Intro
Discover key facts about Amlodipine, a blood pressure medication, including its uses, side effects, and interactions, to manage hypertension and cardiovascular health effectively.
As one of the most widely prescribed medications globally, amlodipine has become a household name for individuals dealing with hypertension and coronary artery disease. Its efficacy in managing these conditions has made it a staple in many treatment plans. However, beyond its common use, there lies a wealth of information about amlodipine that can help patients and healthcare providers alike understand its benefits, potential side effects, and how it works. Let's delve into the world of amlodipine, exploring its mechanism of action, benefits, and what patients can expect when taking this medication.
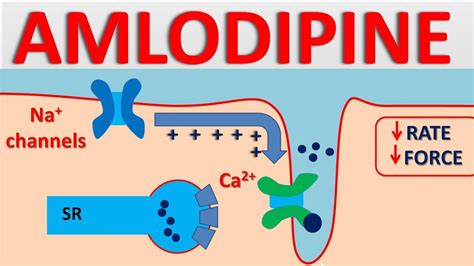
Amlodipine belongs to a class of drugs known as calcium channel blockers. These medications work by inhibiting the influx of calcium ions into smooth muscle cells and cardiac muscles. By doing so, amlodipine helps to relax and widen blood vessels, reducing blood pressure and increasing oxygen supply to the heart. This dual action not only helps in managing hypertension but also in alleviating symptoms of angina by reducing the heart's workload.
The importance of understanding how amlodipine works cannot be overstated. For patients, knowing the mechanism behind their medication can empower them to take a more active role in their healthcare. It also underscores the potential benefits of amlodipine, such as its ability to reduce the risk of cardiovascular events when used as part of a comprehensive treatment plan. Furthermore, recognizing the potential side effects, which can include edema, dizziness, and palpitations, allows for better management and minimization of these effects.
Amlodipine's Mechanism of Action
Benefits of Amlodipine
The benefits of amlodipine are multifaceted, making it a valuable addition to the treatment regimen of patients with hypertension and coronary artery disease. Some of the key benefits include: - **Reduced Blood Pressure:** Amlodipine's ability to lower blood pressure reduces the risk of stroke, heart attack, and kidney problems. - **Relief from Angina Symptoms:** By improving blood flow to the heart and reducing the heart's workload, amlodipine can help alleviate chest pain associated with angina. - **Improved Exercise Tolerance:** Patients with angina may find that they can perform daily activities and exercise with less discomfort.Side Effects and Precautions

Interactions and Contraindications
Amlodipine can interact with other medications, altering its efficacy or increasing the risk of side effects. Patients should inform their healthcare provider about all medications, including supplements and herbal products, they are taking. Certain medications, such as grapefruit and grapefruit juice, should be avoided as they can significantly increase the levels of amlodipine in the blood.Usage and Dosage

Monitoring and Follow-Up
Regular monitoring of blood pressure and follow-up appointments with the healthcare provider are crucial for patients taking amlodipine. These visits allow for the assessment of the medication's effectiveness and the adjustment of the treatment plan as necessary. Additionally, monitoring can help in the early detection of potential side effects, enabling prompt intervention.Patient Education and Empowerment

Lifestyle Modifications
In addition to medication, adopting a healthy lifestyle can further reduce the risk of cardiovascular events. Recommendations include: - **Dietary Changes:** Consuming a balanced diet low in salt, sugar, and saturated fats. - **Regular Exercise:** Engaging in physical activity, such as walking, for at least 30 minutes a day. - **Stress Management:** Practicing stress-reducing techniques like meditation or yoga. - **Smoking Cessation:** Quitting smoking to reduce cardiovascular risk.Future Directions and Research

Personalized Medicine Approach
The concept of personalized or precision medicine involves tailoring treatment plans to the individual characteristics of each patient. This approach considers genetic factors, lifestyle, and other health conditions to optimize the efficacy and safety of medications like amlodipine. As our understanding of genetics and pharmacogenomics grows, so does the potential for more effective and targeted therapies.Conclusion and Next Steps

We invite you to share your thoughts and experiences with amlodipine in the comments below. Your insights can help others better understand this medication and its role in managing cardiovascular health. Additionally, if you found this article informative, please consider sharing it with others who might benefit from this comprehensive overview of amlodipine.
What is amlodipine used for?
+Amlodipine is primarily used to treat high blood pressure and coronary artery disease. It works by relaxing blood vessels, which helps to lower blood pressure and increase oxygen supply to the heart.
What are the common side effects of amlodipine?
+Common side effects of amlodipine include edema (swelling of the feet, ankles, and hands), dizziness, headache, fatigue, and nausea. If these side effects are severe or bothersome, patients should discuss them with their healthcare provider.
Can I stop taking amlodipine if I feel better?
+No, patients should not stop taking amlodipine without consulting their healthcare provider. Stopping the medication abruptly can lead to a rebound effect, causing blood pressure to spike and potentially leading to serious cardiovascular events.
