Intro
Discover key facts about Amoxicillin Clav, a broad-spectrum antibiotic, including its uses, side effects, and interactions, to understand its role in treating bacterial infections, respiratory issues, and more.
The use of antibiotics has become a cornerstone in the treatment of bacterial infections, and one of the most commonly prescribed antibiotics is amoxicillin-clavulanate, also known as Augmentin. This combination of amoxicillin, a penicillin-like antibiotic, and clavulanate, a beta-lactamase inhibitor, has been widely used to treat a variety of infections, including those of the respiratory tract, skin, and urinary tract. Understanding the key aspects of amoxicillin-clavulanate is essential for both healthcare professionals and patients to ensure its safe and effective use.
Amoxicillin-clavulanate is designed to overcome certain types of antibiotic resistance. Many bacteria produce beta-lactamase enzymes that can inactivate amoxicillin, rendering it ineffective against these bacteria. By combining amoxicillin with clavulanate, a beta-lactamase inhibitor, the effectiveness of amoxicillin is extended to include bacteria that are resistant to amoxicillin alone. This dual-action approach makes amoxicillin-clavulanate a powerful tool in the fight against bacterial infections.
The importance of understanding and properly using antibiotics like amoxicillin-clavulanate cannot be overstated. With the rise of antibiotic resistance, it's crucial that these medications are used judiciously to preserve their effectiveness for future generations. Patients should be aware of the potential side effects, the importance of completing the full treatment course, and the signs of allergic reactions or other adverse effects. Moreover, the role of amoxicillin-clavulanate in treating various infections, its benefits over other antibiotics, and its limitations are all critical pieces of information for both healthcare providers and patients.
Introduction to Amoxicillin-Clavulanate

How Amoxicillin-Clavulanate Works
The mechanism of action of amoxicillin-clavulanate involves the synergistic effects of its two components. Amoxicillin works by inhibiting cell wall synthesis in bacteria, ultimately leading to cell lysis and death. Clavulanate, on the other hand, inhibits beta-lactamase enzymes, which are produced by certain bacteria to confer resistance to beta-lactam antibiotics like amoxicillin. By inhibiting these enzymes, clavulanate allows amoxicillin to reach its site of action within the bacterial cell wall, where it can exert its bactericidal effect.Benefits of Amoxicillin-Clavulanate

Common Uses of Amoxicillin-Clavulanate
Amoxicillin-clavulanate is indicated for the treatment of various bacterial infections, including: - Community-acquired pneumonia - Acute bacterial sinusitis - Acute otitis media - Skin and skin structure infections - Urinary tract infections - Intra-abdominal infections Its broad spectrum of activity and efficacy against beta-lactamase-producing organisms make it a versatile antibiotic that can be used in both outpatient and inpatient settings.Side Effects and Precautions

Precautions and Contraindications
Amoxicillin-clavulanate is contraindicated in patients with a history of allergic reactions to any penicillin or beta-lactam antibiotic. It should also be used with caution in patients with a history of asthma, eczema, or other allergies, as these conditions may increase the risk of an allergic reaction. Additionally, patients with renal impairment may require dose adjustments to prevent accumulation of the drug and its metabolites.Dosage and Administration
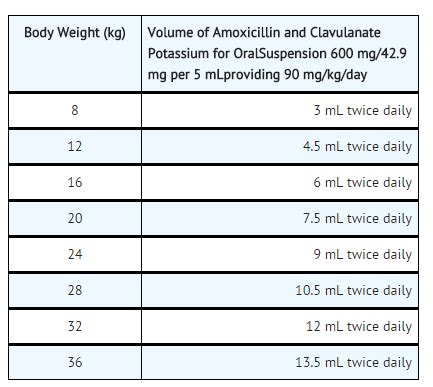
Importance of Completing the Full Treatment Course
It's crucial for patients to complete the full treatment course as prescribed by their healthcare provider, even if symptoms improve before finishing the antibiotic. Stopping the antibiotic too soon can lead to the development of antibiotic resistance and increase the risk of treatment failure.Resistance and Future Perspectives

Alternative Treatments and Future Directions
Research into new antibiotics and alternative treatments, such as bacteriophage therapy and antimicrobial peptides, is ongoing. These innovations hold promise for addressing the challenge of antibiotic resistance and providing effective treatments for bacterial infections in the future.Conclusion and Final Thoughts
We invite you to share your thoughts and experiences with amoxicillin-clavulanate in the comments below. Your insights can help others understand the importance of responsible antibiotic use and the role of amoxicillin-clavulanate in treating bacterial infections. Please consider sharing this article with others who may benefit from this information.
What is amoxicillin-clavulanate used for?
+Amoxicillin-clavulanate is used to treat a variety of bacterial infections, including respiratory tract infections, skin infections, urinary tract infections, and intra-abdominal infections.
How does amoxicillin-clavulanate work?
+Amoxicillin-clavulanate works by combining the bactericidal effects of amoxicillin with the beta-lactamase inhibitory effects of clavulanate, allowing it to effectively treat infections caused by beta-lactamase-producing bacteria.
What are the common side effects of amoxicillin-clavulanate?
+The most common side effects of amoxicillin-clavulanate include diarrhea, nausea, vomiting, and rash. More severe side effects can include allergic reactions and Clostridioides difficile-associated diarrhea.
Why is it important to complete the full treatment course of amoxicillin-clavulanate?
+Completing the full treatment course is crucial to ensure that the infection is fully cleared and to prevent the development of antibiotic resistance.
Can amoxicillin-clavulanate be used in patients with renal impairment?
+Yes, but with caution. Patients with renal impairment may require dose adjustments to prevent accumulation of the drug and its metabolites.
