Intro
Treat Athletes Foot Rash with effective remedies, including antifungal creams, powders, and natural treatments, to alleviate itching, burning, and fungal infections, promoting healthy foot care and prevention.
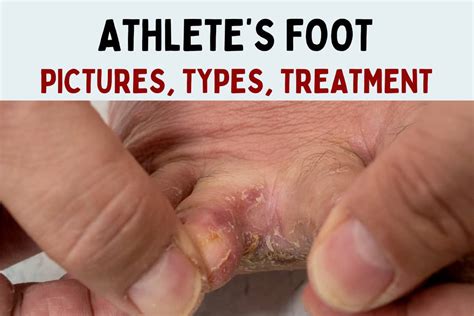
Athlete's foot, also known as tinea pedis, is a common fungal infection that affects the feet. It is characterized by a rash that can be itchy, scaly, and uncomfortable. The infection thrives in warm, moist environments, making the feet an ideal breeding ground. Athlete's foot can be treated with a combination of self-care measures, over-the-counter medications, and prescription medications.
The importance of treating athlete's foot cannot be overstated. If left untreated, the infection can spread to other parts of the body, such as the hands, face, and groin area. Additionally, athlete's foot can lead to secondary bacterial infections, which can be more difficult to treat. Furthermore, the discomfort and pain caused by athlete's foot can significantly impact a person's quality of life, making it essential to seek treatment as soon as symptoms appear.
Athlete's foot is highly contagious and can be spread through direct contact with an infected person or by walking barefoot in areas where the fungus is present. The infection can also be spread through shared personal items, such as towels, socks, and shoes. To prevent the spread of athlete's foot, it is essential to practice good hygiene, wear shoes in public areas, and avoid sharing personal items.
Athlete's Foot Symptoms and Causes

The causes of athlete's foot are primarily related to the growth of fungi in warm, moist environments. The fungus that causes athlete's foot is called Trichophyton, which thrives in temperatures between 75°F and 85°F. The fungus can be spread through direct contact with an infected person or by walking barefoot in areas where the fungus is present.
Types of Athlete's Foot
There are several types of athlete's foot, including: * Interdigital athlete's foot: This type of athlete's foot occurs between the toes and is characterized by itching, burning, and stinging sensations. * Moccasin athlete's foot: This type of athlete's foot affects the soles of the feet and is characterized by dry, scaly skin. * Vesicular athlete's foot: This type of athlete's foot is characterized by blisters and ulcers on the feet.Athlete's Foot Treatment Options

In severe cases, prescription medications may be necessary to treat athlete's foot. These medications can include oral antifungal medications, such as itraconazole and fluconazole, as well as topical creams and ointments. In some cases, a combination of medications may be necessary to effectively treat athlete's foot.
Home Remedies for Athlete's Foot
There are several home remedies that can help to treat athlete's foot, including: * Tea tree oil: This essential oil has antifungal properties and can be applied directly to the affected area. * Garlic: Garlic has antifungal properties and can be applied directly to the affected area. * Vinegar: Vinegar has antifungal properties and can be used to soak the feet.Athlete's Foot Prevention

Athlete's Foot and Other Health Conditions
Athlete's foot can be a sign of an underlying health condition, such as diabetes or a weakened immune system. People with these conditions are more susceptible to athlete's foot and may experience more severe symptoms.Athlete's Foot in Different Populations

Athlete's Foot and Footwear
Footwear can play a significant role in the development of athlete's foot. Wearing shoes that are too tight or do not allow for airflow can create a warm, moist environment that fosters the growth of fungi.Athlete's Foot and Lifestyle Changes
Athlete's Foot and Mental Health
Athlete's foot can have a significant impact on mental health, particularly if left untreated. The discomfort and pain associated with athlete's foot can lead to anxiety, depression, and stress.Athlete's Foot and Future Directions

Athlete's Foot and Public Health
Athlete's foot is a significant public health concern, particularly in areas where people are more likely to walk barefoot or share personal items. Public health campaigns can help to raise awareness about athlete's foot and promote prevention and treatment.What are the symptoms of athlete's foot?
+The symptoms of athlete's foot include itching, burning, and stinging sensations on the feet, especially between the toes. The skin may also become scaly, cracked, and dry, leading to pain and discomfort.
How is athlete's foot treated?
+Athlete's foot can be treated with a combination of self-care measures, over-the-counter medications, and prescription medications. Self-care measures include keeping the feet clean and dry, wearing shoes that allow for airflow, and using antifungal powders or sprays.
Can athlete's foot be prevented?
+Yes, athlete's foot can be prevented by practicing good hygiene, wearing shoes in public areas, avoiding shared personal items, and using antifungal powders or sprays.
What are the complications of athlete's foot?
+The complications of athlete's foot include secondary bacterial infections, which can be more difficult to treat. Additionally, athlete's foot can lead to anxiety, depression, and stress if left untreated.
How long does it take to recover from athlete's foot?
+The recovery time for athlete's foot depends on the severity of the infection and the effectiveness of treatment. Mild cases of athlete's foot can be treated in a few weeks, while more severe cases may take several months to recover from.
In conclusion, athlete's foot is a common fungal infection that can be treated and prevented with a combination of self-care measures, over-the-counter medications, and prescription medications. It is essential to practice good hygiene, wear shoes that allow for airflow, and avoid shared personal items to prevent athlete's foot. By understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatment options for athlete's foot, individuals can take steps to promote overall foot health and prevent the discomfort and pain associated with this infection. We encourage readers to share their experiences with athlete's foot, ask questions, and seek medical attention if symptoms persist.
