and supportive individuals who encourage and motivate you to maintain sobriety.
Preventing Relapse
Preventing relapse is crucial to maintaining long-term sobriety. The following strategies can help prevent relapse: * Identify triggers: Recognize situations, emotions, and people that may trigger cravings or relapse. * Develop coping skills: Learn healthy coping mechanisms, such as mindfulness, exercise, or creative activities, to manage stress and emotions. * Stay connected: Maintain regular contact with support groups, therapists, and loved ones to ensure ongoing support and encouragement. * Monitor progress: Regularly assess progress and adjust recovery strategies as needed.Conclusion and Next Steps
If you or someone you know is struggling with alcohol addiction, it is essential to seek medical attention and support. Consult a healthcare professional for guidance and treatment, and consider joining a support group to connect with others who have experienced similar challenges. Remember, recovery is a journey, and it is possible to overcome alcohol withdrawal symptoms and achieve a healthier, happier life.
We invite you to share your thoughts and experiences with alcohol withdrawal symptoms in the comments below. Your insights and stories can help others who are struggling with addiction and inspire hope and motivation for recovery.
What are the symptoms of alcohol withdrawal?
+The symptoms of alcohol withdrawal can range from mild to severe and include anxiety, tremors, nausea, vomiting, headaches, and fatigue. In severe cases, symptoms can include seizures, delirium tremens, and cardiovascular complications.
How long do alcohol withdrawal symptoms last?
+The duration of alcohol withdrawal symptoms can vary depending on the individual and the severity of symptoms. Mild symptoms can last for several days, while severe symptoms can persist for several weeks or even months.
Can I manage alcohol withdrawal symptoms at home?
+While some individuals may be able to manage mild alcohol withdrawal symptoms at home, it is generally recommended to seek medical attention to ensure safe and effective treatment. Severe symptoms can be life-threatening and require immediate medical attention.
What are the treatment options for alcohol withdrawal?
+Treatment options for alcohol withdrawal may include medication, such as benzodiazepines or anti-seizure medications, and therapeutic interventions, such as counseling and support groups. The primary goal of treatment is to manage symptoms, prevent complications, and support long-term recovery.
How can I prevent relapse after alcohol withdrawal?
+Preventing relapse requires a comprehensive approach that includes identifying triggers, developing coping skills, staying connected with support groups, and monitoring progress. It is also essential to maintain regular contact with healthcare professionals and therapists to ensure ongoing support and encouragement.
