Intro
Discover Clindamycin uses and benefits, a broad-spectrum antibiotic treating bacterial infections, acne, and skin conditions, with applications in dental, respiratory, and bone infections, offering effective relief and prevention.
The world of antibiotics is vast and complex, with various medications designed to combat different types of bacterial infections. Among these, clindamycin stands out as a versatile and effective antibiotic that has been used for decades to treat a wide range of infections. Understanding the uses and benefits of clindamycin is crucial for both medical professionals and patients alike, as it can be a valuable tool in the fight against bacterial infections. In this article, we will delve into the world of clindamycin, exploring its mechanisms, applications, and the advantages it offers in treating various conditions.
Clindamycin is a lincosamide antibiotic that works by inhibiting protein synthesis in bacteria, ultimately leading to their death. This mechanism of action makes it particularly effective against a broad spectrum of bacterial infections, including those caused by anaerobic bacteria, which are bacteria that thrive in environments with little to no oxygen. The versatility of clindamycin is evident in its ability to treat infections in various parts of the body, from the skin and soft tissues to the respiratory and abdominal regions.
The importance of clindamycin in modern medicine cannot be overstated. With the rise of antibiotic resistance, having a range of effective antibiotics is crucial for treating infections that might not respond to other medications. Clindamycin's efficacy against certain resistant strains of bacteria makes it a valuable option for healthcare providers. Moreover, its ability to penetrate bone and soft tissues effectively makes it an ideal choice for treating infections in these areas, such as osteomyelitis and septic arthritis.
Introduction to Clindamycin

Clindamycin's introduction into the medical world marked a significant advancement in the treatment of bacterial infections. Its development and subsequent approval for use in humans paved the way for a new era in antibiotic therapy. The drug's unique mechanism of action and its broad spectrum of activity made it an attractive option for treating a variety of infections. Over the years, clindamycin has proven itself to be a reliable and effective antibiotic, earning its place as a staple in the arsenal against bacterial infections.
How Clindamycin Works
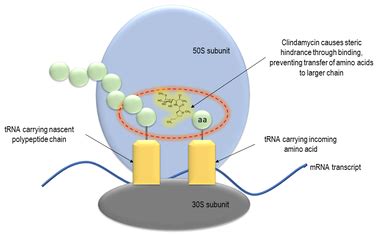
Understanding how clindamycin works is essential to appreciating its benefits. By inhibiting protein synthesis in bacteria, clindamycin prevents the bacteria from producing the proteins necessary for their survival and replication. This action is specific to bacterial cells, making clindamycin a targeted therapy that minimizes harm to human cells. The drug's ability to concentrate within bacterial cells further enhances its effectiveness, ensuring that the bacteria are exposed to high levels of the antibiotic.
Benefits of Clindamycin
The benefits of clindamycin are numerous and significant. Some of the key advantages include: - **Broad Spectrum of Activity**: Clindamycin is effective against a wide range of bacteria, including both aerobic and anaerobic bacteria. - **Penetration into Bone and Soft Tissues**: Its ability to penetrate into bone and soft tissues makes it ideal for treating infections in these areas. - **Oral and Parenteral Administration**: Clindamycin can be administered both orally and parenterally, offering flexibility in treatment options. - **Effective Against Resistant Strains**: Clindamycin has shown efficacy against certain strains of bacteria that are resistant to other antibiotics.Uses of Clindamycin

The uses of clindamycin are diverse and reflect its broad spectrum of activity. It is commonly used to treat:
- Skin and Soft Tissue Infections: Including abscesses, wound infections, and cellulitis.
- Respiratory Tract Infections: Such as pneumonia, particularly when caused by anaerobic bacteria.
- Abdominal Infections: Including peritonitis and intra-abdominal abscesses.
- Bone and Joint Infections: Osteomyelitis and septic arthritis are among the conditions treated with clindamycin.
Precautions and Side Effects
While clindamycin is a valuable antibiotic, it is not without its precautions and potential side effects. Patients should be aware of: - **Clostridioides difficile (C. diff) Infection**: Clindamycin use can lead to an overgrowth of C. diff, causing diarrhea and potentially life-threatening colitis. - **Allergic Reactions**: Ranging from mild skin rashes to severe anaphylactic reactions. - **Gastrointestinal Side Effects**: Nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea are common side effects.Administration and Dosage

The administration and dosage of clindamycin depend on the specific infection being treated, as well as the patient's age, weight, and renal function. Clindamycin can be administered orally in the form of capsules or liquid, or parenterally through intravenous (IV) or intramuscular (IM) injections. The dosage ranges from 150 mg to 450 mg orally every 6 hours, or 300 mg to 900 mg IV/IM every 6 to 8 hours.
Special Considerations
Special considerations must be taken into account when prescribing clindamycin, especially in: - **Pregnant Women**: Clindamycin should be used only when clearly needed, as it can affect the fetus. - **Breastfeeding Mothers**: Caution is advised, as clindamycin can be excreted in breast milk. - **Patients with Renal Impairment**: Dosage adjustments may be necessary to prevent accumulation of the drug.Resistance and Future Directions
The emergence of antibiotic resistance is a global health concern, and clindamycin is no exception. As bacteria develop resistance to clindamycin, the need for new antibiotics and alternative treatments becomes increasingly urgent. Research into new mechanisms of action and the development of novel antibiotics is crucial for the future of infectious disease treatment.
Combination Therapies
Combination therapies, where clindamycin is used in conjunction with other antibiotics, may offer a solution to the problem of resistance. By targeting bacteria in multiple ways, these combination therapies can enhance efficacy and reduce the development of resistance.Conclusion and Final Thoughts

In conclusion, clindamycin is a valuable antibiotic with a broad spectrum of activity and numerous benefits. Its effectiveness against a wide range of bacterial infections, including those caused by anaerobic bacteria, makes it a staple in the treatment of various conditions. However, the emergence of antibiotic resistance and the potential for side effects necessitate careful use and ongoing research into new treatments.
We invite our readers to share their thoughts and experiences with clindamycin, and to engage in a discussion about the future of antibiotic therapy. As we move forward in the fight against bacterial infections, it is crucial that we continue to develop new treatments and strategies to combat resistance. By working together, we can ensure that effective antibiotics like clindamycin remain a viable option for generations to come.
What is clindamycin used for?
+Clindamycin is used to treat a variety of bacterial infections, including skin and soft tissue infections, respiratory tract infections, abdominal infections, and bone and joint infections.
How does clindamycin work?
+Clindamycin works by inhibiting protein synthesis in bacteria, which prevents the bacteria from producing the proteins necessary for their survival and replication.
What are the common side effects of clindamycin?
+Common side effects of clindamycin include nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, and allergic reactions. More serious side effects can include Clostridioides difficile (C. diff) infection and pseudomembranous colitis.
