Intro
Discover Amoxicillin uses and benefits, including antibiotic treatment for bacterial infections, respiratory issues, and skin conditions, with its advantages and side effects.
The discovery of antibiotics has been a significant milestone in the history of medicine, revolutionizing the way we treat bacterial infections. Among the various antibiotics available, amoxicillin stands out as one of the most widely used and effective medications. Amoxicillin is a penicillin-type antibiotic that has been used for decades to treat a range of bacterial infections, from mild to severe. Its broad-spectrum activity, ease of use, and relatively low cost have made it a favorite among healthcare professionals and patients alike.
Amoxicillin's mechanism of action involves inhibiting the growth of bacteria by interfering with the synthesis of their cell walls. This leads to the death of the bacterial cells, thereby curing the infection. The medication is effective against a wide range of bacteria, including Streptococcus, Haemophilus, and Escherichia species. Its broad-spectrum activity makes it an ideal choice for treating various infections, including respiratory tract infections, skin and soft tissue infections, and urinary tract infections.
The importance of amoxicillin cannot be overstated, as it has saved countless lives and improved the quality of life for millions of people worldwide. Its benefits extend beyond its therapeutic effects, as it has also played a significant role in reducing the economic burden of bacterial infections on individuals and societies. With the rising concern of antibiotic resistance, it is essential to use amoxicillin and other antibiotics judiciously, ensuring that they remain effective for future generations.
Introduction to Amoxicillin

Pharmacokinetics and Pharmacodynamics
Amoxicillin's pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics play a crucial role in its effectiveness. The medication is well absorbed in the gastrointestinal tract, with peak plasma concentrations achieved within 1-2 hours. Amoxicillin is distributed throughout the body, with high concentrations found in the liver, kidneys, and lungs. Its half-life is approximately 1-2 hours, which means that it needs to be taken multiple times a day to maintain therapeutic levels.Benefits of Amoxicillin

Common Uses of Amoxicillin
Amoxicillin is used to treat a range of bacterial infections, including: * Respiratory tract infections: Amoxicillin is effective against infections such as pneumonia, bronchitis, and sinusitis. * Skin and soft tissue infections: Amoxicillin is used to treat infections such as cellulitis, impetigo, and abscesses. * Urinary tract infections: Amoxicillin is effective against infections such as cystitis and pyelonephritis. * Gastrointestinal infections: Amoxicillin is used to treat infections such as gastroenteritis and diverticulitis.Amoxicillin Dosage and Administration
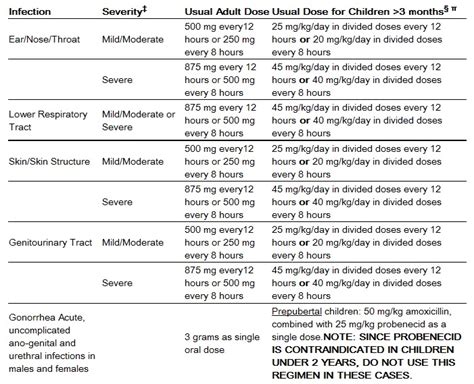
Side Effects and Interactions
While amoxicillin is generally well-tolerated, it can cause side effects such as: * Gastrointestinal upset: Nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea are common side effects. * Allergic reactions: Amoxicillin can cause allergic reactions, ranging from mild rashes to life-threatening anaphylaxis. * Interactions: Amoxicillin can interact with other medications, such as warfarin and methotrexate, increasing the risk of adverse effects.Resistance and Misuse
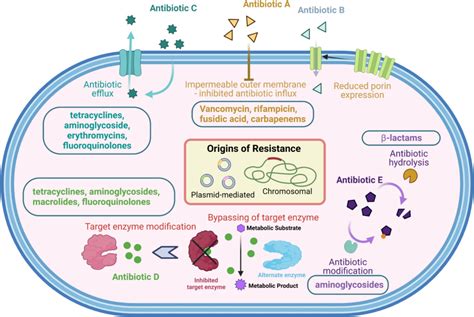
Future Directions
The development of new antibiotics and the discovery of alternative treatments are essential to addressing the growing problem of antibiotic resistance. Researchers are exploring new avenues, such as bacteriophage therapy and antimicrobial peptides, to combat bacterial infections. Meanwhile, healthcare professionals must continue to use antibiotics responsibly, ensuring that they remain effective for future generations.Conclusion and Recommendations

We recommend that healthcare professionals and patients work together to use antibiotics responsibly, completing the full course of treatment and avoiding the misuse of these valuable medications. By doing so, we can ensure that amoxicillin and other antibiotics remain effective for future generations, saving countless lives and improving the quality of life for millions of people worldwide.
What is amoxicillin used for?
+Amoxicillin is used to treat a range of bacterial infections, including respiratory tract infections, skin and soft tissue infections, and urinary tract infections.
How does amoxicillin work?
+Amoxicillin works by inhibiting the growth of bacteria by interfering with the synthesis of their cell walls, leading to the death of the bacterial cells.
What are the common side effects of amoxicillin?
+Common side effects of amoxicillin include gastrointestinal upset, allergic reactions, and interactions with other medications.
Can amoxicillin be used to treat viral infections?
+No, amoxicillin should not be used to treat viral infections, as it is ineffective against viruses and can contribute to the growing problem of antibiotic resistance.
How can I use amoxicillin responsibly?
+To use amoxicillin responsibly, complete the full course of treatment, avoid using it for viral infections, and follow the recommended dosage and administration guidelines.
We invite you to share your thoughts and experiences with amoxicillin in the comments below. Have you used amoxicillin to treat a bacterial infection? What were your experiences with the medication? Share your story and help others understand the importance of using antibiotics responsibly.
