Intro
Unlock the meaning of INR medical acronym, related to blood clotting, prothrombin time, and international normalized ratio, to understand its significance in healthcare and medical diagnosis, particularly in patients on warfarin therapy.
The medical field is filled with acronyms and abbreviations that can be confusing for patients and even for some medical professionals. One such acronym is INR, which stands for International Normalized Ratio. Understanding what INR means and its significance in medical diagnosis and treatment is crucial for managing certain health conditions effectively.
INR is a test used to measure the time it takes for the blood to clot and is primarily used to monitor patients on warfarin therapy. Warfarin is a blood thinner that helps prevent blood clots from forming or growing. It is often prescribed for people at risk of developing blood clots due to conditions such as atrial fibrillation, deep vein thrombosis, or pulmonary embolism. The INR test helps healthcare providers determine if the dose of warfarin is appropriate for the patient.
Given the complexity of the human body and the intricacies of medical treatments, understanding acronyms like INR is vital for both medical professionals and patients. It helps in making informed decisions about health care and ensures that treatments are effective and safe. The importance of such knowledge cannot be overstated, as it directly impacts the quality of care and patient outcomes.
What is INR and Its Medical Significance

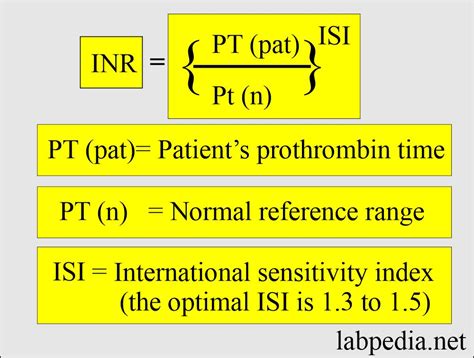
The INR test is a critical tool in managing anticoagulation therapy. It measures the ratio of a patient's prothrombin time (PT) to the normal PT, which helps in assessing the blood's clotting tendency. A normal INR range for someone not on anticoagulant therapy is typically around 1.0. For patients on warfarin, the target INR range varies depending on the condition being treated but usually falls between 2.0 and 3.0. This range indicates that the blood is thin enough to prevent clots but not so thin that it causes bleeding problems.
Understanding INR Ranges
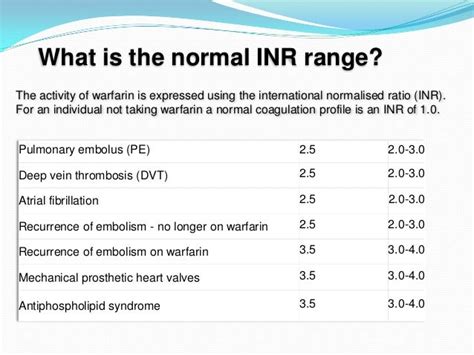
- INR below 2.0: This suggests that the blood is not thin enough, and the patient may be at risk of forming blood clots.
- INR between 2.0 and 3.0: This is the target range for most conditions, indicating that the blood is appropriately thinned.
- INR above 3.0: This indicates that the blood is too thin, and the patient may be at risk of bleeding.
How INR is Used in Medical Practice
In medical practice, INR is used to adjust the dose of warfarin. If the INR is too low, the dose of warfarin may need to be increased to prevent clot formation. Conversely, if the INR is too high, the dose may need to be decreased to reduce the risk of bleeding. Regular INR monitoring is essential for patients on warfarin to ensure that their blood is within the therapeutic range.
Factors Affecting INR Levels
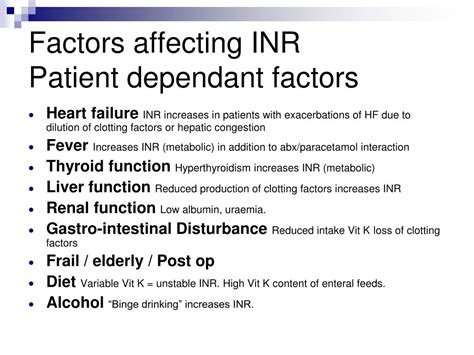
Several factors can affect INR levels, including:
- Diet: Foods high in vitamin K, such as leafy green vegetables, can decrease INR levels.
- Medications: Certain medications, including antibiotics and anti-inflammatory drugs, can interact with warfarin and affect INR levels.
- Alcohol consumption: Excessive alcohol consumption can increase the risk of bleeding in patients on warfarin.
- Illness: Certain illnesses, such as liver disease or kidney disease, can affect how the body processes warfarin.
Challenges and Considerations in INR Management

Managing INR levels can be challenging due to the narrow therapeutic window of warfarin and the numerous factors that can affect INR levels. Healthcare providers must closely monitor patients on warfarin and adjust their treatment plans as necessary to minimize the risk of complications.
Role of Patient Education
Patient education plays a crucial role in effective INR management. Patients should be informed about the importance of regular monitoring, the factors that can affect INR levels, and the signs and symptoms of bleeding or clotting. This knowledge enables patients to take an active role in their care, helping to ensure that their treatment is safe and effective.
Alternatives to Warfarin and INR Monitoring

In recent years, new anticoagulants have been developed that do not require regular INR monitoring. These include direct oral anticoagulants (DOACs) such as dabigatran, rivaroxaban, apixaban, and edoxaban. DOACs have a more predictable pharmacokinetic profile than warfarin and are associated with a lower risk of intracranial bleeding. However, they are not suitable for all patients, and the decision to use a DOAC versus warfarin should be made on an individual basis.
Future Directions in Anticoagulation Therapy
The field of anticoagulation therapy is continually evolving, with ongoing research into new anticoagulants and monitoring technologies. Advances in genetics and genomics may also allow for more personalized anticoagulation therapy in the future. As our understanding of the complex interactions between anticoagulants, genetics, and patient factors improves, so too will our ability to provide safe and effective care for patients at risk of thrombosis.
Conclusion and Final Thoughts

In conclusion, understanding the INR medical acronym and its significance is vital for both patients and healthcare providers. Effective management of INR levels is crucial for preventing complications in patients on anticoagulation therapy. By staying informed about the latest developments in anticoagulation therapy and taking an active role in their care, patients can work with their healthcare providers to achieve the best possible outcomes.
As we look to the future, it's clear that the management of anticoagulation therapy will continue to evolve. With the development of new medications and technologies, the potential for more personalized and effective care is on the horizon. For now, a thorough understanding of INR and its role in anticoagulation therapy remains a cornerstone of high-quality patient care.
What does INR stand for in medical terms?
+INR stands for International Normalized Ratio, which is a test used to measure the time it takes for blood to clot.
Why is INR monitoring important for patients on warfarin?
+INR monitoring is important because it helps healthcare providers adjust the dose of warfarin to prevent blood clots and minimize the risk of bleeding.
What factors can affect INR levels in patients on warfarin?
+Several factors can affect INR levels, including diet, other medications, alcohol consumption, and certain illnesses.
We invite you to share your thoughts and experiences with INR and anticoagulation therapy. Your insights can help others better understand the importance of this aspect of medical care. Feel free to comment below or share this article with someone who might find it helpful. Together, we can promote a deeper understanding of health topics and support informed decision-making.
