Intro
Discover the nutritional benefits of oranges, rich in vitamin C, flavonoids, and fiber, making them a healthy snack for boosting immunity and supporting overall well-being, with potential anti-inflammatory effects.
Oranges are one of the most widely consumed fruits in the world, and their popularity can be attributed to their sweet taste, versatility, and perceived health benefits. For decades, oranges have been touted as a superfood, with many people believing that they are an excellent source of essential nutrients, vitamins, and minerals. But are oranges really as healthy as we think they are? In this article, we will delve into the nutritional profile of oranges, explore their potential health benefits, and examine the scientific evidence to determine whether oranges are indeed a healthy addition to our diets.
The importance of oranges in our diets cannot be overstated. They are an excellent source of vitamin C, a powerful antioxidant that plays a crucial role in boosting our immune systems and protecting us against infections. Oranges are also rich in fiber, potassium, and folate, making them a nutritious snack for people of all ages. Furthermore, oranges contain a range of phytochemicals, including flavonoids and carotenoids, which have been shown to have anti-inflammatory properties and may help reduce the risk of chronic diseases such as heart disease and cancer.
Despite their numerous health benefits, oranges are not without their drawbacks. They are relatively high in sugar and calories, which can be a concern for people who are trying to manage their weight or control their blood sugar levels. Additionally, oranges are often consumed in the form of juice, which can be high in sugar and low in fiber and other essential nutrients. Therefore, it is essential to consume oranges in moderation and as part of a balanced diet to reap their potential health benefits.
Introduction to Oranges

Nutritional Profile of Oranges
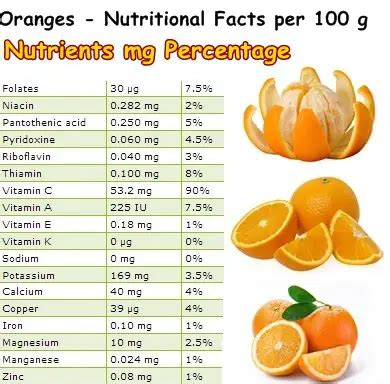
Oranges are an excellent source of essential nutrients, including vitamin C, potassium, and folate. They are also rich in fiber, which can help promote digestive health and support healthy blood sugar levels. The nutritional profile of oranges is as follows: * Calories: 60-70 per medium-sized orange * Carbohydrates: 15-20 grams per medium-sized orange * Fiber: 2-3 grams per medium-sized orange * Protein: 1-2 grams per medium-sized orange * Vitamin C: 100-150% of the daily recommended intake per medium-sized orange * Potassium: 10-15% of the daily recommended intake per medium-sized orange * Folate: 10-15% of the daily recommended intake per medium-sized orangeHealth Benefits of Oranges

Potential Risks and Side Effects
While oranges are generally considered a healthy food, they can pose some risks and side effects, particularly when consumed in excess. Some of the potential risks and side effects of oranges include: * High sugar content: Oranges are relatively high in sugar, which can be a concern for people who are trying to manage their weight or control their blood sugar levels. * Interactions with medications: The high vitamin C content in oranges may interact with certain medications, such as blood thinners, and reduce their effectiveness. * Allergic reactions: Some people may be allergic to oranges, which can cause symptoms such as hives, itching, and swelling.How to Incorporate Oranges into Your Diet

Tips for Selecting and Storing Oranges
To get the most nutritional benefits from oranges, it is essential to select and store them properly. Some tips for selecting and storing oranges include: * Choosing oranges that are heavy for their size: This indicates that they are juicy and ripe. * Avoiding oranges with soft spots or mold: These can be signs of spoilage and may reduce the nutritional content of the orange. * Storing oranges in a cool, dry place: This can help preserve their nutritional content and keep them fresh for longer.Conclusion and Final Thoughts
We hope this article has provided you with a comprehensive overview of the nutritional profile and health benefits of oranges. Whether you enjoy them as a snack, add them to salads, or use them in cooking, oranges are a versatile and nutritious food that can be incorporated into your diet in a variety of ways. So next time you reach for an orange, remember the numerous health benefits it provides and enjoy it as a healthy and delicious addition to your diet.
Are oranges a good source of protein?
+Oranges are not a significant source of protein, with a medium-sized orange containing only about 1-2 grams of protein.
Can oranges help lower blood pressure?
+Yes, the potassium content in oranges may help lower blood pressure by counteracting the effects of sodium and promoting healthy blood vessel function.
Are oranges a good food for people with diabetes?
+Oranges can be a good food for people with diabetes, but they should be consumed in moderation due to their relatively high sugar content. The fiber and water content in oranges can help regulate blood sugar levels and promote feelings of fullness.
We invite you to share your thoughts and experiences with oranges in the comments section below. Have you incorporated oranges into your diet and noticed any health benefits? Do you have any favorite recipes or tips for selecting and storing oranges? Share your stories and help us create a community of like-minded individuals who are passionate about healthy eating and nutrition.
