Intro
The human body is a complex system, comprising various enzymes that play crucial roles in maintaining overall health. One such enzyme is alkaline phosphatase, which is found in multiple tissues throughout the body. Alkaline phosphatase is a vital enzyme that facilitates various physiological processes, and its dysfunction can lead to several health issues. Understanding the function of alkaline phosphatase is essential for appreciating its significance in human health and disease.
Alkaline phosphatase is an enzyme that catalyzes the hydrolysis of phosphate esters, removing phosphate groups from various molecules. This enzyme is present in high concentrations in the liver, bones, kidneys, and intestines, where it performs distinct functions. In the liver, alkaline phosphatase is involved in the metabolism of bile acids, lipids, and other nutrients. In the bones, it plays a crucial role in bone mineralization and the formation of hydroxyapatite, a key component of bone tissue.
The importance of alkaline phosphatase cannot be overstated, as it is involved in numerous physiological processes that are essential for maintaining overall health. For instance, alkaline phosphatase helps regulate the levels of phosphate and calcium in the body, which is critical for maintaining strong bones and teeth. Additionally, this enzyme is involved in the metabolism of various nutrients, including lipids, carbohydrates, and proteins. Dysregulation of alkaline phosphatase activity has been implicated in several diseases, including osteoporosis, liver disease, and kidney disease.
Introduction to Alkaline Phosphatase
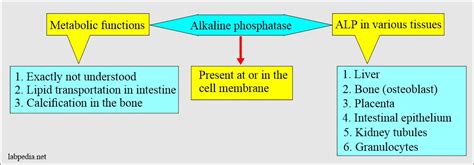
Structure and Function of Alkaline Phosphatase
The structure of alkaline phosphatase is characterized by a homodimeric arrangement, with each subunit consisting of a large and small domain. The large domain contains the active site, while the small domain is involved in substrate recognition. The enzyme undergoes a conformational change upon binding to its substrate, which facilitates the hydrolysis of phosphate esters.Physiological Roles of Alkaline Phosphatase
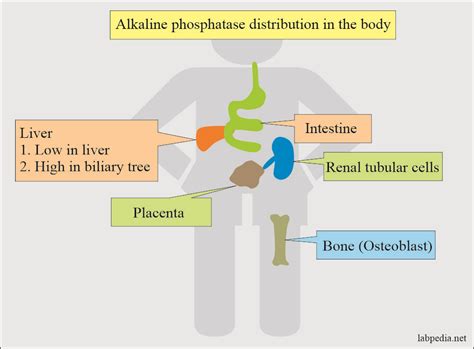
Regulation of Alkaline Phosphatase Activity
The activity of alkaline phosphatase is regulated by various mechanisms, including: * Hormonal regulation: Hormones such as parathyroid hormone and vitamin D regulate the expression and activity of alkaline phosphatase. * Substrate availability: The availability of phosphate esters can regulate the activity of alkaline phosphatase. * Inhibitors: Certain compounds, such as levamisole, can inhibit the activity of alkaline phosphatase.Clinical Significance of Alkaline Phosphatase

Measurement of Alkaline Phosphatase Activity
The activity of alkaline phosphatase can be measured using various assays, including: * Colorimetric assays: These assays measure the hydrolysis of phosphate esters, resulting in a color change. * Fluorometric assays: These assays measure the hydrolysis of phosphate esters, resulting in the production of a fluorescent product. * Electrophoretic assays: These assays separate and detect alkaline phosphatase isoforms based on their charge and size.Alkaline Phosphatase Isoforms
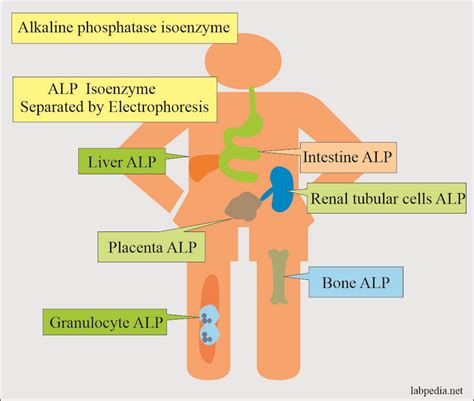
Alkaline Phosphatase Deficiency
Deficiency of alkaline phosphatase can lead to various health issues, including: * Hypophosphatasia: A rare genetic disorder characterized by low levels of alkaline phosphatase. * Osteomalacia: A condition characterized by softening of the bones due to impaired mineralization.Alkaline Phosphatase Inhibitors
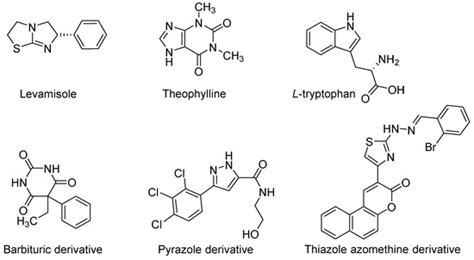
Alkaline Phosphatase Activators
Alkaline phosphatase activators are compounds that can increase the activity of alkaline phosphatase. These activators include: * Magnesium ions: Magnesium ions can increase the activity of alkaline phosphatase. * Zinc ions: Zinc ions can increase the activity of alkaline phosphatase.Alkaline Phosphatase in Disease Diagnosis
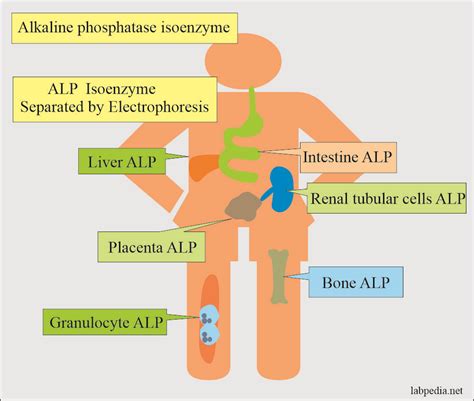
Alkaline Phosphatase in Cancer Diagnosis
Alkaline phosphatase is also used in cancer diagnosis, as its levels can indicate the presence of certain types of cancer. Elevated levels of alkaline phosphatase have been associated with: * Osteosarcoma: A type of bone cancer that can cause elevated levels of alkaline phosphatase. * Hepatocellular carcinoma: A type of liver cancer that can cause elevated levels of alkaline phosphatase.What is alkaline phosphatase?
+Alkaline phosphatase is a hydrolase enzyme that catalyzes the removal of phosphate groups from various molecules.
What are the physiological roles of alkaline phosphatase?
+Alkaline phosphatase plays a vital role in various physiological processes, including bone mineralization, liver function, kidney function, and intestinal function.
What are the clinical significance of alkaline phosphatase?
+Alkaline phosphatase is a clinically significant enzyme, as its dysfunction can lead to various health issues, including liver disease, bone disease, and kidney disease.
In summary, alkaline phosphatase is a vital enzyme that plays a crucial role in various physiological processes. Its dysfunction can lead to several health issues, and its levels can indicate the presence of certain diseases. Understanding the function and regulation of alkaline phosphatase is essential for appreciating its significance in human health and disease. We encourage readers to share their thoughts and experiences with alkaline phosphatase in the comments section below. Additionally, we invite readers to explore other articles on our website that discuss the importance of enzymes in human health and disease. By working together, we can gain a deeper understanding of the complex mechanisms that govern human health and develop effective strategies for preventing and treating diseases.
