Intro
Discover the causes and risks of high blood urea nitrogen levels, a key indicator of kidney function, and learn how to manage and reduce elevated BUN levels through diet and treatment, improving overall renal health and preventing complications.
Blood urea nitrogen (BUN) is a waste product that occurs in the blood when the body breaks down protein. Normally, this waste is removed by the kidneys, but when the kidneys are not functioning properly, BUN levels can rise. High blood urea nitrogen levels can be a sign of a serious health issue, and it's essential to understand what causes them and how they can be treated. In this article, we will delve into the world of BUN, exploring its importance, causes, symptoms, and treatment options.
High BUN levels can be a cause for concern, as they can indicate kidney disease, dehydration, or other health problems. The kidneys play a crucial role in removing waste and excess fluids from the body, and when they are not functioning correctly, it can lead to a buildup of toxins. This can cause a range of symptoms, from mild to severe, and can even lead to life-threatening complications if left untreated. It's essential to understand the risks associated with high BUN levels and to take proactive steps to maintain good kidney health.
The importance of monitoring BUN levels cannot be overstated. By keeping track of BUN levels, healthcare professionals can diagnose and treat kidney disease and other health issues early on, reducing the risk of complications and improving treatment outcomes. Additionally, understanding the causes and symptoms of high BUN levels can help individuals take steps to prevent kidney disease and maintain good overall health. Whether you're at risk for kidney disease or simply want to learn more about BUN, this article will provide you with the information you need to make informed decisions about your health.
What is Blood Urea Nitrogen?
How is Blood Urea Nitrogen Measured?
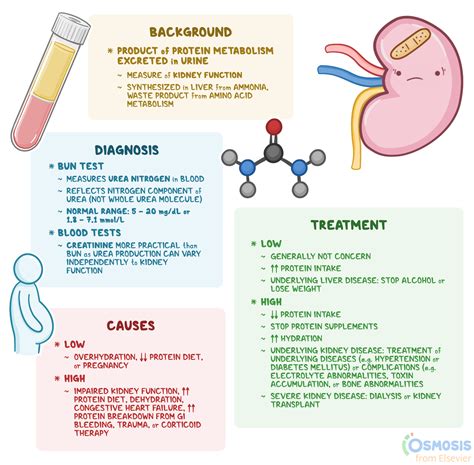
BUN levels are typically measured using a blood test. The test involves drawing a sample of blood from a vein in the arm, which is then sent to a laboratory for analysis. The results are usually reported in milligrams per deciliter (mg/dL). A normal BUN level is typically between 6 and 24 mg/dL, but this can vary depending on the laboratory and the individual's overall health.Causes of High Blood Urea Nitrogen Levels
Symptoms of High Blood Urea Nitrogen Levels
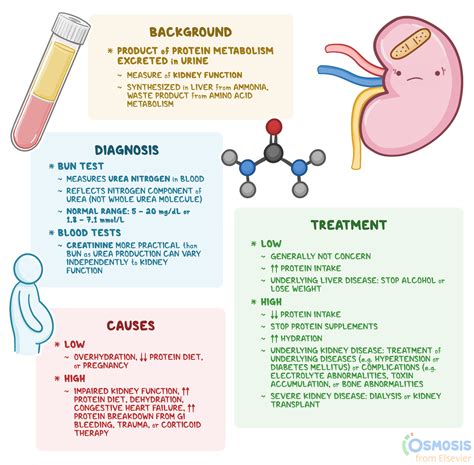
The symptoms of high BUN levels can vary depending on the underlying cause. Some common symptoms include: * Fatigue * Weakness * Nausea and vomiting * Diarrhea * Abdominal pain * Shortness of breath * Swelling in the legs, ankles, and feetTreatment Options for High Blood Urea Nitrogen Levels
Prevention of High Blood Urea Nitrogen Levels
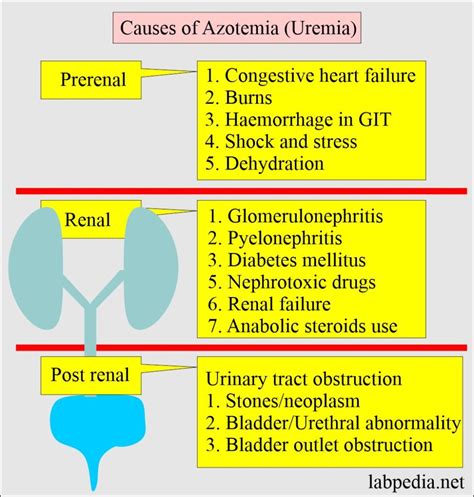
There are several steps that can be taken to prevent high BUN levels, including: * Drinking plenty of water to stay hydrated * Reducing protein intake * Managing underlying medical conditions such as diabetes and high blood pressure * Avoiding certain medications that can cause an increase in BUN production * Getting regular check-ups with a healthcare provider to monitor kidney functionComplications of High Blood Urea Nitrogen Levels
Risk Factors for High Blood Urea Nitrogen Levels
There are several risk factors for high BUN levels, including: * Age: Older adults are at a higher risk of developing high BUN levels. * Family history: A family history of kidney disease can increase the risk of developing high BUN levels. * Diabetes: Diabetes can increase the risk of developing high BUN levels. * High blood pressure: High blood pressure can increase the risk of developing high BUN levels. * Obesity: Obesity can increase the risk of developing high BUN levels.Diagnosis of High Blood Urea Nitrogen Levels

Monitoring and Follow-up
Monitoring and follow-up are essential for managing high BUN levels. This may include: * Regular blood tests to monitor BUN levels * Regular urine tests to monitor protein and other waste products in the urine * Regular imaging tests to monitor kidney function * Regular check-ups with a healthcare provider to monitor overall health and adjust treatment as neededWhat is the normal range for blood urea nitrogen levels?
+A normal BUN level is typically between 6 and 24 mg/dL, but this can vary depending on the laboratory and the individual's overall health.
What are the symptoms of high blood urea nitrogen levels?
+The symptoms of high BUN levels can vary depending on the underlying cause, but may include fatigue, weakness, nausea and vomiting, diarrhea, abdominal pain, shortness of breath, and swelling in the legs, ankles, and feet.
How are high blood urea nitrogen levels treated?
+The treatment options for high BUN levels depend on the underlying cause, but may include medications, dialysis, kidney transplant, and lifestyle changes such as increasing fluid intake and reducing protein intake.
Can high blood urea nitrogen levels be prevented?
+Yes, high BUN levels can be prevented by drinking plenty of water to stay hydrated, reducing protein intake, managing underlying medical conditions, and avoiding certain medications that can cause an increase in BUN production.
What are the complications of high blood urea nitrogen levels?
+High BUN levels can lead to several complications, including kidney failure, heart disease, electrolyte imbalance, and osteoporosis.
In conclusion, high blood urea nitrogen levels can be a sign of a serious health issue, and it's essential to understand the causes, symptoms, and treatment options. By taking proactive steps to maintain good kidney health and monitoring BUN levels, individuals can reduce their risk of complications and improve their overall health. We encourage readers to share their experiences and ask questions in the comments below, and to consult with a healthcare provider if they have any concerns about their BUN levels or overall health.
