Intro
Discover 5 surprising Smz Tmp facts, exploring its tmp file uses, tmp folder management, and tmp data storage, to enhance your understanding of temporary files and system performance optimization.
The world of antibiotics is vast and complex, with numerous medications designed to combat various bacterial infections. Among these, Sulfamethoxazole/Trimethoprim, commonly referred to as SMZ/TMP, stands out as a widely prescribed antibiotic. Its effectiveness against a broad spectrum of bacterial infections makes it a crucial component of modern medicine. Understanding SMZ/TMP is essential for both medical professionals and patients alike, as it can significantly impact treatment outcomes and patient care.
SMZ/TMP has been a cornerstone in the treatment of bacterial infections for decades. Its popularity stems from its efficacy, relatively low cost, and the convenience of oral administration. However, like all medications, SMZ/TMP comes with its own set of benefits and risks. It's crucial for individuals to be informed about this antibiotic to ensure safe and effective use. Whether you're a healthcare provider looking to prescribe SMZ/TMP or a patient considering this treatment, understanding its mechanisms, benefits, and potential side effects is vital.
The importance of SMZ/TMP in modern medicine cannot be overstated. It has played a significant role in managing and treating various infections, from urinary tract infections to more severe conditions like pneumonia. Its broad-spectrum activity allows it to target a wide range of bacteria, making it a versatile option for healthcare providers. Moreover, the combination of sulfamethoxazole and trimethoprim works synergistically, enhancing its bactericidal effects. This synergy is key to its effectiveness and is a significant factor in its widespread use.
Introduction to SMZ/TMP

Benefits of SMZ/TMP

Common Uses of SMZ/TMP
SMZ/TMP is commonly used to treat urinary tract infections, ear infections, bronchitis, traveler's diarrhea, methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) skin infections, and pneumonia. Its broad-spectrum activity makes it an effective choice for infections where the causative agent is not yet identified. However, the use of SMZ/TMP should always be guided by susceptibility testing to ensure the bacteria are sensitive to the antibiotic.Working Mechanism of SMZ/TMP
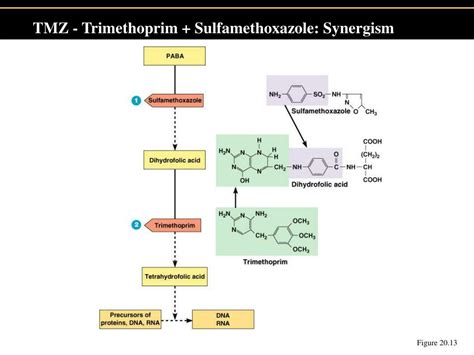
Resistance to SMZ/TMP
Resistance to SMZ/TMP is a growing concern. Bacteria can develop resistance through several mechanisms, including alterations in the target enzymes, decreased uptake of the drug, or increased efflux of the drug from the cell. The use of SMZ/TMP should be judicious and based on susceptibility testing to minimize the development of resistance.Side Effects and Precautions

Contraindications and Precautions
SMZ/TMP is contraindicated in patients with a known hypersensitivity to sulfonamides or trimethoprim. It should be used with caution in patients with renal or hepatic impairment, as it can exacerbate these conditions. Patients with glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase (G6PD) deficiency are at risk of hemolysis and should be monitored closely.Administration and Dosage

Special Considerations
In patients with renal impairment, the dose of SMZ/TMP may need to be adjusted to prevent accumulation of the drug. Similarly, in patients with hepatic impairment, close monitoring is required due to the potential for increased levels of the drug.Interaction with Other Medications
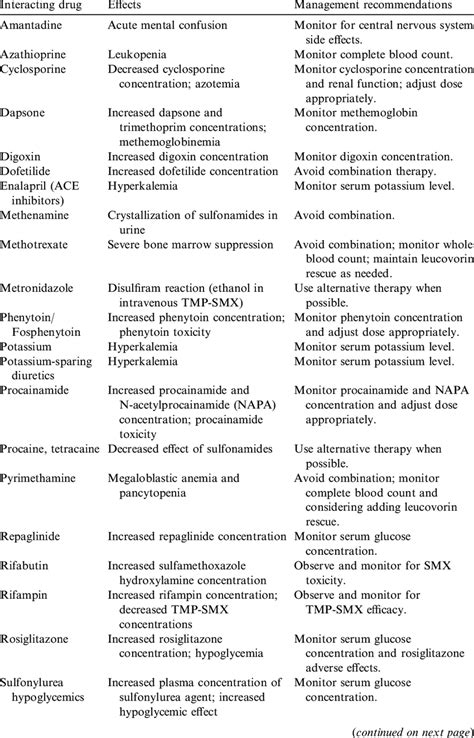
Monitoring and Follow-Up
Patients taking SMZ/TMP should be monitored for signs of side effects and for the effectiveness of the treatment. Regular follow-up appointments with a healthcare provider are essential to adjust the treatment regimen as needed and to manage any complications that may arise.Conclusion and Future Perspectives

As we move forward, it's essential to continue researching and understanding the mechanisms of action of antibiotics like SMZ/TMP, as well as the mechanisms of resistance. This knowledge will be crucial in the development of strategies to combat antibiotic resistance and ensure the continued effectiveness of these life-saving medications.
What is SMZ/TMP used for?
+SMZ/TMP is used to treat various bacterial infections, including urinary tract infections, ear infections, bronchitis, traveler's diarrhea, and pneumonia.
How does SMZ/TMP work?
+SMZ/TMP works by inhibiting the production of tetrahydrofolic acid, which is essential for bacterial DNA synthesis and cell division.
What are the common side effects of SMZ/TMP?
+Common side effects include nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, and rash. More severe side effects can include Stevens-Johnson syndrome and severe hypersensitivity reactions.
We invite you to share your thoughts and questions about SMZ/TMP in the comments below. Your engagement is valuable in creating a community that promotes the safe and effective use of antibiotics. If you found this article informative, please consider sharing it with others who might benefit from this information. Together, we can work towards a better understanding of antibiotics and their role in modern medicine.
