Intro
Discover 5 uses of Amlodipine, a calcium channel blocker, for hypertension, angina, coronary artery disease, heart failure, and stroke prevention, exploring its benefits and side effects in cardiovascular health management.
Amlodipine is a medication that has been widely used for several decades to treat various cardiovascular conditions. Its primary function is as a calcium channel blocker, which means it works by relaxing the muscles of the heart and blood vessels. This action helps to improve blood flow and reduce blood pressure, making it an essential drug for managing conditions like hypertension and angina. The importance of understanding the uses of amlodipine cannot be overstated, as it is a commonly prescribed medication with a significant impact on public health. By exploring the different uses of amlodipine, individuals can better appreciate its role in maintaining cardiovascular health and preventing complications associated with high blood pressure and other heart-related issues.
The role of amlodipine in modern medicine is multifaceted, reflecting its efficacy in addressing a range of cardiovascular challenges. From its initial approval for the treatment of hypertension and angina, the scope of amlodipine's applications has expanded, driven by ongoing research and clinical experience. Today, it is recognized not only for its ability to lower blood pressure and reduce the frequency of angina attacks but also for its potential benefits in managing other conditions that affect the heart and blood vessels. As the global population ages and the prevalence of cardiovascular diseases continues to rise, the significance of amlodipine and similar medications will only continue to grow, underscoring the need for comprehensive information on their uses and benefits.
The mechanism by which amlodipine exerts its effects is key to understanding its therapeutic applications. By inhibiting the influx of calcium ions into cardiac and vascular smooth muscle cells, amlodipine promotes vasodilation and reduces cardiac afterload, thereby decreasing myocardial oxygen demand. This dual action is crucial for alleviating the symptoms of angina and for controlling high blood pressure, which are among the most common reasons for prescribing amlodipine. Furthermore, the drug's pharmacokinetic profile, characterized by a long half-life and gradual onset of action, contributes to its popularity among both patients and healthcare providers, as it allows for once-daily dosing and a stable therapeutic effect.
Primary Uses of Amlodipine
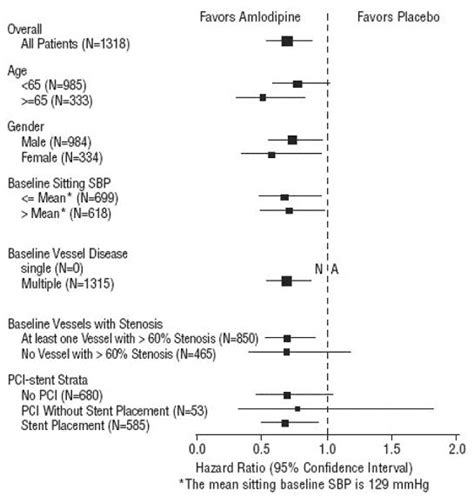
Amlodipine's primary uses can be categorized based on its effects on the cardiovascular system. The most notable applications include the treatment of hypertension (high blood pressure), angina pectoris (a condition characterized by chest pain due to reduced blood flow to the heart), and certain types of arrhythmias (irregular heartbeats). In each of these contexts, amlodipine's ability to dilate blood vessels and reduce the heart's workload plays a critical role in alleviating symptoms and improving quality of life for patients.
Treatment of Hypertension
The management of hypertension is one of the most significant uses of amlodipine. High blood pressure is a major risk factor for cardiovascular diseases, including heart attack, stroke, and kidney disease. Amlodipine helps to lower blood pressure by relaxing the blood vessels, allowing blood to flow more easily and reducing the strain on the heart. This action not only helps to control hypertension but also reduces the risk of developing complications associated with high blood pressure.Secondary Benefits and Uses

Beyond its primary applications, amlodipine may offer secondary benefits that contribute to its therapeutic value. These include potential protective effects against certain cardiovascular events, improvements in exercise performance for patients with angina, and a possible reduction in the risk of stroke and myocardial infarction (heart attack) in patients with hypertension. Additionally, amlodipine's role in managing conditions like coronary artery disease, where it helps to reduce the frequency of angina attacks and improve overall cardiac function, underscores its versatility as a cardiovascular medication.
Management of Angina
Amlodipine is particularly effective in the management of angina pectoris, a condition that results from reduced blood flow to the heart muscle, leading to chest pain. By reducing myocardial oxygen demand through vasodilation and a subsequent decrease in blood pressure, amlodipine helps to decrease the frequency and severity of angina attacks. This effect significantly improves the quality of life for patients with angina, enabling them to engage in physical activity with reduced risk of chest pain.Pharmacological Properties
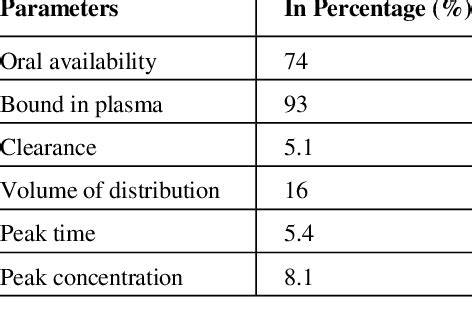
Understanding the pharmacological properties of amlodipine is crucial for appreciating its therapeutic effects and potential side effects. The drug's pharmacokinetics, including its absorption, distribution, metabolism, and excretion, influence its efficacy and safety profile. Amlodipine is known for its high bioavailability, extensive distribution into tissues, and slow elimination, which supports its once-daily dosing regimen. These pharmacological characteristics contribute to amlodipine's popularity as a treatment option for hypertension and angina, offering patients a convenient and effective way to manage their conditions.
Side Effects and Interactions
While amlodipine is generally well-tolerated, it can cause side effects, and its use may be associated with drug interactions. Common side effects include edema (swelling of the feet, ankles, and hands), dizziness, headache, and palpitations. More severe side effects, though rare, can include hypotension (low blood pressure), worsening of angina, and, in susceptible individuals, exacerbation of heart failure. Additionally, amlodipine can interact with other medications, such as certain antihypertensives, grapefruit juice, and cyclosporine, which may necessitate dose adjustments or careful monitoring.Clinical Evidence and Guidelines
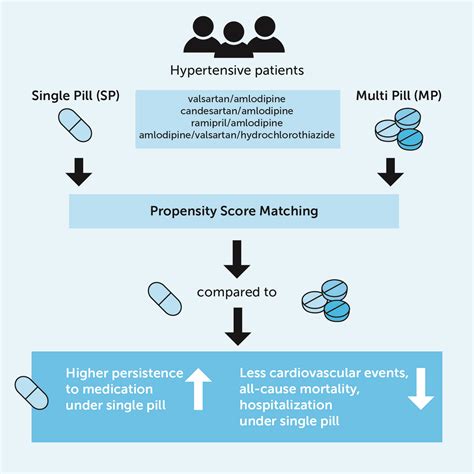
The clinical evidence supporting the use of amlodipine is extensive and has been evaluated in numerous studies and clinical trials. These investigations have demonstrated amlodipine's efficacy in reducing blood pressure, alleviating angina symptoms, and improving outcomes in patients with cardiovascular diseases. Clinical guidelines, such as those issued by the American Heart Association (AHA) and the European Society of Cardiology (ESC), often recommend amlodipine as a first-line treatment for hypertension and angina, reflecting its established role in cardiovascular medicine.
Future Perspectives
As research into cardiovascular diseases continues, the future perspectives on amlodipine's use are likely to evolve. Ongoing studies are exploring the potential benefits of amlodipine in new contexts, such as its effects on endothelial function, its role in preventing cardiovascular events in high-risk patients, and its potential interactions with emerging therapeutic agents. These investigations may uncover new applications for amlodipine or provide further insights into its optimal use in clinical practice, ensuring that this medication remains a valuable tool in the management of cardiovascular health.Conclusion and Final Thoughts

In conclusion, amlodipine is a versatile and effective medication with a wide range of applications in cardiovascular medicine. Its primary uses in treating hypertension and angina are well-established, and its secondary benefits, including potential protective effects against cardiovascular events, contribute to its therapeutic value. As the medical community continues to explore new uses and benefits of amlodipine, patients and healthcare providers can rely on this medication as a cornerstone of cardiovascular treatment, helping to improve outcomes and quality of life for those affected by heart disease.
We invite readers to share their experiences or ask questions about amlodipine and its uses in the comments section below. Your feedback and engagement are invaluable in creating a comprehensive and supportive community focused on cardiovascular health. Additionally, we encourage you to share this article with others who may benefit from the information provided, helping to spread awareness and promote better understanding of this essential medication.
What is the primary mechanism of action of amlodipine?
+Amlodipine works as a calcium channel blocker, relaxing the muscles of the heart and blood vessels, which improves blood flow and reduces blood pressure.
What are the most common side effects of amlodipine?
+Common side effects of amlodipine include edema, dizziness, headache, and palpitations. More severe side effects are rare but can include hypotension and worsening of angina.
Can amlodipine be used in combination with other medications?
+Yes, amlodipine can be used in combination with other medications, but it's essential to consult with a healthcare provider, as interactions can occur. Certain medications and substances, like grapefruit juice, may require dose adjustments or careful monitoring.
