Intro
The importance of PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction) tests cannot be overstated, especially in the context of global health crises and the need for accurate diagnostic tools. PCR tests have become a cornerstone in the detection of various pathogens, including viruses and bacteria, by amplifying specific DNA sequences. This technology has revolutionized the field of molecular biology and has been instrumental in disease diagnosis, research, and forensic analysis. Understanding how PCR tests work and how to interpret their results is crucial for both healthcare professionals and the general public.
The process of conducting a PCR test involves several steps, starting from sample collection to the final analysis of the amplified DNA. The accuracy and reliability of PCR test results depend on various factors, including the quality of the sample, the primers used, and the conditions under which the PCR reaction is carried out. Given the complexity and the critical nature of PCR tests, it is essential to follow best practices and guidelines to ensure that the results are accurate and reliable.
The application of PCR tests extends beyond clinical diagnostics to include fields such as genetic engineering, where it is used to amplify genes of interest, and in forensic science, where it helps in identifying individuals based on their DNA profiles. The versatility and sensitivity of PCR have made it an indispensable tool in modern biology. However, like any diagnostic or analytical technique, PCR tests are not without their limitations and challenges, including the potential for contamination, the requirement for specialized equipment, and the need for skilled personnel to interpret the results.
Understanding PCR Tests
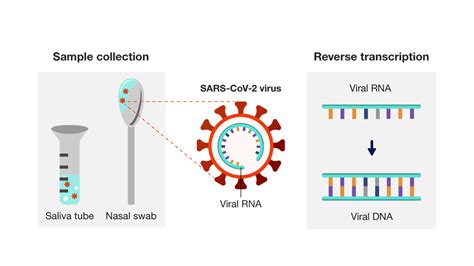
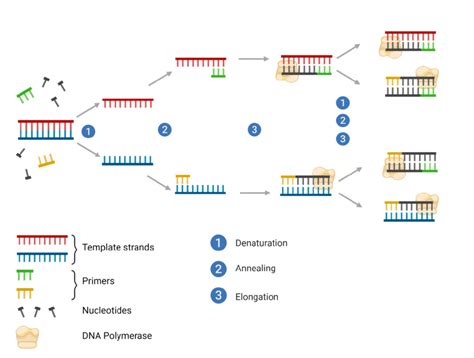
To fully appreciate the value of PCR tests, it's necessary to delve into the basics of how they work. PCR is a laboratory technique that allows for the amplification of specific segments of DNA, making it possible to generate millions of copies from a small initial sample. This process involves the use of thermal cycling, where the DNA is repeatedly heated and cooled in the presence of primers, nucleotides, and an enzyme called Taq polymerase. The primers are designed to bind to the target DNA sequence, and the Taq polymerase synthesizes a new DNA strand by adding nucleotides to the primer.
Key Components of PCR Tests
The key components of PCR tests include the DNA template, primers, nucleotides, Taq polymerase, and the buffer solution. Each of these components plays a critical role in the PCR process. The DNA template is the sample that contains the target sequence to be amplified. Primers are short pieces of DNA that are complementary to the target sequence and serve as starting points for DNA synthesis. Nucleotides are the building blocks of DNA, and Taq polymerase is the enzyme responsible for adding these nucleotides to the growing DNA strand.Benefits of PCR Tests

PCR tests offer several benefits, including high sensitivity, specificity, and the ability to detect minimal amounts of DNA. This makes PCR an invaluable tool for diagnosing infectious diseases, identifying genetic disorders, and detecting minimal residual disease in cancer patients. Additionally, PCR tests can provide rapid results, which is crucial in clinical settings where timely decision-making is essential.
Applications of PCR Tests
The applications of PCR tests are diverse and continue to expand. In clinical diagnostics, PCR is used to detect a wide range of pathogens, including bacteria, viruses, and parasites. It is also used in genetic testing to identify genetic mutations associated with inherited diseases. In research, PCR is a fundamental technique used in cloning, sequencing, and gene expression studies.Interpreting PCR Test Results
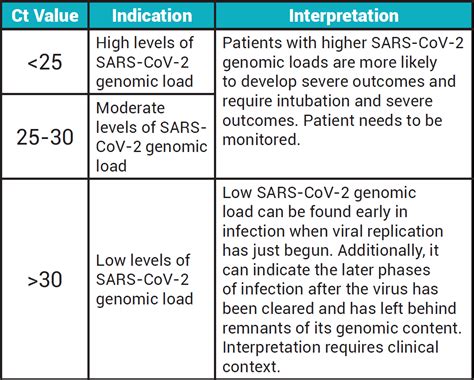
Interpreting PCR test results requires a good understanding of the technique and its limitations. A positive result indicates the presence of the target DNA sequence, while a negative result suggests its absence. However, false positives and false negatives can occur due to contamination, primer mismatch, or insufficient DNA template. Therefore, it's essential to follow strict laboratory protocols and to consider PCR results in the context of clinical symptoms and other diagnostic findings.
Challenges and Limitations
Despite its advantages, PCR testing faces several challenges and limitations. One of the significant challenges is the risk of contamination, which can lead to false-positive results. Additionally, PCR requires specialized equipment and trained personnel, making it less accessible in resource-limited settings. The development of point-of-care PCR devices and improvements in PCR technology aim to address these challenges.5 PCR Test Tips
For individuals undergoing PCR tests, here are five tips to keep in mind:
- Understand the Test: Before undergoing a PCR test, it's essential to understand what the test is for and what the results might indicate.
- Follow Pre-Test Instructions: Adhering to any pre-test instructions, such as fasting or avoiding certain activities, can help ensure accurate results.
- Ask About Results: Don't hesitate to ask your healthcare provider about your test results, including what they mean and any necessary next steps.
- Consider a Second Opinion: If you're unsure about your test results or have questions, consider seeking a second opinion from a specialist.
- Stay Informed: Keep yourself updated with the latest information on PCR tests and their applications, which can help you make informed decisions about your health.
Future of PCR Tests
The future of PCR tests looks promising, with ongoing research focused on improving the sensitivity, specificity, and accessibility of PCR technology. Advances in point-of-care diagnostics and the development of portable PCR devices are expected to make PCR testing more widely available, including in resource-limited settings.Conclusion and Next Steps

In conclusion, PCR tests are a powerful diagnostic tool with a wide range of applications in healthcare, research, and beyond. By understanding how PCR tests work, their benefits, and their limitations, individuals can better navigate the complex landscape of molecular diagnostics. As technology continues to evolve, we can expect PCR tests to play an even more significant role in disease diagnosis, treatment, and prevention.
Call to Action
If you have questions about PCR tests or are interested in learning more about molecular diagnostics, we encourage you to reach out to healthcare professionals or reputable health organizations. Sharing knowledge and experiences can help foster a community that values informed decision-making and promotes better health outcomes.What is a PCR test?
+A PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction) test is a laboratory technique used to amplify specific segments of DNA, making it possible to detect minimal amounts of DNA in a sample.
How accurate are PCR tests?
+PCR tests are highly accurate when performed correctly, with sensitivity and specificity rates that are very high. However, factors like contamination and primer design can affect accuracy.
What are the applications of PCR tests?
+PCR tests have a wide range of applications, including clinical diagnostics for infectious diseases, genetic testing for inherited disorders, and research applications in molecular biology.
We hope this article has provided you with a comprehensive understanding of PCR tests and their significance in modern healthcare and research. If you have any further questions or would like to share your experiences with PCR tests, please don't hesitate to comment below. Your feedback and insights are invaluable in creating a community that values knowledge sharing and health awareness.
