Intro
Learn about Atrial Septal Defect, a heart condition where a hole in the septum separates atria, causing blood flow issues, requiring diagnosis and treatment to prevent complications like arrhythmias and heart failure.
Atrial septal defect, commonly referred to as ASD, is a type of congenital heart defect that affects the heart's structure and function. This condition occurs when there is an abnormal opening in the atrial septum, which is the wall of tissue that separates the heart's two upper chambers, known as the atria. As a result, blood can flow between the left and right atria, leading to various health complications. In this article, we will delve into the world of atrial septal defects, exploring their causes, symptoms, diagnosis, treatment options, and more.
The importance of understanding atrial septal defects cannot be overstated, as this condition can have significant implications for an individual's quality of life and overall health. ASDs are relatively common, affecting approximately 1 in every 1,500 births, and can occur in both children and adults. While some individuals may not exhibit any symptoms, others may experience a range of health issues, including shortness of breath, fatigue, and increased risk of heart failure. By gaining a deeper understanding of ASDs, we can better appreciate the need for early diagnosis and treatment, as well as the importance of ongoing care and management.
Atrial septal defects are often detected during childhood, but some cases may go undiagnosed until later in life. This can be due to the fact that some individuals may not exhibit any noticeable symptoms, or because the condition is not severe enough to cause significant health problems. However, if left untreated, ASDs can lead to serious complications, such as heart failure, arrhythmias, and increased risk of stroke. Therefore, it is essential to seek medical attention if you or a loved one is experiencing any symptoms or has been diagnosed with an ASD.
Atrial Septal Defect Causes and Risk Factors
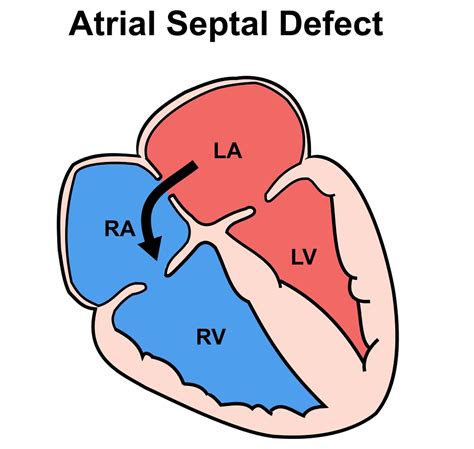
Atrial septal defects are typically present at birth, although they can also develop later in life due to various factors. The exact cause of ASDs is often unknown, but several risk factors have been identified. These include genetics, maternal infection during pregnancy, and certain medical conditions, such as diabetes and rubella. Additionally, individuals with a family history of heart defects are more likely to develop an ASD. Understanding the causes and risk factors of ASDs is crucial for developing effective prevention and treatment strategies.
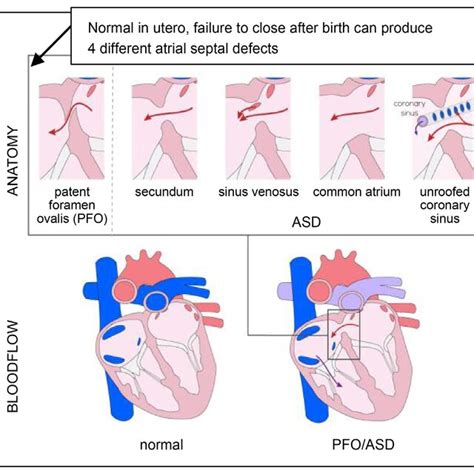
Types of Atrial Septal Defects
There are several types of atrial septal defects, each with distinct characteristics and treatment options. The most common types of ASDs include: * Ostium secundum: This is the most common type of ASD, accounting for approximately 70% of all cases. It occurs when there is a hole in the middle part of the atrial septum. * Ostium primum: This type of ASD occurs when there is a hole in the lower part of the atrial septum, near the tricuspid and mitral valves. * Sinus venosus: This is a rare type of ASD that occurs when there is a hole in the upper part of the atrial septum, near the superior vena cava. * Coronary sinus: This is a rare type of ASD that occurs when there is a hole in the coronary sinus, which is a small venous structure that collects blood from the heart.Atrial Septal Defect Symptoms and Diagnosis
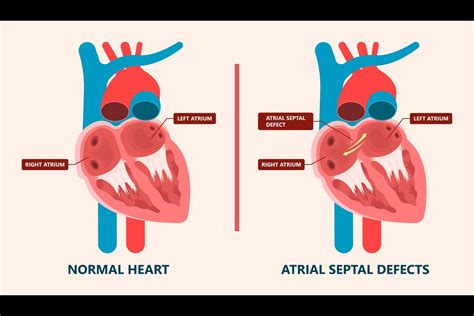
The symptoms of atrial septal defects can vary widely, depending on the size and location of the defect, as well as the individual's overall health. Common symptoms of ASDs include:
- Shortness of breath
- Fatigue
- Pale skin
- Poor appetite
- Frequent respiratory infections
- Heart palpitations
- Swelling in the legs, ankles, or feet
Diagnosing an atrial septal defect typically involves a combination of physical examination, medical history, and diagnostic tests. These tests may include:
- Electrocardiogram (ECG or EKG)
- Chest X-ray
- Echocardiogram
- Cardiac catheterization
- Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI)
Treatment Options for Atrial Septal Defects
The treatment options for atrial septal defects depend on the size and location of the defect, as well as the individual's overall health. In some cases, ASDs may not require treatment, especially if they are small and do not cause any symptoms. However, larger defects may require surgical or catheter-based closure. The goal of treatment is to close the defect, prevent complications, and improve the individual's quality of life.Atrial Septal Defect Treatment and Management
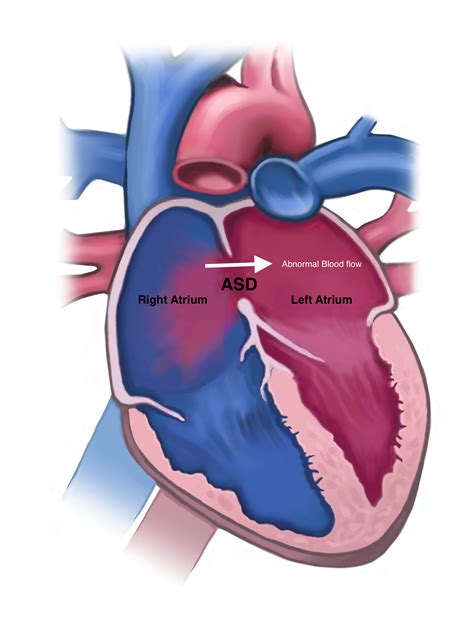
Treatment options for atrial septal defects may include:
- Watchful waiting: This involves monitoring the individual's condition with regular check-ups and diagnostic tests.
- Medications: These may be prescribed to manage symptoms, such as diuretics to reduce fluid buildup and beta blockers to slow the heart rate.
- Surgical closure: This involves open-heart surgery to close the defect.
- Catheter-based closure: This is a minimally invasive procedure that uses a catheter to deliver a device that closes the defect.
- Hybrid procedure: This is a combination of surgical and catheter-based closure.
Living with an Atrial Septal Defect
Living with an atrial septal defect requires ongoing care and management to prevent complications and improve quality of life. This may include: * Regular check-ups with a cardiologist * Monitoring for signs of complications, such as heart failure or arrhythmias * Maintaining a healthy lifestyle, including a balanced diet and regular exercise * Avoiding certain activities, such as scuba diving or contact sports, that may increase the risk of complicationsAtrial Septal Defect Complications and Prognosis
If left untreated, atrial septal defects can lead to serious complications, including:
- Heart failure
- Arrhythmias
- Increased risk of stroke
- Pulmonary hypertension
- Respiratory infections
The prognosis for individuals with atrial septal defects is generally good, especially if treatment is received early. With proper care and management, most individuals with ASDs can lead active and healthy lives.
Atrial Septal Defect Prevention
While it is not possible to prevent all cases of atrial septal defects, there are steps that can be taken to reduce the risk of developing this condition. These include: * Maintaining a healthy lifestyle during pregnancy, including a balanced diet and regular exercise * Avoiding certain medications and substances during pregnancy * Getting regular check-ups with a cardiologist if you have a family history of heart defectsAtrial Septal Defect Research and Future Directions
Research into atrial septal defects is ongoing, with scientists working to develop new and improved treatment options. Some areas of research include:
- Developing new devices and techniques for catheter-based closure
- Improving surgical techniques and outcomes
- Investigating the genetic causes of ASDs
- Developing new medications and therapies to manage symptoms and prevent complications
Atrial Septal Defect Support and Resources
Living with an atrial septal defect can be challenging, but there are many resources available to support individuals and families affected by this condition. These include: * Support groups and online forums * Educational resources and websites * Cardiac rehabilitation programs * Mental health counseling and therapyWhat is an atrial septal defect?
+An atrial septal defect is a type of congenital heart defect that occurs when there is an abnormal opening in the atrial septum, which is the wall of tissue that separates the heart's two upper chambers.
What are the symptoms of an atrial septal defect?
+The symptoms of an atrial septal defect can vary widely, but may include shortness of breath, fatigue, pale skin, poor appetite, and frequent respiratory infections.
How is an atrial septal defect diagnosed?
+An atrial septal defect is typically diagnosed using a combination of physical examination, medical history, and diagnostic tests, such as electrocardiogram, chest X-ray, echocardiogram, and cardiac catheterization.
What are the treatment options for an atrial septal defect?
+The treatment options for an atrial septal defect depend on the size and location of the defect, as well as the individual's overall health, and may include watchful waiting, medications, surgical closure, catheter-based closure, or a hybrid procedure.
What is the prognosis for individuals with an atrial septal defect?
+The prognosis for individuals with an atrial septal defect is generally good, especially if treatment is received early, and most individuals with ASDs can lead active and healthy lives with proper care and management.
In conclusion, atrial septal defects are a type of congenital heart defect that can have significant implications for an individual's quality of life and overall health. By understanding the causes, symptoms, diagnosis, treatment options, and management of ASDs, we can better appreciate the need for early diagnosis and treatment, as well as the importance of ongoing care and management. If you or a loved one has been diagnosed with an atrial septal defect, it is essential to seek medical attention and follow the recommended treatment plan to prevent complications and improve quality of life. We invite you to share your experiences and ask questions in the comments below, and to explore the many resources available to support individuals and families affected by this condition.
