Intro
Identify 7 virus symptoms, including fever, fatigue, and cough. Learn to recognize common viral infection signs, such as headache, sore throat, and body aches, to seek timely medical attention and prevent complications.
The world of viruses is complex and fascinating, with new strains and variants emerging regularly. Understanding the symptoms of viral infections is crucial for early detection, treatment, and prevention of complications. Viral infections can range from mild to severe, affecting different parts of the body and causing a wide array of symptoms. In this article, we will delve into the common symptoms of viral infections, exploring what they are, how they manifest, and why it's essential to recognize them.
Viral infections can affect anyone, regardless of age or health status. They are highly contagious and can spread through various means, including direct contact with an infected person, contaminated food and water, or through the air when an infected person coughs or sneezes. The symptoms of viral infections can vary significantly depending on the type of virus and the part of the body it affects. For instance, respiratory viruses like the flu or COVID-19 primarily affect the lungs and respiratory system, causing symptoms such as cough, fever, and shortness of breath. On the other hand, gastrointestinal viruses like norovirus lead to symptoms such as diarrhea, vomiting, and stomach cramps.
Recognizing the symptoms of viral infections is the first step towards seeking appropriate medical care. Early diagnosis and treatment can significantly improve outcomes, reduce the risk of complications, and prevent the spread of the infection to others. Moreover, understanding the symptoms of viral infections can help individuals take preventive measures, such as practicing good hygiene, getting vaccinated against certain viruses, and avoiding close contact with people who are sick. In the following sections, we will explore the common symptoms of viral infections in more detail, discussing their causes, manifestations, and importance in seeking medical care.
Common Virus Symptoms

The symptoms of viral infections can be categorized into systemic and localized symptoms. Systemic symptoms affect the whole body and include fever, headache, fatigue, and muscle aches. These symptoms occur because the virus triggers an immune response, which can lead to inflammation and the release of chemical mediators that cause these symptoms. Localized symptoms, on the other hand, are specific to the part of the body affected by the virus. For example, a viral infection of the eye can cause redness, itching, and discharge, while a viral infection of the throat can cause soreness and difficulty swallowing.
Systemic Symptoms
Systemic symptoms are common in many viral infections and can be quite debilitating. They include: - Fever: A high body temperature, usually above 100.4°F (38°C), which is a sign of the body's immune response to the infection. - Headache: A pain in the head, which can range from mild to severe, often caused by the inflammation and chemical mediators released during the immune response. - Fatigue: Feeling extremely tired or lacking energy, which is a result of the body's effort to fight the infection. - Muscle aches: Pain or discomfort in the muscles, which can be widespread or localized to specific areas.Localized Symptoms
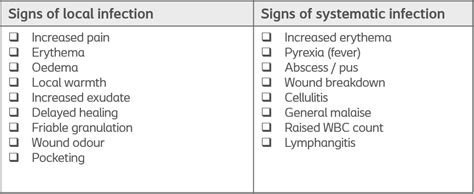
Localized symptoms depend on the site of the viral infection. For instance:
- Respiratory symptoms: Cough, runny nose, sneezing, and shortness of breath are common in viral respiratory infections like the common cold or flu.
- Gastrointestinal symptoms: Diarrhea, vomiting, stomach cramps, and nausea are typical of viral gastrointestinal infections like norovirus or rotavirus.
- Skin symptoms: Rashes, blisters, or lesions can occur in viral skin infections such as herpes simplex or varicella-zoster virus.
Viral Infection Sites
Different viruses target different parts of the body, leading to a variety of symptoms based on the infection site. Understanding these sites and their associated symptoms can help in diagnosing and managing viral infections. For example: - Central Nervous System (CNS): Viral infections like meningitis or encephalitis can cause severe symptoms such as headache, stiff neck, confusion, and seizures. - Eyes: Viral conjunctivitis can lead to redness, itching, and discharge from the eyes. - Liver: Viral hepatitis can cause jaundice, dark urine, and pale stools, indicating liver dysfunction.Diagnosis and Treatment
Diagnosing viral infections often involves a combination of physical examination, medical history, and laboratory tests. Treatment options vary depending on the virus and the severity of the symptoms. While there are antiviral medications available for certain viral infections, many viral infections are managed symptomatically, focusing on relieving the symptoms and supporting the body's immune response. Rest, hydration, and over-the-counter medications for pain and fever are common recommendations.
Prevention
Preventing viral infections is crucial and involves several strategies: - Vaccination: Getting vaccinated against certain viruses can provide immunity and prevent infection. - Hygiene: Practicing good hygiene, such as washing hands frequently, especially after using the bathroom and before eating, can significantly reduce the spread of viral infections. - Avoiding close contact: Staying away from people who are sick can prevent the spread of viral infections. - Healthy lifestyle: Maintaining a healthy diet, exercising regularly, and getting enough sleep can help boost the immune system and reduce the risk of viral infections.Complications of Viral Infections
While many viral infections are self-limiting and resolve on their own, some can lead to serious complications, especially in vulnerable populations such as the elderly, young children, and people with compromised immune systems. Complications can include:
- Secondary bacterial infections: Viral infections can sometimes lead to secondary bacterial infections, which can be severe and require antibiotic treatment.
- Organ dysfunction: In severe cases, viral infections can lead to dysfunction of vital organs such as the liver, kidneys, or heart.
- Neurological complications: Certain viral infections can cause neurological complications, including seizures, meningitis, or encephalitis.
Long-term Effects
Some viral infections can have long-term effects on health, even after the initial infection has resolved. For example: - Chronic fatigue syndrome: Some people may experience persistent fatigue and other symptoms after a viral infection, a condition known as chronic fatigue syndrome. - Autoimmune diseases: There is evidence to suggest that certain viral infections may trigger autoimmune diseases in susceptible individuals. - Mental health impacts: The stress and trauma of experiencing a severe viral infection can have long-term impacts on mental health.Future Directions

The field of virology is constantly evolving, with new technologies and discoveries offering hope for better diagnosis, treatment, and prevention of viral infections. Future directions include:
- Development of new antiviral drugs: Research into the development of new antiviral medications that can target a wide range of viruses.
- Improved vaccination strategies: Enhancing existing vaccines and developing new ones to protect against emerging and re-emerging viral threats.
- Public health initiatives: Implementing effective public health measures to prevent the spread of viral infections, including education campaigns, contact tracing, and quarantine measures.
Global Cooperation
The global nature of viral infections necessitates international cooperation and collaboration. Sharing data, coordinating public health responses, and supporting research efforts globally can help in combating viral infections more effectively. This includes: - Surveillance: Enhancing global surveillance to quickly identify and respond to new and emerging viral threats. - Research collaboration: Collaborating on research to understand the mechanisms of viral infections, develop new treatments, and improve vaccination strategies. - Public health policy: Developing and implementing effective public health policies that can be adapted and implemented globally to prevent and control the spread of viral infections.As we conclude our exploration of viral infection symptoms, it's clear that understanding these symptoms is crucial for early detection, treatment, and prevention of complications. By recognizing the signs of viral infections, taking preventive measures, and supporting research and public health initiatives, we can work towards reducing the impact of these infections on individuals and communities worldwide. We invite you to share your thoughts and experiences with viral infections, and to spread awareness about the importance of recognizing and addressing these symptoms promptly.
What are the most common symptoms of viral infections?
+The most common symptoms include fever, headache, fatigue, and muscle aches. These can vary depending on the type of virus and the part of the body affected.
How are viral infections diagnosed?
+Diagnosis often involves a combination of physical examination, medical history, and laboratory tests such as blood tests or swabs to identify the virus.
Can all viral infections be treated with antiviral medications?
+No, not all viral infections can be treated with antiviral medications. Treatment depends on the type of virus and the severity of the symptoms. Many viral infections are managed symptomatically.
